Today’s Current Affairs: 20th April 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Lakshmana Tirtha River : Dried Up

Due to severe drought conditions and intense heat, the Lakshmana Tirtha River, has now completely dried up.
- Lakshmana Tirtha River is a tributary of the river Kaveri in Karnataka. It originates in the Brahmagiri hills, Kodagu or Coorg District, Karnataka, and flows eastward. It joins the Kaveri River in the Krishna Raja Sagara Lake.
- Lakshmanatirtha Falls, or the Irupu Falls, is a much-visited fresh water cascade located on the river, bordering Kerala, on the way to Nagerhole National Park.
- Kaveri River rises at an elevation of 1,341 m at Talakaveri on the Brahmagiri range near Cherangala village of Kodagu district of Karnataka.
- It drains into the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar, in the Mayiladuthurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Cauvery Basin extends over the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and Union Territory of Puducherry.
- It is bounded by the Western Ghats on the west, by the Eastern Ghats on the east and south and by the ridges separating it from the Krishna basin and Pennar basin on the north.
Global Alliance For Incinerator Alternatives:

The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific has called on the ASEAN to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
- Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) is a worldwide alliance of more than 1,000 grassroots groups, non-governmental organizations and individuals.
- It aims to power a transition away from our current linear and extractive economy and towards a circular system that supports people’s right to a safe and healthy environment.
- It envisions a just, zero-waste world built on respect for ecological limits and community rights, where people are free from the burden of toxic pollution and resources are sustainably conserved, not burned or dumped.
- This entails fighting pollution and building regenerative solutions in cities through local campaigns, shifts in policy and finance, research and communication initiatives, and movement building.
- They work on four primary points of intervention: incineration, zero waste, plastic, and climate.
- Incineration is the process of burning hazardous materials at temperatures high enough to destroy contaminants.
- Incineration is conducted in an “incinerator,” which is a type of furnace designed for burning hazardous materials in a combustion chamber.
- Many different types of hazardous materials can be treated by incineration, including soil, sludge, liquids and gases.
Gross Fixed Capital Formation:

The failure of private investment, as measured by private Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) as a percentage of GDP at current prices, to pick up pace has been one of the major issues plaguing the Indian economy.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) refers to the growth in the size of fixed capital in an economy.
- Fixed assets/capital are tangible or intangible assets produced as outputs from production processes that are used repeatedly or continuously, for more than one year.
- It consists of resident producers’ investments, deducting disposals, in fixed assets during a given period.
- It also includes certain additions to the value of non-produced assets realized by producers or institutional units.
- Private GFCF can serve as a rough indicator of how much the private sector is willing to invest.
- Overall GFCF also includes capital formation as a result of investment by the government.
- It matters because fixed capital, by helping workers produce a greater amount of goods and services each year, helps to boost economic growth and improve living standards.
- In other words, fixed capital is what largely determines the overall output of an economy and, hence, what consumers can actually purchase in the market.
- Developed economies such as the U.S. possess more fixed capital per capita than developing economies such as India.
- GFCF in the Indian economy increased significantly from INR 32.78 lakh crore in 2014-15 to INR 54.35 lakh crore in 2022-2023.
- This surge in capital formation reflects substantial investments in infrastructure, industry, and public goods.
Clouded Tiger Cat : Discovered

A new species of tiger cat, the clouded tiger cat, discovered in Brazil, faces threats from deforestation and illegal hunting.
- Clouded Tiger Cat is a new species of forest-dwelling tiger cat. Its scientific name is Leopardus pardinoides
- It is found in the cloud forests of the southern Central American and Andean Mountain chains, which stretch from Costa Rica through Panama, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, and Argentina.
- It is a long-tailed cat with short-round ears, weighing 2.27 kg.
- It has a remarkably margay-looking head, which has a nice dense soft fur of a rich reddish/orangish/grayish-yellow background color adorned with irregularly shaped medium-large ‘cloudy’ rosettes that are strongly marked and often coalesce.
Mount Ruang : Erupted

Mount Ruang initiated its eruption recently, propelling an ash cloud upwards of a mile into the sky.
- Mount Ruang is a stratovolcano located in Indonesia’s North Sulawesi province. Its summit stands 10,932 feet above sea level, with a caldera that is about two miles wide.
- Stratovolcano is a tall, steep and cone-shaped type of volcano. Unlike flat shield volcanoes, they have higher peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
- It comprises the largest percentage (~60%) of the Earth’s individual volcanoes, and most are characterized by eruptions of andesite and dacite, lavas that are cooler and more viscous than basalt.
- These more viscous lavas allow gas pressures to build up to high levels.
- Therefore, these volcanoes often suffer explosive eruptions.
Dragonfly Mission : NASA

NASA confirmed Dragonfly rotorcraft mission to Saturn’s organic compound-rich moon Titan with a budget of $3.35 billion and a launch date set for July 2028.
- Dragonfly Mission is a “dual quadcopter” designed to fly across the surface of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon.
- It will explore a variety of locations on Saturn’s moon Titan.
- It will spend most of its time on the moon’s surface making science measurements. It will use a radioisotope power system like the Curiosity rover on Mars.
- Its flights, data transmission and most science operations will happen during the day, and it will have a lot of time to recharge during night on Titan.
- It is a rotorcraft, targeted to arrive at Titan in 2034, will fly to dozens of promising locations on the moon, looking for prebiotic chemical processes common on both Titan and the early Earth before life developed.
- It marks the first time NASA will fly a vehicle for science on another planetary body. The rotorcraft has eight rotors and flies like a large drone.
DURGA-2 : Testing

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is reported to be testing a prototype of its DURGA-2 (Directionally Unrestricted Ray Gun Array) system.
- DURGA-2 damages or destroys its target using focused energy by means of lasers, microwaves or particle beams.
- These weapons have several advantages over conventional munitions.
- They transmit lethal force at the speed of light (about 300,000 kilometers per second).
- Their beams are not affected by the constraining effects of gravity or atmospheric drag.
- They are extremely precise. Fourth, their effects can be tailored by varying the type and intensity of energy delivered against targets.
- The aerospace industry can transform the way wars will be fought.
- This will enable us to produce cutting edge platforms, weapons, sensors, and networks essential to fight and win a future war.
GPS Spoofing:
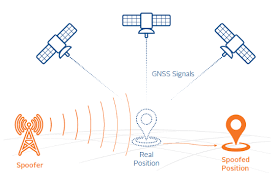
Israel reportedly used GPS jamming to confuse Iran’s missile targeting teams ahead of Iran’s direct attack on Israel.
- This technique, similar to what the US allegedly did during India’s Kargil war in 1999, can hinder military operations by degrading GPS signals.
- The US initially employed “selective availability” to degrade GPS accuracy for India during the Kargil war, prompting India to develop its own navigation system called NavIC.
- In the recent incident, Israeli locals found their GPS showing them in Cairo or Beirut, causing confusion about throwing off Iran’s missiles.
GPS Spoofing:
- GPS spoofing, also known as GPS simulation, involves manipulating or tricking a GPS receiver by broadcasting false GPS signals.
- This leads the receiver to believe it is located somewhere it is not, resulting in inaccurate location data.
- This cyberattack undermines the reliability of GPS data, critical for navigation, time synchronization, and more.
- While initially a theoretical threat, GPS spoofing has become a practical concern due to affordable software and hardware capable of transmitting fake signals.
- This evolution poses risks and security challenges for industries, governments, and individuals.
CDP-SURAKSHA:

The Central government has launched a new platform called CDP-SURAKSHA to disburse subsidies to horticulture farmers under the Cluster Development Programme (CDP).
- This will boost the growth of India’s horticulture sector, which contributes nearly one-third to the agriculture gross value addition (GVA).
CDP-SURAKSHA:
- SURAKSHA stands for “System for Unified Resource Allocation, Knowledge, and Secure Horticulture Assistance.”
- The platform will allow an instant disbursal of subsidies to farmers in their bank accounts by utilising the e-RUPI voucher from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- It has features such as database integration with PM-KISAN, cloud-based server space from NIC, UIDAI validation, eRUPI integration, local government directory (LGD), content management system, geotagging, and geo-fencing.
- The platform allows access to farmers, vendors, implementing agencies (IA), cluster development agencies (CDAs), and officials of the National Horticulture Board (NHB).
- A farmer can login using their mobile number, place an order and contribute their share of the cost of planting material.
- After payment, an e-RUPI voucher will be generated. This voucher will then be received by a vendor, who will provide the required planting material to the farmer.
- After the delivery of material, farmers have to verify the delivery through geo-tagged photos and videos of their field.
- After verification, the implementing agencies (IA) will release the money to the vendor for the e-RUPI voucher. The vendor will be required to upload an invoice of the payment on the portal.
- The IA will collect all the documents and share them with the CDA for subsidy release, then only the subsidy will be released to the IA.
- The farmer, who raised the demand for the plant material using the platform, can avail of the subsidy at the first stage only.
Regulatory Sandbox : TRAI

The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has issued significant recommendations for customer onboarding and the oversight of the Regulatory Sandbox (RS).
- Eligibility for the RS in the Digital Communication Sector is limited to Indian nationals or entities, aiming to promote innovative technologies, services, use cases, and business models.
- Customer onboarding in the RS requires specific voluntary consent, emphasising ethical and legal customer engagement.
- Adherence to the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, is crucial for customer onboarding and data processing, highlighting the importance of data protection laws and regulations.
- Applicants must disclose details of licensing or regulatory relaxations sought for testing purposes and provide a clear exit strategy for the testing phase, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance.
- The oversight and governance of the RS is recommended to be managed by the National Telecommunications Institute for Policy Research, Innovation, and Training (NTIPRIT), with involvement from the Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC) and academic institutions as needed.
Commonwealth Games : Malaysia Rejected To Host

Malaysia rejected the offer to host the Commonwealth Games (CWG) citing short notice and insufficient funds.
- The Commonwealth Games (CWG) is a quadrennial international multi-sport event among athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations, which mostly consists of territories of the former British Empire.
- The Commonwealth is a collective of 56 countries, primarily former British colonies.
- Established in 1949 by the London Declaration.
- Members are mainly situated in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and the Pacific, with notable emerging economies.
- It was created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration of 1926.
- The chief institutions of the organisation are Commonwealth Secretariat and Commonwealth Foundation which focuses on intergovernmental aspects and non-governmental relations among member states respectively.
100 % FDI In Space Sector:

The Finance Ministry has notified amended rules under the Foreign Exchange Management Act to operationalise its earlier decision to allow up to 100 per cent foreign direct investment (FDI) for the space sector. The new rules came into effect from April 16.
- The Union Cabinet had approved the amendment to the FDI policy for the space sector, allowing up to 100 per cent investment in certain categories.
- As per the latest Finance Ministry notification, 100 per cent FDI has been allowed for the space sector category of manufacturing and operation of satellites, satellite data products, and ground segment and user segment, out of which up to 74 per cent would be through the automatic route and government nod would be required for investment beyond 74 per cent.
- Under the earlier policy, any foreign investment in manufacturing and operating satellites is allowed only with government approval.
- Manufacturing of components and systems or sub-systems for satellites, ground segment and user segment will be fully under the 100 per cent automatic route.
- Automatic FDI has also been permitted up to 49 per cent for launch vehicles and associated systems or subsystems, and creation of spaceports for launching and receiving spacecraft. Government approval would be required for investments beyond 49 per cent.
- The notification dated April 16 comes ahead of Tesla chief Elon Musk’s visit to India early next week where he is expected to meet space startups, make a push for his space venture Starlink’s plans and announce his electric vehicle (EV) investment plans.
About FDI:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is defined as an investment in which a company takes controlling ownership of a business entity in another country.
- Therefore, foreign companies get directly involved with day-to-day operations in other countries.
- India gets FDI through two routes:
- (a) Automatic route: Under this route, the non-resident or Indian company does not require a prior nod from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) or the government of India for FDI.
- (b) Government route: Under this route, the government’s approval is mandatory.
- The company will have to apply through Foreign Investment Facilitation Portal, which facilitates single-window clearance.




