Today’s Current Affairs: 17th January 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Chatham Islands:
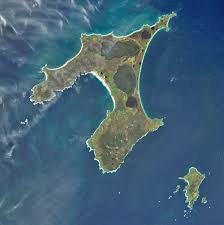
A bloom of phytoplankton—tiny photosynthetic organisms that become visible to satellites when their numbers explode—encircled the Chatham Islands in austral summer recently
- Chatham Islands is an island group in the South Pacific Ocean.
- These islands are New Zealand’s most easterly territory.
- Composed of 10 islands, they are primarily of volcanic formation, but areas of limestone indicate that they may once have been part of New Zealand.
- Only the two main islands are inhabited: Chatham Island and Pitt Island.
- Chatham Island, the largest of the islands, has a high southern tableland flanked by towering cliffs and a gentle northern portion encompassing extensive waterways, low peatlands and long sandy beaches.
- The Chatham Islands is the first inhabited place in the world to see the rising sun each day.
- The islands were first inhabited by Moriori, who named the islands ‘Rekohu’ – translated as ‘misty skies’ or ‘misty sun’.
- European sealers and whalers were next to arrive, followed by Māori from New Zealand, who named the islands ‘Wharekauri’.
- Descendants of Moriori still reside on the Chatham Islands today.
- The main settlement is Waitangi. Other settlements are Te One, Port Hutt, Kāingaroa, and Ōwenga.
- The economy of the Chatham Islands is heavily dependent on fishing, farming, and tourism.
Vitamin A : New Study

Recently uncovered new ways a vitamin A-derived molecule can interfere with the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
- Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin primarily stored in the liver.
- There are two types of vitamin A that are found in the diet.
- Preformed vitamin A is found in animal products such as meat, fish, poultry, and dairy foods.
- Precursors to vitamin A, also known as provitamin A, are found in plant-based foods such as fruits and vegetables.
- These compounds are converted to the active form in your body.
- The most common type of provitamin A is beta-carotene.
- Foods with the highest levels of vitamin A include:
- Beef liver and other organ meats
- Some types of fish such as herring and salmon and cod fish oil
- Eggs
- Dairy products such as cheese and fortified milk
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Orange and yellow vegetables and fruits, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, mangos, and cantaloupe
- Broccoli, spinach, and most dark green, leafy vegetables
- Vitamin A helps form and maintain healthy teeth, skeletal and soft tissue, mucus membranes, and skin.
- It is also known as retinol because it produces the pigments in the retina of the eye.
- Vitamin A promotes good eyesight, especially in low light.
- It also has a role in healthy pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- If you do not get enough vitamin A, you have more risk of eye problems such as:
- Reversible night blindness
- Non-reversible corneal damage known as xerophthalmia
- It can also lead to hyperkeratosis or dry, scaly skin.
- Vitamin A deficiency can be treated with vitamin A supplements.
Dardanelles Strait:
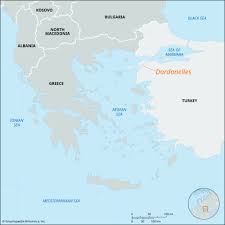
Southbound ship traffic is set to resume in Turkey’s Dardanelles Strait after a tanker experienced engine failure recently.
- Dardanelles Strait is a very important narrow waterway in northwestern Turkey.
- It connects the Aegean Sea (an arm of the Mediterranean Sea) to the Sea of Marmara.
- This strait acts like a natural border, separating the continent of Asia on its eastern side from Europe on its western side.
- It is entirely within Turkey. It forms a key part of the Turkish Straits, which also include the Bosphorus Strait and the Sea of Marmara.
- It is a vital shipping lane for countries around the Black Sea, like Russia and Ukraine.
- Their ships must pass through the Dardanelles to reach the Mediterranean Sea and the rest of the world’s oceans.
Gegeneophis valmiki:

Indian scientists recently discovered a rare subterranean amphibian species in the northern Western Ghats of Maharashtra and named it Gegeneophis valmiki.
- It is a rare, subterranean amphibian species, discovered in the northern Western Ghats of Maharashtra.
- The name Gegeneophis valmiki honors the historic Maharshi Valmiki Mandir located near the discovery site.
- It belongs to the genus Gegeneophis, commonly called blind caecilians.
- Caecilians, often called “hidden amphibians”, are limbless, worm-like creatures that spend most of their lives underground.
- Their burrowing improves soil aeration and structure, their feeding helps regulate soil invertebrates, and they form part of the food web for birds, reptiles and small mammals.
- They also represent a key evolutionary link between aquatic and terrestrial vertebrates.
Conference of Speakers and Presiding Officers of the Commonwealth (CSPOC):

The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the 28th Conference of Speakers and Presiding Officers of the Commonwealth (CSPOC) in New Delhi, highlighting India’s commitment to sharing open-source tech platforms with the Global South.
- It brings together the Speakers and Presiding Officers of the national parliaments of the independent sovereign states of the Commonwealth.
- It was created in 1969 as an initiative of the then Speaker of the House of Commons of Canada, Lucien Lamoureux.
- Since its inception, Canada has provided CSPOC with a secretariat to support its activities.
- The Conference is an independent group and has no formal affiliation with the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association, the Commonwealth Secretariat, or the Commonwealth Heads of Government.
- CSPOC operates on a two-year cycle, holding a conference of the full membership every two years, usually early in January, and a meeting of the Standing Committee at the same time the intervening year.
- The Conference aims to:
- Maintain, foster, and encourage impartiality and fairness on the part of Speakers and Presiding Officers of Parliaments;
- Promote knowledge and understanding of parliamentary democracy in its various forms; and
- Develop parliamentary institutions
- Commonwealth is a voluntary association of 56 independent countries, almost all of which were formerly under British rule.
- It differs from other international bodies such as the United Nations or the World Trade Organization.
- It has no formal constitution or bylaw
- The members have no legal or formal obligation to one another; they are held together by shared traditions, institutions, and experiences as well as by economic self-interest.
- Commonwealth action is based upon consultation between members, which is conducted through correspondence and through conversations in meetings.
Root Wilt Disease:

Phytoplasma-induced root wilt disease has destroyed large tracts of traditional coconut-growing areas in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala States.
- Root Wilt Disease is caused by phytoplasma (bacteria) is one of the most devasting diseases of coconut palms.
- It is classified as a non-fatal disease of coconut palm and was first identified more than a century and a half ago in Erattupetta in Kerala.
- It is not lethal; but it debilitates the production potential of the palms.
- The disease spreads through insect vectors, aided by the movement of wind and uninterrupted stretches of coconut plantations.
- The root (wilt) disease occurs in all major soil types but the spread is faster in sandy, sandy loam and alluvial soil.
- Factors accelerating spread: Erratic temperatures, especially extremes, and the rise of new sucking pests, particularly whiteflies, have significantly accelerated its spread.
- Symptoms of Root Wilt Disease:
- Tapering of terminal portion of the trunk
- Reduction of leaf size
- Abnormal bending or Ribbing of leaf lets termed as flaccidity.
- Flowering is delayed and also yield is considerably reduced.
- The characteristic symptom is the flaccidity of leaflets.
- The tree quickly becomes unproductive, sheds all its nuts, and assumes a distorted appearance.
- Breeding resistant and tolerant varieties remains one of the most successful tools for managing phytoplasma.
Foundation Day of Lokpal of India:

The Lokpal of India observed its Foundation Day on 16th January, marking the coming into force of Section 3 of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, which provided for the establishment of the Lokpal in 2014.
- The idea of a Lokpal was first mooted in 1963, inspired by the Ombudsman model, and was formally recommended by the First Administrative Reforms Commission in 1966.
- India ratified the UN Convention Against Corruption in 2011, leading to the passage of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act in 2013, which came into force on 16th January 2014, formally establishing the Lokpal under Section 3 of the Act.
- Before the enactment of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, several states had already set up Lokayukta institutions through their own laws, with Maharashtra being the first to establish a Lokayukta in 1971.
- The Lokpal consists of a Chairperson and up to eight Members, with at least 50% being Judicial Members and a mandatory 50% representation from SC, ST, OBC, minorities, and women.
- Members hold office for five years or until attaining the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier, ensuring both expertise and social inclusivity in the institution.
- The Chairperson and Members of the Lokpal are appointed by the President of India based on the recommendations of a Selection Committee comprising the Prime Minister, Speaker of the Lok Sabha, Leader of Opposition, the Chief Justice of India or a nominee, and one eminent jurist nominated by the President.
- The Chairperson must be a serving or former Chief Justice of India or a Supreme Court Judge.
- Judicial Members are drawn from serving or former Supreme Court Judges or Chief Justices of High Courts.
- Non-Judicial Members must possess impeccable integrity and at least 25 years of experience in fields specified under the Act.
- The Lokpal has jurisdiction over the Prime Minister (with exclusions relating to national security, foreign relations, atomic energy, space, and public order), Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and Group A to D Central Government officials.
- It also covers entities receiving substantial government funding or foreign contributions under specified conditions.
- The Lokpal has powers of superintendence over investigations conducted by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in cases referred to it and exercises powers of a civil court during preliminary inquiries.
- It can authorise search and seizure, recommend prosecution or disciplinary action, issue guidelines to the CVC, and suggest systemic reforms to address institutional corruption.
- Any individual, NGO, company, trust, limited liability partnership (LLP) even foreign nationals (with passport) can file complaints.
- Complaints must relate to offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- Complaints can be submitted online or offline in the prescribed format under the Lokpal (Complaint) Rules, 2020, within a limitation period of seven years.
- The Lokpal ensures strict confidentiality of complainants, witnesses, and public servants during inquiry and investigation.
- Complaint Handling Mechanism: Complaints are generally placed before the Lokpal Bench within 15 working days after scrutiny.
- Even defective complaints are considered, with opportunities given for rectification, and public servants are granted multiple stages to present their defence, ensuring adherence to principles of natural justice.
CSIR Integrated Skill Initiative:

CSIR Integrated Skill Initiative has trained more than 1.90 lakh individuals through 5200+ skill-based trainings.
- It is a flagship national programme implemented by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- It is aimed at bridging the gap between scientific research and industry requirements, and employable skills.
- Objective is to seamlessly integrate skill development with science and technology by leveraging CSIR’s vast research infrastructure, widespread network domains.
- It provides inclusive accessibility, catering to a diverse spectrum of beneficiaries ranging from
- Students, young researchers, technical staff, and working professionals to school dropouts, ITI diploma holders, farmers, and rural communities
- It emphasizes to align skill training with real-world industrial, societal, and entrepreneurial demands.
- Features of CSIR Integrated Skill Initiative:
- It provides structured short-term and long-term skill development modules comprising training, internships, certification courses, and hands-on laboratory exposure.
- It equips participants with comprehensive skill development in advanced and rapidly evolving technologies interconnected with industry requirements.
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins:
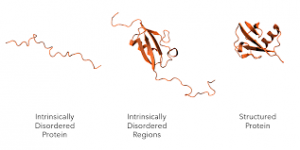
Researchers have developed a deep-learning tool named Disobind that can predict how Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDP) latch on to their binding partners.
- Intrinsically disordered proteins are defined as proteins or regions of proteins that lack a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure under biological conditions.
- Also called natively unfolded or intrinsically unstructured proteins.
- These are important for cellular signaling and regulation.
- Functions of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins:
- They are shape shifting molecules vital to cellular communication.
- They don’t form a fixed structure.
- They guide signalling networks.
- They help proteins move and find partners within the cell, regulate which genes are switched on or off,
- IDP support protein folding and quality control, and assemble flexible cellular hubs called condensates.
- Disobind Tool is developed by the researchers of National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS), Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bengaluru.
- Disobind Tool is open-source and freely available for researchers worldwide.
- It analyses the protein sequences and uses protein language models (a form of AI trained on millions of known protein sequences).
- No structural info needed: It does not require any structural information or sequence alignments, making it super convenient.
- High accuracy: Disobind outperformed popular tools like AlphaFold-multimer and AlphaFold3 in tests on new protein pairs.
- Disobind delivered consistently higher accuracy when tested on new protein pairs it had not seen before.
- Applications of the tool could span from disease biology to drug design.
Gorakhnath Temple:

A massive wave of devotion swept through the Gorakhnath Temple recently, a day ahead of the main Makar Sankranti festival, as lakhs of devotees gathered to offer khichdi to Mahayogi Guru Gorakhnath.
- It is a Hindu temple situated in Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh.
- The temple belongs to the Nath monastic group of the Nath tradition (a Shaiva sub-sect in Hinduism), which was instituted by Guru Matsyendranath.
- It is named after the Guru Gorakhnath, who was one of the notable disciples of Guru Matsyendranath and well-known for his Hatha Yoga, a renowned branch of Yoga.
- It serves as the epicenter of the Nath tradition.
- It is a blend of traditional and modern North Indian architectural styles, reflecting the heritage and simplicity of the Nath sect.
- The heart of the Gorakhnath Temple is the central shrine, which houses a sacred image of Gorakhnath as a deity and a Shiva Linga, as the Nath sect sees Gorakhnath as an incarnation of Lord Shiva.
- Intricate stonework and marble structures surround the inner shrine.
- Carved pillars and symbolic motifs around the sanctum highlight the Nath sect’s emphasis on inner spirituality.
One of the striking features is the temple’s dome, which is tall and conical, visible from a distance. - A significant feature of the Gorakhnath Temple is the Samadhi (final resting place) of Gorakhnath, which is a sacred spot within the temple complex.
Global Risks Report 2026:

The World Economic Forum (WEF) Global Risks Report 2026 has identified cybersecurity as the biggest risk for India in 2026, while geoeconomic confrontation has emerged as the single most severe global risk, overtaking armed conflict and climate threats.
- The Global Risks Report 2026 identifies cybersecurity as India’s biggest risk and geoeconomic confrontation as the most severe global threat, with rising inequality, weak public services, and strategic instability amplifying the impact of external shocks on India’s governance and economy.
- Addressing these risks requires stronger digital and economic resilience, treating inequality as a macro-risk, countering hybrid threats and disinformation, and embedding climate resilience into India’s long-term development and security strategy.
Key Findings of the Global Risks Report 2026:
- In the immediate term (2026), Geoeconomic Confrontation has emerged as the biggest global risk, overtaking armed conflict and extreme weather events as the most likely trigger of a global crisis.
- Geoeconomic Confrontation refers to the strategic use of economic tools such as trade restrictions, sanctions, investment controls, and technology bans by states to advance geopolitical interests and constrain rivals, weakening multilateralism and rising protectionism.
- State-based armed conflict ranks second globally, reflecting ongoing wars and regional spillover risks.
- Climate-related risks like extreme weather events rank next, alongside societal polarisation.
- Technological risks are rising globally, with misinformation and disinformation ranking 5th worldwide, reflecting growing threats to democratic processes and social trust.
- At the same time, adverse outcomes of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies have entered the top 10 global risks, highlighting concerns over job displacement, ethical misuse, and security challenges.
- Cyber insecurity ranks 9th globally, underscoring increasing digital vulnerability as economies and governance systems become more digitally dependent.
- Over the long term (next ten years), climate-related risks dominate, with extreme weather events, biodiversity loss, and critical changes to Earth systems at the top.
Guidelines for Virtual Digital Assets:

The Financial Intelligence Unit–India (FIU-IND) has introduced stringent new Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) guidelines for Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) service providers to curb financial crimes in India’s cryptocurrency ecosystem.
New FIU-IND Guidelines for Virtual Digital Assets:
- Mandatory live selfie with liveliness detection (eye-blink/head movement) and geographic tracking (latitude, longitude, timestamp, IP) during user onboarding to prevent static/deepfake fraud.
- Requires PAN + secondary ID (Aadhaar/Passport/Voter ID), OTP verification for email/mobile, and “penny-drop” bank account confirmation via a Rs 1 transaction.
- KYC updates every 6 months for high-risk clients and annually for others; enhanced due diligence for entities linked to tax havens, FATF grey/black lists, politically exposed persons (PEPs) or non-profit organisations (NPOs).
- Strongly discourages Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Initial Token Offerings (ITOs) and prohibits facilitation of anonymity-enhancing crypto tumblers and mixers.
- Crypto tumblers and mixers are services that enhance transaction privacy by pooling and scrambling funds from multiple users, then redistributing them to break the traceable link on the public blockchain ledger.
- Crypto exchanges must register as PMLA reporting entities, maintain 5-year client/transaction records, and report suspicious transactions to the FIU.
- A cryptocurrency exchange is a digital platform that allows users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies for other digital assets or traditional fiat money. E.g., Coinbase.
National Startup Day:
On the occasion of National Startup Day (16th January 2026), Prime Minister highlighted a decade of the Startup India Initiative at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, marking India’s transformation from a policy-led push for entrepreneurship in 2016 to one of the world’s largest startup ecosystems, aligned with the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.Startup India Initiative launched on 16th January 2016, the Startup India Initiative aims to support entrepreneurs, strengthen the startup ecosystem, and shift India from a job-seeking to a job-creating economy.A startup is a small, new, or young company founded by entrepreneurs to introduce a new product or service, disrupt an existing market, or even create a new one.The Startup India Initiative is implemented by a dedicated Startup India team under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
Rani Ahilyabai Holkar : Demolised
An inquiry has been ordered into allegations that a structure containing a statue of Devi Ahilyabai Holkar was demolished during renovation work at Manikarnika Ghat in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh.The Manikarnika Ghat renovation project, undertaken under a private company’s CSR initiative, aims to modernise facilities and address environmental issues. Ahilyabai was born on 31st May 1725 in Chondi, Ahmednagar (Maharashtra), her father, Mankoji Rao Shinde, was the village head.She was married to Khanderao Holkar in 1733, the son of Malhar Rao Holkar, the ruler of Malwa and the founder of the Holkar dynasty.Ahilyabai was widowed in 1745 after Khanderao died in the siege of Kumher Fort.Malhar Rao Holkar prevented Ahilyabai from committing sati and trained her in military and administrative matters. After the death of Malhar Rao Holkar in 1766 and her son Male Rao Holkar in 1767, Ahilyabai Holkar took charge of Malwa and became the ruler of Indore in 1767.She appointed Tukoji Rao Holkar as army commander and made Maheshwar in Madhya Pradesh the Holkar dynasty’s capital.Ahilyabai Holkar rebuilt the Kashi Vishwanath and Somnath temples in the 18th century, restoring key Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva, and patronised scholars such as Khushali Ram, Marathi poet Moropant, and Shahir Anantaphandi.
China’s In Spice Market:
China has begun cultivating and exporting chillies and cumin, two of India’s most critical spice exports, at lower and more competitive prices, posing a potential challenge to India’s long-standing dominance as the world’s largest spice supplier.Chillies form the backbone of India’s spice exports, accounting for over 25% of total export volume and value. Cumin, meanwhile, is among the most in-demand high-value spices, particularly in West Asia, Europe, and the Americas, where it is widely used in food processing and culinary applications.In 2024–25, India recorded strong growth in spice export volumes, with chilli powder exports rising 35% to 80.6 million kg and total chilli exports increasing 19% to over 700,000 tonnes, compared to 15% growth in 2023–24.Despite higher volumes, chilli export earnings declined 11% due to severe global price pressure, even as cumin exports surged 39% to 2.29 lakh tonnes from 1.65 lakh tonnes in 2023–24.China is strengthening its presence in the global spice market by focusing on high-demand chilli varieties such as paprika (for colour and mild flavour) and Teja chilli (for high pungency and pharmaceutical use), while importing raw Indian chillies, processing them domestically, and re-exporting finished products to third-country markets at competitive prices.
World’s First Repository of Mountain Ice Cores:
Scientists inaugurated the world’s first global repository of mountain ice cores at Concordia Research Station on the Antarctic Plateau to preserve vital climate records threatened by rapid glacier loss due to global warming.The facility, known as the Ice Memory Sanctuary, has been developed by the Ice Memory Foundation, a consortium of European research institutions from France, Italy, and Switzerland.The ice vault is a cave carved into compacted snow and maintained at a constant temperature of around –52°C, ensuring long-term preservation of ice cores for future scientific research.The first ice cores stored in the sanctuary were drilled from Mont Blanc in France and the Grand Combin massif in Switzerland, and transported to Antarctica over a 50-day journey using refrigerated ships and aircraft.Ice cores act as atmospheric time capsules, formed through long-term compaction of snow and preserving traces of gases, aerosols, dust, pollutants, and other indicators of past climate conditions.These samples enable scientists to reconstruct historical changes in climate, including atmospheric composition, environmental pollution, and the pace and causes of climate change across centuries.
The Ice Memory project, launched in 2015, has already identified and drilled cores from 10 glacier sites worldwide, with plans to expand storage and establish an international convention over the next decade to safeguard these samples for future generations.




