Today’s Current Affairs: 18th February 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
INS Tarangini:

The sail training ship INS Tarangini is among several Indian and foreign naval vessels that arrived in Visakhapatnam for the international fleet review and MILAN exercise beginning February 18.
- It is the Indian Navy’s first Sail Training Ship (STS).
- It became the first Indian naval ship to navigate the globe in 2003-2004.
- The primary role of the ship is to foster time-honored virtues of courage, camaraderie, and endurance in officer cadets embarking on a naval career.
- It provides an ideal setting for firsthand experience of the natural elements by imparting training which includes sailing, setting and furling of sails, watch-keeping, and sail manoeuvres.
Lake Michigan:

More than 150 years after it sank in a powerful storm, the remains of the luxury steamer Lac La Belle have finally been found at the bottom of Lake Michigan.
- It is the third largest of the five Great Lakes of North America and the only one lying wholly within the United States.
- It is the fourth largest freshwater lake and the fifth largest lake in the world, ranked by surface area.
- It is connected directly to Lake Huron, into which it drains, through the broad Straits of Mackinac.
- Water flows into Lake Michigan from several rivers, including the Fox-Wolf, the Grand, the St. Joseph, and the Kalamazoo rivers, among others.
Khorramshahr-4 Missile:

Iran recently released dramatic footage of its Khorramshahr‑4 ballistic missile — one of Tehran’s most powerful medium‑range missiles — as tensions with the United States continue to rise.
- Also known as the Kheibar missile, it is a medium-range ballistic missile developed by Iranian state-owned defence company Aerospace Industries Organization (AIO).
- It is liquid-fuelled and has an operational range of approximately 2,000 kilometers.
- The missile travels faster than the speed of sound.
Tulbul Navigation Barrage Project:

The Jammu & Kashmir government is mulling to take advantage of the suspended Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) by diverting, for the first time, water from the Ravi river in Punjab to the Jammu region, and pushing for the revival of the Tulbul Navigation Barrage project.
- The Tulbul Navigation Barrage Project, also known as the Wular Barrage, is a navigation lock-cum-control structure located at the outlet of Wular Lake, in J&K.
- It was designed to facilitate navigation on the Jhelum River during lean winter months.
- The barrage, once completed, would regulate the water of the Wular Lake to maintain a minimum draft in the river up to Baramulla during the winter season.
- Besides, the project would provide water and helped in firming up power generation in downstream hydroelectric plants such as the Uri I and II hydro projects.
- Wular Lake is the largest freshwater lake in India and the second largest freshwater lake in Asia.
- It is located in the Bandipore district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is fed by the Jhelum River.
- The lake basin was formed as a result of tectonic activity.
- In 1990, it was designated as a Wetland of International Importance under the Ramsar Convention.
SAHI and BODH Initiative:

The Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare will launch two key national initiatives namely SAHI and BODH at the India AI Summit at Bharat Mandapam.
- The Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare for India (SAHI) is a national guidance framework to enable the safe, ethical, evidence-based, and inclusive adoption of Artificial Intelligence across India’s healthcare system.
- It aims to provide strategic direction on governance, data stewardship, validation, deployment, and monitoring of AI solutions, while supporting States and institutions in responsible adoption aligned with public health priorities.
- The Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI (BODH)developed by the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur in collaboration with the National Health Authority,
- It is a privacy-preserving benchmarking platform that enables rigorous evaluation of AI models using diverse, real-world health data without sharing underlying datasets.
- It is a digital public good under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission,
- It is designed to strengthen trust, transparency, and quality assurance in Health AI deployment.
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India:

The Supreme Court has asked the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to consider introducing mandatory front-of-package warning labels (FOPL) on packaged food products high in sugar, salt and saturated fat.
- It has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- FSSAI is responsible for setting food standards, regulating the manufacture, storage, distribution, sale and import of food and ensuring the availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption.
- Nodal Ministry was established under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- It formulates standards for various food products, ensuring they are safe for consumption.
- It provides guidelines for businesses to implement effective food safety management practices.
- FSSAI manages the licensing process for food businesses, ensuring they comply with food safety regulations.
- Regular inspections and audits are conducted to assess compliance with food safety standards.
- Initiatives to educate the public about food safety, hygiene, and nutrition are a key focus area.
- FSSAI also directly monitors compliance of food regulations food licence issued by FSSAI., especially in the area of food imports to India.
- The FSSAI is also responsible for the accreditation of food testing laboratories throughout India.
Loggerhead Turtle:

It is observed that warmer oceans and depleting food have affected the ubiquitous marine Loggerhead turtle’s reproductive and migratory patterns, and even its size.
- It is a species of oceanic turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae.
- It is named Loggerhead for their large heads that support powerful jaw muscles.
- It is the world’s largest hard-shelled turtle, slightly larger at average and maximum mature weights than the green sea turtle and the Galapagos tortoise.
- It is also the world’s second largest extant turtle after the leatherback sea turtle.
- It uses the geomagnetic field as a map when navigating large distances.
- They may be found hundreds of miles out to sea, as well as in inshore areas such as bays, lagoons, salt marshes, creeks.
- It inhabits the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans and the Mediterranean Sea.
- It is omnivorous, feeding mainly on bottom-dwelling invertebrates, such as gastropods, bivalves, and decapods.
- Conservation status:
- IUCN: Vulnerable
- Threats: Climate change, direct harvest of turtles and eggs, Loss and degradation of nesting habitat, Ocean pollution/marine debris and by catch in fishing gear.
India-AI Impact Summit 2026:

The India-AI Impact Summit 2026 commenced at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, organised by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), marking the first major global Artificial Intelligence (AI) summit hosted in the Global South and showcasing India’s leadership in inclusive, development-focused AI.
- The Summit is hosted under the India AI Mission, shifting the global narrative from “AI Safety” to “AI for Development and Impact.”
Key Highlights of the India-AI Impact Summit 2026:
- Theme and Philosophy: The summit is anchored in Indian ethos, specifically the motto “Sarvajana Hitaya, Sarvajana Sukhaya” (Welfare for all, happiness for all).
- It is structured around two conceptual frameworks:
- The Three Sutras (Pillars): People, Planet, and Progress.
- People: Developing AI that empowers citizens through healthcare, education, and financial inclusion.
- Planet: Using AI for sustainable practices, climate resilience, and resource efficiency.
- Progress: Harnessing AI for economic growth, governance, and public service delivery.
- The Three Sutras (Pillars): People, Planet, and Progress.
- The Seven Chakras (Working Groups): Focused themes including Health, Agriculture, Safe & Trusted AI, Science, Inclusion, Democratizing AI Resources, and Economic Development.
NGT Approved Great Nicobar Project:
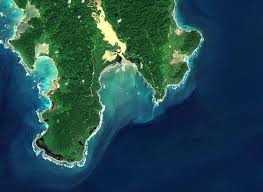
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has approved the Rs 81,000-crore Great Nicobar project, stating that it found “no good ground” to intervene, while imposing stringent conditions to safeguard the environment.
- NGT acknowledged the “strategic importance of the project” and noted that “adequate safeguards” have been incorporated in the environmental clearance to mitigate ecological impacts.
- The NGT directed that construction (including foreshore development) must not cause erosion or adverse shoreline changes near the project area or along any of the islands.
- It specifically ordered that there shall be “no loss of sandy beaches,” recognizing these beaches as critical nesting sites for turtles and birds, and as natural protection for the islands.
- It ordered the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) to take “all measures” to protect coral reefs along the coastal stretch and to ensure “coral regeneration through proven scientific methods.” Any existing scattered coral must be “translocated” as per Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) suggestions.
- The environmental clearance contains specific conditions for the protection of Leatherback sea turtles, Nicobar megapode, Saltwater crocodiles, Robber crab, Nicobar macaque and other endemic bird species of the Great Nicobar island.
- The NGT stipulated that the government is bound by the conditions in the environmental clearance and must ensure these are not violated at any stage of project implementation.
International Conference on Dam Safety 2026:

The International Conference on Dam Safety (ICDS) 2026 concluded successfully in Bengaluru, serving as a pivotal platform for strengthening India’s dam safety ecosystem.
Key Highlights of ICDS 2026:
- Dam Safety Framework: The conference emphasized the implementation of the Dam Safety Act, 2021 and the Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP) to ensure the safety and longevity of India’s dams.
- Sediment Management: Reservoir sedimentation was identified as a major threat to water security, highlighting the need for preventive measures such as catchment treatment and remote sensing.
- Experts recommended simplified risk screening and dam-break assessment tools to prioritize safety measures across India’s large dam portfolio.
- Flood Management: The importance of forecast-informed and basin-level coordinated reservoir operations was underscored, utilizing dynamic rule curves and real-time data sharing to manage floods and droughts.
- Emergency Preparedness: The conference called for strengthening Emergency Action Plans (EAPs), floodplain zoning, and early warning systems to enhance community preparedness and institutional response.
India–Thailand Air Exercise:
The Indian Air Force (IAF) conducted an In-situ Exercise with the Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), expanding strategic partnership under India’s Act East Policy 2014.The IAF deployed Su-30MKI multirole fighters, IL-78 mid-air refuelling tankers, and Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) aircraft. The RTAF participated with its SAAB Gripen jets. IAF forces operated from airbases in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, while Thai Gripens operated from bases within Thailand.It aimed to demonstrate IAF’s reach and interoperability with a Friendly Foreign Country (FFC) in the IOR, highlighting the strategic importance of the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) as a forward hub.This exercise reflects the deepening “Act East” partnership between India and Thailand, expanding into the aerospace domain.This is complemented by Thailand’s own ‘Act West’ policy 2016, which aligns with India’s regional outreach, underpinned by their maritime proximity.
Exercise Vajra Ghaat:
The Indian Army conducted Exercise Vajra Ghaat at the Pokhran Field Firing Range in Jaisalmer, demonstrating the operational readiness and combat capabilities of the K9 Vajra self-propelled artillery gun system in desert warfare conditions. The primary aim was to validate refined Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTP) for enhancing battlefield survivability and operational effectiveness.The exercise was spearheaded by the White Tiger Division. It showcased the Army’s ability to swiftly deploy heavy artillery assets in the harsh terrain of the Thar Desert.The validation of refined TTPs during the drill is expected to strengthen the Army’s combat posture in the western sector.K9 Vajra is a tracked self-propelled howitzer derived from South Korea’s K9 Thunder, the backbone of the South Korean Army.Designed for long-range fire with a high rate of accuracy, it is compatible with Indian and North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO)-standard ammunition and features all-welded steel armour for protection.The system was procured under the ‘Buy Global’ category of the Defence Procurement Procedure.




