Today’s Current Affairs: 20th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Char Dham Yatra : Death Of 11 Pilgrims

With nearly twice the number of pilgrims embarking on the Char Dham yatra in Uttarakhand since it commenced on May 10, the state government has reported the death of 11 pilgrims in the first five days.
- The pilgrimage to Yamunotri, Gangotri, and Kedarnath Dham commenced on May 10, while the doors to Badrinath Dham opened on May 12.
- Over 1.55 lakh pilgrims have already journeyed to Kedarnath, over 70,000 to Yamunotri, and over 63,000 to Gangotri. Within just three days, Badrinath Dham has welcomed over 45,000 pilgrims.
- The Chota Char Dham Yatra is a significant pilgrimage in India, particularly in the state of Uttarakhand, also known as Devbhoomi or the Land of Gods. The term ‘Char Dham’ in Hindi translates to ‘four religious destinations’.
- This Yatra or pilgrimage is a tour of four holy sites nestled high up in the Himalayas.
- The pilgrimage sites are Yamunotri and Gangotri in Uttarkashi district, Kedarnath in Rudraprayag and Badrinath in Chamoli.
- While Kedarnath is the highest at around 11,700 ft, Gangotri is the lowest at around 10,200 ft.
- The Yamunotri temple is lodged in a narrow gorge close to the source of River Yamuna, the second-most sacred Indian river after River Ganga, in Uttarkashi district. It is dedicated to Goddess Yamuna.
- Gangotri: Located in the Uttarkashi district, Gangotri is dedicated to Goddess Ganga, the most sacred of all Indian rivers.
- Kedarnath: Located in the Rudraprayag district, Kedarnath is dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- Badrinath: Home to the sacred Badrinarayan Temple, Badrinath is dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- The Yatra is believed to be completed in a clockwise direction, starting from Yamunotri, proceeding towards Gangotri, onto Kedarnath, and finally ending at Badrinath.
- The high-altitude shrines remain shut for around six months every year, opening in summers (April or May) and closing with the onset of winter (October or November).
- Some devotees even do a Do Dham Yatra or a pilgrimage to two shrines – Kedarnath and Badrinath.
Sailfin Armoured Catfish:

Scientists from CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) have discovered that the invasive armoured sailfin catfish has proliferated to 60% of the water bodies in the Eastern Ghats, causing harm to fishing nets and disrupting the ecosystem.
- The sailfin armoured catfish, a collection of several morphologically similar species belonging to the genus Pterygoplichthys of the Loricariidae from South America, has been widely introduced to tropical and subtropical freshwater environments worldwide and has caused serious ecological impacts.
- It is one of the most serious invasive species.
- In India, the fish species was originally introduced for its distinct appearance and its capacity to remove algal growth in tanks and aquariums, but its population has since increased dramatically.
- Sailfin catfish have worm-like dark markings on the head over a dark-golden background, stout pectoral fins with rough surfaces, and a disc-like, protrusible mouth used like a suction cup to attach and feed on algae.
- Female fish are generally smaller, while those larger than 18 inches are likely to be male.
- Sailfin catfish live in various slow-moving water bodies and are most commonly found near the shore and in shallow waters.
- They are known to create spawning burrows along shorelines, sometimes undermining canal banks and lake shorelines.
Global Report On Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD) Of 2024:

Ahead of the World Health Assembly 77th session, the World Health Organization (WHO) released its Global report on neglected tropical diseases (NTD) of 2024.
- The report provides an account of the progress made in 2023 towards the implementation of the Road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030.
Key highlights of the WHO Report:
- As of December 2023, a total of 50 countries have successfully eliminated at least one NTD, marking the halfway point towards the 2030 target of 100 countries.
- 5 countries were acknowledged by WHO for eliminating one NTD, and 1 country for eliminating two NTDs.
- In July 2023, Iraq became the 50th country to eliminate at least one NTD. This event marks the halfway point towards achieving the 100-country target set for 2030.
- Noma was added to the list of NTDs in 2023.
- In October 2023, Bangladesh became the first country to be validated by WHO for eliminating visceral leishmaniasis as a public health problem.
- India was certified free of NTDs like dracunculiasis and yaws.
- India, which has the highest disease burden, treated about 117 million fewer people for lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in 2022 compared to 2021.
- 40.56% of India’s population needed interventions against NTDs in 2022.
National Savings Certificate: Investment

The Prime Minister recently declared Rs 9.12 lakh investment in the National Savings Certificate (NSC) scheme in his nomination filing.
- National Savings Certificate (NSC) is a fixed-income investment scheme launched by the government of India.
- It aims at encouraging users, who are primarily low- to mid-income investors, to invest as well as save taxes.
- You can invest in NSC from the nearest post office in your name, for a minor or with another adult as a joint account.
- The certificates earn an annual fixed interest, which is revised every quarter by the government, thus guaranteeing a regular income for the investor.
- Maturity Period: Five years.
- The amount of NSCs that can be purchased has no upper limit.
- As a government-backed tax-saving scheme, the principal invested in NSC qualifies for tax savings under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs annually.
- It can be easily bought from any post office on submission of the required KYC documents.
- Also, it is easy to transfer the certificate from one PO to another, as well as from one person to another, without impacting the interest accrual/maturity of the original certificate.
- NSC certificates are accepted as collateral or security for secured loans in Banks and NBFCs.
- The investor can nominate any family member (even a minor) so that they can inherit it in the unfortunate event of the investor’s demise.
- Generally, one cannot exit the scheme early except on the death of an investor, on a court order, or on forfeiture by a pledgee who is a Gazetted Government Officer for it.
MATES Migration Scheme:

The Australian Federal Budget Document, released recently, announced the start date for the Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES) for Indian Nationals.
- Australia and India entered into a Migration and Mobility Partnership Arrangement (MMPA).
- The MMPA is a bilateral framework that supports and promotes two-way migration and mobility between our two countries while addressing issues pertaining to illegal and irregular migration.
- The Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-Professionals Scheme, or ‘MATES’, is a new scheme established under the MMPA to enable the temporary mobility of Indian university graduates and early career professionals.
- MATES aims to encourage mutually beneficial skills and knowledge transfer between Australia and India.
- Under the scheme, Indian graduates and early career professionals (aged 18 to 30 years) with knowledge and skills in targeted fields of study will be offered a new temporary mobility pathway, to live and work in Australia for up to two years.
- Eligibility Criteria for MATES: MATES will be open to Indian Nationals who are:
- Must be 30 years old or younger at the time of application
- Have not previously participated in MATES
- Have proficient English language skills
- Have graduated within two years from an eligible educational institution at the time of application
- Hold a qualification (Bachelor’s degree or higher) in target fields of study
- There will be no requirement for sponsorship by an Australian employer to be eligible to apply for a visa as part of MATES.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor:
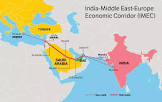
An Indian delegation recently paid a visit to the UAE for the first time to hold discussions with the key entities there on the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) was announced on the sidelines of the G20 meeting in New Delhi when a memorandum of understanding was signed between the European Union and seven countries, namely India, the US, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), France, Germany, and Italy.
- The corridor will provide a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network to supplement existing maritime routes.
- It intends to increase efficiency, reduce costs, secure regional supply chains, increase trade accessibility, enhance economic cooperation, generate jobs, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- The IMEEC will comprise two separate corridors, the east corridor connecting India to the Gulf and the northern corridor connecting the Gulf to Europe.
- The corridor will include a shipping route connecting Mumbai and Mundra (Gujarat) with the UAE, and a rail network connecting the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan with the Israeli port of Haifa to reach the shores of the Mediterranean Sea.
- Haifa will then be connected by sea to the port of Piraeus in Greece to eventually be connected to Europe.
- Beyond the transport infrastructure, undersea cables would facilitate the exchange of data, while long-distance hydrogen pipelines would boost the participants’ climate and decarbonisation goals.
Phtheirospermum lushaiorum : Hemi-Parasitic Terrestrial Plant

A rare hemi-parasitic terrestrial plant named Phtheirospermum lushaiorum has been found in Phawngpui National Park in Mizoram.
- Phtheirospermum lushaiorum is a new species of hemi-parasitic terrestrial plant.
- These hemi-parasitic plants lack a fully developed root system and form connections with another plant, from which they obtain some or all of their water and minerals.
- Such plants have chlorophyll and produce their own food by photosynthesis, and in some cases, are capable of limited growth in the absence of the host plant.
- They tap into the sap-conducting tissue of the host by means of specialized structures called haustoria.
- The new species has been found in Phawngpui National Park of Mizoram.
- Phtheirospermum lushaiorum attaches themselves to the roots of their host and appear like normal plants growing in the soil.
- They flower only during July to September and fruits are produced during August to October.
- The specific epithet “lushaiorum” is named after the “Lushai” tribe of Mizoram.
SPECULOOS-3b : New Dwarf Planet

An international team of astronomers recently detected a new, Earth-sized planet named SPECULOOS-3b, just 55 light years away, orbiting an ultra-cool red dwarf star.
- SPECULOOS-3b is an Earth-size planet orbiting an ultracool red dwarf star, 55 light-years away from Earth.
- This red dwarf, though similar in size to Jupiter, emits light 100 times dimmer than the sun and has half the temperature.
- The planet is only the second of its kind to be discovered around this type of star.
- SPECULOOS-3b receives high levels of radiation from its sun, probably leaving the planet without an atmosphere.
- The planet receives almost 16 times more energy per second than Earth receives from the Sun.
- It takes around 17 hours to complete an orbit of the star.
- The planet is thought to be tidally locked, so the same side, known as the dayside, always faces the star, like the Moon to Earth. The nightside would be locked in never-ending darkness.
- The discovery was made by the team from the SPECULOOS (Search for Planets EClipsing ULtra-cOOl Stars) project, which is led by the University of Liège, in Belgium, in collaboration with the Universities of Birmingham, Cambridge, Bern, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, using the observatory located in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile.
- The SPECULOOS project was established to search for exoplanets orbiting ultra-cool dwarf stars using a network of robotic telescopes based around the world.
Vishing : Cybercrime

The government released a circular warning its employees of a sophisticated cybercrime— vishing.
- Vishing is short form of voice+phishing, is carried out through a call on a mobile phone or landline.
- It’s a technique wherein a threat actor calls the victim over the phone and tries to trick him/her into clicking on malicious files or emails, which can then take one to a legitimate-looking website asking to share personal information.
- In other cases, the attacker can solicit sensitive information from the victim.
- It can be so tricky that the caller might appear as the manager or colleague of the victim, enticing her to share sensitive information, at times using urgency as the tactic.
RoseTTAFold : AI-Based Prediction Tool
AI-based prediction tool RoseTTAFold has provided a major scientific breakthrough in the last four years in the area of computational drug development.
- RoseTTAFold is developed by researchers at the University of Washington, U.S.
- It uses generative diffusion-based architectures (one kind of AI model) to predict structural complexes.
- The tools’ neural networks use massive amounts of input data to produce the desired output — the three-dimensional structures of proteins.
- It uses deep learningto quickly and accurately predict protein structures based on limited information. Without the aid of such software, it can take years of laboratory work to determine the structure of just one protein.
- It is a “three-track” neural network, meaning it simultaneously considers patterns in protein sequences, how a protein’s amino acids interact with one another, and a protein’s possible three-dimensional structure.
- It has the capability to predict not just static structures of proteins and protein-protein interactions but also their ability to predict structures and interactions for any combination of protein, DNA, and RNA.




