Today’s Current Affairs: 19th February 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
APEDA : In News

The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA), in collaboration with AgroStar and Kay Bee Exports, successfully completed India’s first-ever commercial trial shipments of premium Sangola and Bhagwa pomegranates, respectively, to Australia via sea.
- APEDA was established by the Government of India under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act passed by the Parliament in 1985.
- The Authority replaced the Processed Food Export Promotion Council (PFEPC).
- It works under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Objective is to develop and promote the export of scheduled products.
- The products specified under the APEDA ACT are called scheduled products, and exporters of such scheduled products are required to register under APEDA.
- It provides financial assistance, information, and guidelines for the development of scheduled products.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- APEDA also functions as the Secretariat to the National Accreditation Board (NAB) for the implementation of accreditation of the Certification Bodies under National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) for Organic exports.
Javelin Anti-Tank Guided Missile:

India and the US recently announced plans to pursue new procurements and co-production arrangements for Javelin anti-tank guided missiles, to meet the defense requirements of India.
- Javelin Anti-Tank Guided Missile is a man-portable, fire-and-forget, anti-tank guided missile.
- It has been developed jointly by American defence majors, Raytheon and Lockheed Martin.
- It was designed to defeat heavily armored vehicles such as main battle tanks and lighter-skinned military vehicles.
- The weapon also has capability against other target types like fortifications, bunkers, and helicopters.
- It has an effective range of 2.5 km.
- It is a fire-and-forget missile with lock-on before launch and automatic self-guidance.
- It uses automatic infrared guidance that allows the user to seek cover immediately after launch.
- The Javelin’s HEAT warhead is capable of defeating modern tanks by attacking them from above where their armor is thinnest, and is also useful against fortifications in a direct attack flight.
Souparnika River : Concern

Environmentalists have raised alarm over an alarming increase in pollution in the Souparnika River, which flows beside the Kollur Mookambika Temple.
- Souparnika River is a west-flowing river in Karnataka.
- The river is surrounded by lush green forests of the Western Ghats.
- Originating from the Kodachadri Hills in the Western Ghats, it flows through the Byndoor taluk, passing near the renowned Mookambika Temple in Kollur, before falling into the Arabian Sea.
- The Souparnika River is deeply associated with Hindu mythology.
- Legend has it that Garuda (the divine bird and vehicle of Lord Vishnu) performed penance on the riverbanks, which is how it got its name “Souparnika” (named after “Suparna,” another name for Garuda).
- A unique feature of the Souparnika River is observed near Maravanthe Beach, where the river runs parallel to the Arabian Sea, separated by a narrow stretch of land.
- This rare geographical phenomenon offers a picturesque landscape, making it a popular spot for tourists and photographers.
Sovereign Green Bonds:

Like several emerging markets, India also turned to sovereign green bonds to help fund its transition to a low-carbon economy, but investor demand remains weak.
- SGBs are debt securities issued by a national government to fund projects that have positive environmental benefits.
- The proceeds from these bonds are exclusively allocated to green initiatives, which can include renewable energy projects, sustainable agriculture, waste management, and more.
- Essentially, these bonds are a way for governments to raise capital while promoting environmental sustainability.
- The Union Budget 2022-23 announced the issue of SGBs. The framework for the SGBs was issued by the government on November 9, 2022.
- The government’s framework is based on the International Capital Market Association’s (ICMA) listed principles for issuing green bonds, which has four components:
- Use of proceeds, project evaluation and selection, management of proceeds, and reporting.
- The government said the bonds’ proceeds will be used for green projects that:
- Encourage energy efficiency
- Reduce carbon emissions and greenhouse gases
- Promote climate resilience and/or adaptation
- Improve natural ecosystems and biodiversity, especially in accordance with the principles of sustainable development goals
- The framework listed investments in solar, wind, biomass, and hydro energy projects, and urban mass transportation projects such as metro rail, green buildings, pollution prevention and control projects.
- The government excluded projects such as fossil fuels, nuclear power generation, and direct waste incineration.
- The eligible expenditure is limited to government spending that occurred not more than 12 months prior to issuance.
- The proceeds should be allocated to projects within 24 months of issuing the bonds.
- If an eligible green project is postponed or cancelled, it will be replaced by another eligible green project.
Earthquake Swarm:

A state of emergency has been declared on Greece’s Santorini and the nearby islands of Ios, Amorgos, and Anafi after a swarm of undersea earthquakes this month.
- It occurs when multiple seismic events of comparable intensity strike a small area in relatively quick succession.
- It involves a series of many (sometimes thousands)low-intensity earthquakes without a discernible main shock that can occur over weeks in active geothermal areas.
- When seismic energy piles up inside the Earth and is released in small amounts from certain points, such a series of earthquakes can occur.
- In volcanic environments, this can be fluid released from deeper magma or circulating within active geothermal areas (in volcanic areas such as the Taupō Volcanic Zone).
- The earthquakes triggered by fluids occur as fault slip on the cracks and faults through which the water is moving.
- Magma movement can also act as the ‘driving mechanism’ for swarms, creating the earthquakes as magma-filled cracks push their way through the Earth’s crust.
- In such a case the earthquakes commonly occur near the crack tip (ahead of the magma where the crack is starting to open), or off to the side of the crack.
- A slow-slip event is essentially an earthquake in slow-motion, and typically involves centimetres to tens of centimetres of movement along a fault, over weeks to years.
- We commonly see slow slip events at the Hikurangi subduction zone, usually at least one or two per year
Ovoid cells:
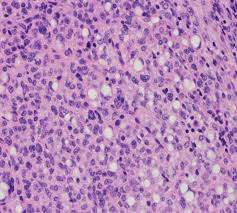
Researchers have discovered a new type of neuron that plays a fundamental role in recognition memory and named “ovoid cells.”
- These cells are named for the distinct egg-like shape of their cell bodies, are present in relatively small numbers within the hippocampus of humans, mice, and other animals.
- These are highly specialized neurons which get activated each time when we encounter something new.
- It triggers a process that stores those objects in memory and allows us to recognize them months, potentially even years later.
- They are quite distinct from other neurons at a cellular and functional level, and in terms of their neural circuitry.
- This discovery provides key insights into how memories form and could aid in the treatment of brain conditions related to object recognition, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Autism Spectrum Disorder and epilepsy.
NAKSHA Programme:

The Union Minister of Rural Development and Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare is inaugurating the NAKSHA Programme at Raisen, Madhya Pradesh.
- The National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations (NAKSHA) programme aims to create and update land records in urban areas to ensure accurate and reliable documentation of land ownership.
- This initiative will empower citizens, improve ease of living, enhance urban planning, and reduce land-related disputes.
- This IT-based system for property record administration will foster transparency, efficiency and support sustainable development.
- The Survey of India is the technical partner for NAKSHA programme, which is responsible for conducting aerial surveys and providing orthorectified imagery, through third party vendors, to State and Union Territory governments.
- The end-to-end web-GIS platform will be developed by the Madhya Pradesh State Electronic Development Corporation (MPSEDC) and storage facilities will be provided by the National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI).
- States and Union Territory governments are scheduled to conduct field surveys and ground truthing using the orthorectified imagery, ultimately leading to the final publication of urban and semi-urban land records.
Exercise Dharma Guardian:

The Exercise Dharma Guardian, between India and Japan is scheduled at Mount Fuji, Japan from February 25 to March 9, the Indian Army.
- It is a joint military exercise between India and Japan.
- It is an annual exercise and conducted alternatively in India and Japan.
- It aims to enhance interoperability between the two forces while undertaking joint urban warfare and counter-terrorism operations under UN mandate.
- 2025 Exercise will focus on a high degree of physical fitness, joint planning and joint tactical drills.
- Drills to be rehearsed during the exercise include advanced special forces skills and various other tactics, techniques and procedures as per the current operational paradigm.
- It will culminate with a 48-hour-long validation to rehearse the tactical drills for counterterrorism operations in desert and semi-desert terrain.
- In addition to tactical manoeuvres, it will foster stronger cultural and professional ties between the participating contingents.
President’s Rule in Manipur:
The Centre has imposed the President’s rule in Manipur under Article 356 of the Indian Constitution and suspended the state assembly after the resignation of its Chief Minister. Central rule will remove allegations of biased handling of ethnic violence, protecting both Kuki-Zo and Meitei communities. Governor-supervised central forces can prevent ethnic clashes and maintain law & order in the state. Prevents governance erosion by ending internal disputes within the ruling party. Ensures fair relief and rehabilitation for 60,000 displaced people in camps for over 20 months.
8th Indian Ocean Conference:
India’s External Affairs minister S Jaishankar represented India in the 8th Indian Ocean Conference (IOC) held in Muscat, Oman with the theme ‘Voyage to New Horizons of Maritime Partnership’. IOC is an annual summit bringing together leaders, policymakers, and experts from the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) to discuss geopolitical, economic, and security challenges.
It was established by the India Foundation (India based think tank) in 2016 in Singapore with participation from 30 countries. It aims to unite key states and maritime partners in the IOR to enhance regional cooperation under the vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
India’s Trade with Afghanistan and Nepal:
India recorded an unusual trade deficit with Afghanistan in the year 2023-24. In another development, soybean oil imports from Nepal surged 14-fold (April-November 2024), possibly due to rule-of-origin (RoO) violations.India’s exports to Afghanistan fell from USD 825.78 million in 2020-21 to USD 355.45 million in 2023-24, while imports rose from USD 509.49 million in 2020-21 to a record USD 642.29 million in 2023-24. Agricultural products like figs, asafoetida, raisins, apples, garlic, saffron, almonds, onions, pomegranates, and walnuts dominate. Nepal: India’s total soybean oil imports rose by 19% to nearly USD 3 billion (April-November 2024) from USD 2.5 billion in 2023. Rule-of-Origin Violation: Nepal imports 98% crude edible oil, refines it, and exports it to India indicating duty structure exploitation.
DRC Conflict and M23 Militia:
The ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has escalated with the M23 militia, backed by Rwanda, capturing the mineral-rich city of Goma. The conflict has resulted in 2,900 deaths, displaced nearly 700,000 people, and spread to South Kivu province, a region rich in resources.M23 Formed in 2012 after the failure of a 2009 peace agreement between the DRC government and Tutsi-led National Congress for the Defence of the People (CNDP).
4th India-EU Urban Forum:
The 4th India-EU Urban Forum, held in New Delhi has strengthened India-EU collaboration on sustainable urban development.India-EU Urban Forum is a high-level platform for dialogue and collaboration between India and the European Union (EU) on smart and sustainable urbanization, established as part of the 2017 Joint Declaration on Partnership for Smart and Sustainable Urbanization.It facilitates discussions among officials, experts, and stakeholders to exchange best practices, policies, and innovative solutions for sustainable urban development.
Nuclear Fusion Reactor:
China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) achieved a record 1,066 seconds of sustained plasma operation at nearly 70 million degrees Celsius in January 2025.EAST (Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak) is a nuclear fusion research reactor designed to test and improve magnetic confinement for controlled fusion. It serves as a testbed for ITER, helping scientists develop technologies for sustained plasma stability.
Gyanesh Kumar has been appointed as the new Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) of India:
Gyanesh Kumar has been appointed as the new Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) of India, succeeding Rajiv Kumar.The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) heads the Election Commission of India (ECI), ensuring free and fair elections.Governed by Article 324 of the Indian Constitution, which vests the superintendence, direction, and control of elections in the Election Commission.
Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation:
The Finance Ministry is considering increasing the deposit insurance limit, which currently stands at ₹5 lakh under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961.DICGC is a subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that provides deposit insurance to bank depositors, ensuring the safety of their money in case of bank failures. Operates under the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance.Aim is to protect depositors’ funds and maintain public confidence in the banking system.
RBI Ombudsman Called As “रिज़र्वबैंक ओम्बड्समैन योजना 2021”:
The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013 mandates the establishment of Lokpal at the Union level and Lokayuktas at the State level to investigate allegations of corruption against public officials. The term “Lokpal” is exclusively designated for the body created under this Act and came into force on January 16, 2024, under Section 3 of the Act. However, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had introduced the Reserve Bank-Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (RB-IOS), 2021, which was erroneously translated into Hindi as “रिज़र्वबैंक-एकीकृत लोकपाल योजना, 2021.”
Fecal Coliform:
High levels of fecal coliform bacteria were detected in the Ganga and Yamuna rivers at Prayagraj during Maha Kumbh 2025, as per a CPCB report submitted to NGT.A subgroup of coliform bacteria that primarily originate from the intestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, including humans. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) standards have set a permissible limit of 2,500 units of faecal coliform per 100 ml of water, while for drinking water, E. coli must be absent.
Union Minister Pabitra Margherita Inaugurates SILKTECH 2025:
The CSB’s International Conference – SILKTECH 2025 was inaugurated by Shri Pabitra Margherita, Hon’ble Minister of State for Textiles & Foreign Affairs, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, as part of the Bharat Tex 2025 mega textile event. The conference, organized by CSB-Central Tasar Research & Training Institute, Ranchi, and CSB-Central Silk Technological Research Institute (CSTRI) under the Ministry of Textiles, focused on emerging technologies in the silk sector to enhance quality, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Nine Years Of Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana:
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), India’s flagship crop insurance scheme, has completed nine years since its launch on February 18, 2016, under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The initiative aims to provide comprehensive crop insurance to Indian farmers, safeguarding them against various risks like natural disasters, pests, and diseases. Over these nine years, the scheme has proven to be a vital tool for farmers, disbursing ₹1.75 lakh crore in claims to over 23.22 crore farmers.
PM-AASHA Scheme Extended:
The Government of India has extended the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) scheme until 2025-26. This move is aimed at providing better income support to farmers by ensuring that they receive remunerative prices for their produce. PM-AASHA also helps stabilize the prices of essential food commodities, benefiting both farmers and consumers alike.The PM-AASHA scheme focuses on several key components that directly benefit farmers. One of the main components is the Price Support Scheme (PSS). This scheme allows the government to procure notified pulses, oilseeds, and copra at the Minimum Support Price (MSP) from pre-registered farmers through designated agencies like NAFED and NCCF. This ensures that farmers get a fair price for their crops, even when market prices are low.
Indian Navy Launches Eighth MCA Barge, LSAM 11:
The Indian Navy marked a significant milestone by launching its eighth Missile Cum Ammunition (MCA) Barge, LSAM 11 (Yard 79). This key event took place in Mira Bhayandar, Maharashtra, at the launch site of M/s SECON Engineering Projects Pvt Ltd, Visakhapatnam. The ceremony was presided over by Commodore N Gopinath, AGM (PL) at Naval Dockyard Mumbai. This addition to the Indian Navy’s fleet is set to strengthen its logistical support and operational capabilities.
Standard Chartered Appoints P.D. Singh as India CEO:
Standard Chartered Bank has secured approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to appoint Prabdev (P.D.) Singh as its Chief Executive Officer for India and South Asia. Singh, a veteran in corporate banking and former CEO of JP Morgan India, will assume his new role on April 1, 2025. He will replace Zarin Daruwala, who is set to retire on March 31, 2025, after leading the bank for nearly a decade.
Tata Group Chairman N. Chandrasekaran Honored with UK Knighthood:
N. Chandrasekaran, Chairman of Tata Group, has been awarded an honorary knighthood by the United Kingdom. This prestigious recognition highlights his remarkable contributions to strengthening business ties between India and the UK. The UK government conferred this honor on February 14, 2025, acknowledging his leadership in driving Tata Group’s investments and collaborations in the UK.




