Insurance Surety Bonds:
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) organised a brainstorming session with stakeholders to expedite the adoption of Insurance Surety Bonds for its contracts.
- Insurance Surety Bonds can be defined in their simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
- These are instruments where insurance companies act as ‘Surety’ and provide the financial guarantee that the contractor will fulfil its obligation as per the agreed terms.
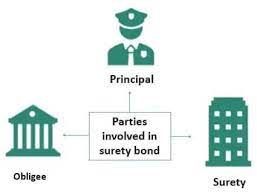
- Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement.
- The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal: The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety: The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee: The party who requires and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organisation.
- It will act as a security arrangement for infrastructure projects and will insulate the contractor as well as the principal.
- The product will cater to the requirements of a diversified group of contractors, many of whom are operating in today’s increasingly volatile environment.




