Today’s Current Affairs: 9th December 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
National Mission on Edible Oils:

The National Mission on Edible Oils (NMEO) embodies India’s commitment to realizing the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by transforming the edible oil sector from an import-dependent
- It aims to strengthen the country’s oilseed ecosystem and achieve self-reliance in edible oil production.
- It targets to increase the area coverage and primary oilseed production.
- It targets domestic edible oil production and seeks to expand oilseed cultivation mainly by targeting rice and potato fallow lands.
- It has two-pronged approach:
- NMEO – Oil Palm (2021):
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, with the aim to enhance the edible oilseeds production and oils availability in the country by area expansion and increasing Crude Palm Oil (CPO) production.
- It is focused on expanding oil palm cultivation and increasing domestic crude palm oil output.
- It focuses on increasing production of seedlings by establishment of seed garden, and nurseries of oil palm in order to assure domestic availability of seedlings as per target fixed under NMEO-OP.
- Implementation: The Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) serves as the nodal central authority.
- NMEO – Oilseeds (2024):
- It is aimed at improving productivity, seed quality, processing, and market linkages for traditional oilseed crops.
- It focuses on increasing production of key primary oilseed crops such as Rapeseed-Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesamum, Safflower, Niger, Linseed and Castor.
- It also focuses on increasing collection and extraction efficiency from secondary sources like cottonseed, coconut, rice bran as well as Tree-Borne Oilseeds (TBOs).
- It will be implemented in all States/UTs with the funding pattern of 60:40 in case of general States, Delhi & Puducherry and 90:10 in case of North-Eastern States and hill States, and 100% funding for UTs and Central Agencies.
Seventh UN Environment Assembly:

The seventh UN Environment Assembly (UNEA-7) is taking place in Nairobi, Kenya.
- It is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on the environment.
- It the universal membership of all UN Member States and the full involvement of major groups and stakeholders.
- It is organised every 2 years.
- UNEA was created in 2012, as an outcome of the UN Conference on Sustainable Development (Rio+20), held in Brazil.
- It sets the global environmental agenda, provides overarching policy guidance, and defines policy responses to address emerging environmental challenges.
- It undertakes policy review, dialogue and the exchange of experiences, sets the strategic guidance on the future direction of the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It fosters partnerships for achieving environmental goals and resource mobilization.
- Seventh UNEA session (2025) Theme: “Advancing sustainable solutions for a resilient planet”.
Measles : Report
Despite a highly effective vaccine, measles caused approximately 95,000 deaths globally in 2024, primarily among unvaccinated children under five.
- Measles is a highly contagious, serious airborne disease caused by a virus.
- It is caused by a virus in the paramyxovirus family.
- It is one of the world’s most contagious diseases, spread by contact with infected nasal or throat secretions (coughing or sneezing) or breathing the air that was breathed by someone with measles.
- The virus remains active and contagious in the air or on infected surfaces for up to two hours.
- The virus infects the respiratory tract, then spreads throughout the body, causing severe disease, complications, and even death.
- Symptoms:
- The first sign of measles is usually high fever, beginning about 10 to 14 days after exposure to the virus and lasting four to seven days.
- A runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks can develop in the initial stage.
- A rash erupts after several days, usually on the face and upper neck. The rash spreads over about three days, eventually reaching the hands and feet, and lasts five to six days before fading.
- Any non-immune person (not vaccinated or vaccinated but did not develop immunity) can become infected.
- Unvaccinated young children and pregnant persons are at the highest risk of severe measles complications.
- Measles is still common, particularly in parts of Africa, the Middle East, and Asia.
- No specific antiviral treatment exists for measles.
- It can be prevented with a safe and effective measles-rubella (MR) vaccine that gives long-term immunity.
- The Government of India (GoI) introduced the measles vaccine in its Universal Immunization Programme in 1985.
National Intelligence Grid:

Officials told that National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) is slowly gathering pace and receiving 45,000 requests a month.
- It is a platform for the police and investigating agencies to securely access government and private databases in real time.
- It is conceptualised as a seamless and secure database for information on terrorists, economic crimes and similar incidents to help bolster India’s capabilities.
- The project was started in 2009 in the aftermath of the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks.
- NATGRID was set up as an attached Office of the Ministry of Home Affairs with effect from December 1, 2010.
- It started its operations on December 31, 2020.
- NATGRID database is available to;
- Intelligence Bureau (IB), the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), the National Investigation Agency (NIA), the Enforcement Directorate (ED), the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI).
Superintendent of Police (SP) rank officers.
- Intelligence Bureau (IB), the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), the National Investigation Agency (NIA), the Enforcement Directorate (ED), the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI).
- It has been mandated to maintain a repository of intelligence databases.
- It works as an integrated intelligence grid that connects databases of core security agencies of the government of India.
- It will have data related to all immigration entry and exit, banking and financial transactions, credit card purchases, telecom, individual taxpayers, air flyers, train travellers besides others to generate intelligence inputs.
- It utilises Big Data and Analytics to study huge amounts of data generated to analyse events in order to get a better picture as well as to trail suspects.
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority: In News

The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) collaborated with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) organised a “Niveshak Shivir” in Jaipur.
- It was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is dedicated to promoting investor awareness and protection through sustained outreach, education, and strategic collaborations.
- It manages the Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF) and promotes investor awareness and financial protection.
- It makes refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc. to investors and promote awareness among investors.
- It is dedicated to safeguarding investor interests by facilitating the return of unclaimed shares and dividends and advancing financial literacy nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Through flagship initiatives such as Niveshak Didi, Niveshak Panchayat, and Niveshak Shivir, IEPFA empowers individuals to make informed financial choices and fosters a financially aware citizenry.
- The IEPF consists of amounts that remained unclaimed for 7 years, including:
- Unpaid dividends,
- Application money is due for refund,
- Matured deposits and debentures,
- Interest on investments from the fund,
- Grants or donations received from the government or other entities.
Hoolock Gibbon:

A stranded family of Hoolock gibbons was rescued in Arunachal Pradesh’s Lower Dibang Valley district by officials.
- Gibbons, the smallest and fastest of all apes, live in tropical and subtropical forests in the southeastern part of Asia.
- The hoolock gibbon is one of 20 species of gibbons on Earth.
- Its distribution in Southeast Asia spans India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and southern China.
- It is the only ape found in India.
- In India, it is found in Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura, south of the Brahmaputra.
- Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary in Assam has the largest concentration of the hoolock gibbon.
- It is categorised into Eastern Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys) found in a specific region of Arunachal Pradesh and Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock hoolock) distributed elsewhere in the northeast.
- Characteristics of Hoolock Gibbon:
- They are diurnal and arboreal, brachiating through the trees with their long arms.
- They are monogamous (same partner throughout life).
- They live in small families and communicate with other gibbons by vocalisation.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:
- Eastern Hoolock Gibbon: Vulnerable
- Western Hoolock Gibbon: Endangered
- Both are on Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972.
Cosmic Filament :
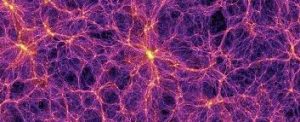
The University of Oxford researchers reported a roughly 50-million-lightyear-long cosmic Filament traced by at least 14 galaxies.
- Cosmic or galaxy filaments are the largest ‘threads’ in the universe’s cosmic web.
- A single cosmic filament is a structure spanning hundreds of millions of lightyears.
- These filaments are the largest known structures in the Universe which are vast, thread-like formations of galaxies and dark matter that form cosmic scaffolding.
- They serve as the nurseries where galaxies grow by accreting pristine gas that fuels their star formation.
- It is formed as a result of gravity pulling in gas, dark matter and galaxies into long, thin strands that link giant clusters of galaxies.
- These filaments also surround large, empty regions of space called voids.
- A filament forms where sheets of matter intersect and collapse; they’re also highways along which gas and smaller galaxies ‘flow’ towards big clusters.
- These filaments help decide where galaxies form, how fast they grow, and how much fresh gas they receive over billions of years.
Haemorrhagic Septicaemia:

Ten blackbucks have died in Jharkhand’s Jamshedpur in Zoological Park due to suspected Haemorrhagic Septicaemia.
- It is also known as Pasteurellosis.
- It is a bacterial disease caused by certain serotypes of Pasteurella multocida.
- The two common serotypes of P. multocida associated with the disease in these species are types B:2 (in Asia ) and E:2 (in Africa ).
- These bacteria are geographically restricted to some areas of Asia, Africa, the Middle East and southern Europe.
- It is a major disease of cattle and buffaloes characterised by an acute, highly fatal septicaemia with high morbidity and mortality.
- In both species, young animals and young adults are more susceptible than older animals.
- Germs of this disease survive longer in humid and waterlogged conditions.
- It can be transmitted by ingestion or inhalation, either during direct contact or via fomites such as contaminated feed and water.
- Animals become dull and have high fever. They refuse to eat and salivate more than normally.
- Swellings develop typically and quickly, especially around the throat, the brisket, the dewlap and sometimes around the head.
- Treatment: Vaccines are available; Antimicrobial treatment administered intravenously soon after the onset of disease can reduce mortality.
Brain–Computer Interface (BCI):
India is exploring neurotechnology and Brain–Computer Interfaces (BCIs) as strategic tools for healthcare, economic growth, and technological leadership amid global advances led by the U.S., China, and Europe.A Brain–Computer Interface (BCI) is a system that interprets brain signals and converts them into digital commands to control external devices such as computers, robotic limbs, or wheelchairs.
BCIs form a two-way communication channel between the brain and machines, aiding restoration of lost functions or enabling new capabilities.Electrodes (invasive or non-invasive) record electrical activity from neurons Machine learning algorithms translate these patterns into intentions (e.g., move arm, select letter).The decoded signals activate an external device—robotic limbs, speech synthesizers, drones, or smart-home systems. Continuous decoding improves accuracy and enables real-time brain-machine interaction.
Japan : Major Earthquake
A major earthquake rocked Japan’s northern coast and also the country’s meteorological agency recorded several tsunami waves. It is an island nation in East Asia, situated in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is bordered by Pacific Ocean (East), Sea of Okhotsk (North), Sea of Japan (West East) and East China Sea (Southwest).Japan comprises a chain of islands. Main Islands(north to south): Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. Volcanic activity: It is located on the Pacific Ring of Fire. Highest peak: Mount Fuji. It is often disturbed by earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions due to tectonic activity.
Saudi UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities (GNLC):
UNESCO has added three more Saudi cities Riyadh, AlUla, and Riyadh Al-Khabra to the Global Network of Learning Cities (GNLC) in its 2025 update.The GNLC is a UNESCO-led international network that recognises cities promoting lifelong learning across all age groups through inclusive, accessible, and sustainable learning ecosystems.Established in 2013, GNLC has grown rapidly and today includes 425 cities from 91 countries, supporting lifelong learning opportunities for nearly 500 million people. UNESCO recognised Riyadh, AlUla, and Riyadh Al-Khabra for meeting rigorous global benchmarks of community-wide learning. Saudi’s total GNLC membership: 8 cities. The expansion aligns with Saudi Vision 2030 and the Human Capability Development Program.
India has three GNLC cities (2022 cohort):
- Warangal (Telangana)
- Thrissur (Kerala)
- Nilambur (Kerala)
Kīlauea Volcano : Erupted
Fresh lava fountains recently erupted from Hawaii’s Kilauea volcano nearly a year after one of the world’s most active volcanoes began its current eruptive phase.It is one of the world’s most active volcanoes.It is a shield-type volcano located in the southeastern part of the island of Hawaii, Hawaii State, United States.Hawaii is the southernmost and largest of the island chain, which owes its existence to the very active Hawaiian hot spot. Kilauea’s slopes merge with those of the nearby volcano Mauna Loa on the west and north.Kilauea has been erupting on a continuous basis since 1983.Kilauea’s frequent eruptions are usually non-explosive.




