Carbon Sequestration:
There has been increasing investments to develop technology in the field of Carbon Sequestration and fight the menace of climate change.
As Global Warming accelerates and society continues to emit greenhouse gases, the idea is gaining of investing in artificial techniques of Carbon Sequestration.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, nations may need to remove between 100 billion and 1 trillion tonnes of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere this century to avert the worst effects of climate change, far more than can be absorbed by simply planting more trees.
Carbon sequestration :
It is the long-term storage of carbon in plants, soils, geologic formations, and the ocean. Carbon sequestration occurs both naturally and as a result of anthropogenic activities and typically refers to the storage of carbon.
Types:
- Terrestrial Carbon Sequestration:
- Terrestrial carbon sequestration is the process through which CO2 from the atmosphere is absorbed by trees and plants through photosynthesis and stored as carbon in soils and biomass (tree trunks, branches, foliage, and roots)
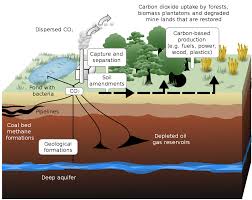
- Geologic Carbon Sequestration:
- CO2 can be stored, including oil reservoirs, gas reservoirs, unmineable coal seams, saline formations and shale formations with high organic content.
- Ocean Carbon Sequestration:
- Oceans absorb, release and store large amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere.
- This can be done in two ways- enhancing productivity of ocean biological systems through Iron fertilization, and injecting CO2 into the deep ocean.
- The dumping of iron stimulates phytoplankton production, which in turn leads to enhanced photosynthesis from these microorganisms, helping in CO2 absorption.




