Today’s Current Affairs: 29th Nov 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
4th ASEAN India Grassroots Innovation Forum:

India and 10 ASEAN Member States (AMS) showcased unity at the launch of the 4th edition of the ASEAN India Grassroots Innovation Forum (AIGIF).
- The event, graced by 200 participants, aims to strengthen the bond between India and AMS through cooperation in Science, Technology, and Innovation (STI).
- The AIGIF, an annual program, is designed to foster collaboration and deepen ties between India and AMS.
- With a focus on social innovations across countries, it also plays a pivotal role in fortifying governance in the grassroots innovation ecosystem.
- This annual initiative is a collaborative effort between the ASEAN Committee on Science, Technology, and Innovation (COSTI); the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Government of India; the National Innovation Foundation (NIF) – India; and the host nation’s Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MOSTI), represented by Yayasan Inovasi Malaysia (YIM) for the year 2023.
- The delegation included 17 student innovators and grassroots innovators from India, contributing to a total representation of 200 from 11 countries.
Christopher Luxon : New Zealand’s Prime Minister

Christopher Luxon sworn in as New Zealand’s prime minister.
- The swearing-in ceremony was presided over by Governor-General Cindy Kiro.
- New Zealand, an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, the southwesternmost part of Polynesia.
- It lies more than 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Australia, its nearest neighbour.
- The country comprises two main islands—the North and the South Island—and a number of small islands, some of them hundreds of miles from the main group.
- The North Island of New Zealand has a ‘spine’ of mountain ranges running through the middle, with gentle rolling farmland on both sides.
- The central North Island is dominated by the Volcanic Plateau, an active volcanic and thermal area.
Green Leaf Volatile : New Research Plant Plant Communication
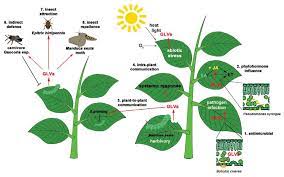
Researchers from Japan have conducted groundbreaking research on plant-plant communication through volatile organic compounds (VOCs) called Green Leaf Volatile (GLV).
- Using real-time fluorescence imaging, they visualized how plants take up VOCs released by damaged neighbours, leading to calcium-dependent defence responses against potential threats.
- The research also revealed that guard cells, responsible for stomatal function, play a crucial role in VOC perception.
- GLVs are common constituents of herbivore-infested plant volatiles. GLVs play an important role in plant defence.
- This discovery enhances understanding of the intricate communication network among plants for timely defence responses.
- The findings showcase nature’s remarkable adaptations and have broader implications beyond plant science
Special Category Status To Bihar:

The Bihar Cabinet has passed a resolution seeking the grant of Special Category Status (SCS) to Bihar.
- The demand comes in the backdrop of the findings from the “Bihar Caste-based Survey, 2022”, which revealed that nearly one-third of Bihar’s population continues to live in poverty.
- Special Category Status is a classification given by the Centre to assist development of states that face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages.
- The Constitution does not make a provision for SCS and this classification was later done on the recommendations of the 5th Finance Commission in 1969.
- Status was first accorded to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland in 1969.
- SCS for plan assistance was granted in the past by the National Development Council of the erstwhile Planning Commission.
- Eleven States including Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Uttarakhand and Telangana have been accorded the special category state status.
- Telangana, the newest State of India, was accorded the status as it was carved out of another state Andhra Pradesh.
- SCS is different from Special status which imparts enhanced legislative and political rights, while SCS deals with only economic and financial aspects.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia:
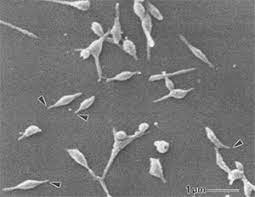
The authorities in China have reported an increase in the incidence of respiratory diseases and have attributed this to the circulation of various pathogens, such as mycoplasma pneumonia.
- Mycoplasma Pneumonia is a type of bacteria that acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It infiltrates both sides of the lungs, increasing cough and breathing difficulties. It damages the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It is not as rapidly infectious as a virus but it can affect our throat and our nasal cavities and descend to the lungs very quickly, causing pneumonia.
- Signs include the breakup of red blood cells, a skin rash and joint pain.
- Children may report a stuffy or runny nose, sore throat, watery eyes, wheezing, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
- The bacteria can cause pneumonia in any age group, especially in children, elderly or those with weakened lungs.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- There are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection
Sagittarius C : James Webb Space Telescope Captured Image

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) captured a image of the dense centre of the Milky Way galaxy with clarity never seen before.
- Sagittarius C (Sgr C) is the star-forming region known to be situated approximately 300 light-years from the Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*.
- It is revealing a bustling cluster of protostars within an infrared-dark cloud.
- These nascent stars are in the process of accumulating mass, their outflows glowing intensely in the infrared spectrum, akin to embers in a cosmic bonfire.
- The cloud that protostars are emerging from is so dense that the light from stars behind it cannot reach Webb.
- Scattered throughout are smaller infrared-dark clouds, akin to celestial voids against the starry backdrop, signalling the birthplaces of future stars.
- Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) has detected extensive emissions from ionised hydrogen on the periphery of the dark cloud, highlighted in a striking cyan hue.
James Webb Space Telescope:
- It was built in collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency(ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency.
- It was launched in December 2021.
- It is presently at a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point.
- Lagrange Point 2 is one of the five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
Gulf Of Aden:
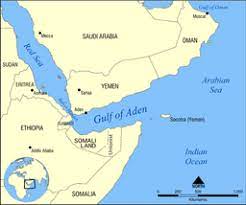
A U.S. Navy warship responded to a distress call from a commercial tanker in the Gulf of Aden that had been seized by armed individuals recently.
- Gulf of Aden is an extension of the Indian Ocean, tucked between the Arabian Peninsula and the African continent.
- The gulf is named after “Aden,” a port city on Yemen’s coast.
- It is bounded to the south by Somalia and the Socotra Islands (part of Yemen), to the north by Yemen, to the east by the Arabian Sea, and to the west by Djibouti.
- The gulf is connected to the Somali Sea to the south by the Guardafui Channel and to the Red Sea on the west by the Strait of Bab el Mandeb.
- It is approximately 900 km long and 500 km wide and covers roughly 410,000 square kilometers.
- It has an average depth of 500 meters and a maximum depth of 2,700 meters.
- The dominant relief feature of the gulf’s terrain is the Sheba Ridge, an extension of the Indian Ocean ridge system, which extends along the middle of the gulf.
- It is also a critical part of the Suez Canal shipping route, which connects the Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Some of the major cities near the gulf include Aden, Mukalla, Ahnwar, Balhaf, Berbera, Bosaso, and Djibouti City.
AstroSat : India’s First Multi-Wavelength Space Telescope

India’s first multi-wavelength space telescope, AstroSat, has successfully detected its 600th Gamma-ray Burst (GRB), an event named GRB 231122B.
- AstroSat is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The spacecraft control centre at Mission Operations Complex (MOX) of ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru, manages the satellite during its entire mission life.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is around 5 years.
- It carries a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- Scientific Objectives:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
Himalayan Black Bear:

An animal keeper died after being attacked by a Himalayan black bear in the animal’s enclosure at Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) recently.
- Himalayan Black Bear is a subspecies of the Asian black bear.
- Scientific Name: Ursus thibetanus laniger
- They live a lot in the Himalayas, in Tibet, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and China.
- In India, they are found throughout the Himalayas, from Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh, and in hilly regions of other northeastern states.
- The species prefers heavily forested, broadleaved, and coniferous forests as habitat.
- It uses orchards, agricultural fields, and human habitation to move between forest patches.
- It has soft and shiny hair, with a white V patch on its chest.
- On average, they range from 1.4 to 1.7 metres in length and weigh from 90 to 200 kg (the higher figure is only likely just prior to hibernation).
- They are omnivorous creatures (like most bears). Their diet consists of acorns, nuts, fruit, honey, roots, and various insects such as termites and beetle larvae.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
Rythu Bandhu Scheme:

The Election Commission recently withdrew the permission given to the Telangana government to disburse financial aid to farmers under the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme also known as the Farmer’s Investment Support Scheme (FISS), is a welfare programme for farmers started by the Telangana government in 2018.
- The objective of this scheme is to provide a timely cash grant for the initial investment needs of farmersand o ensure that farmers do not fall into the debt trap.
- Under the scheme, financial assistance of Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer each season is directly transferred to each farmer’s account.
- This financial support was distributed biannually, allocated for both the kharif and rabi harvests.
- The assistance can be used for the purchase of inputs like seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labour, and other investments in the field operations of Farmer’s choice for the crop season.
- The scheme is open to all resident farmers in the state who own land.
- Farmers cultivating the land in the forest, a majority of them from Scheduled Tribe communities and having a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR) document, are also eligible to receive benefits under the scheme.
- It is the country’s first direct farmer investment support scheme where cash is paid directly to the beneficiary.




