Today Current Affairs: 2nd July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Black Carbon And Its Impacts On Health:

A team of researchers conducted a Study on black carbon and its impacts on health.
Key findings:
- Black Carbon has a significant adverse effect on human health and can lead to a premature death.
- The Indo-Gangetic plain is exposed to Black Carbon (BC) with serious implications on regional climate and human health.
- Mortality rises linearly with an increase in air pollutants level and shows adverse impact at higher levels.
- The inclusion of BC as a potential health hazard inspires and provides a background for more epidemiological studies to provide evidence of health effects of air pollutants from different parts of India.
- This will help government and policy-makers for better planning to mitigate the adversity associated with changing climate-air pollution-health nexus.
Black Carbon:
- Black carbon results from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass. BC is produced both naturally and by human activities as a result of the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuels, and biomass.
- Primary sources include emissions from diesel engines, cook stoves, wood burning and forest fires.
- It is a short-lived pollutant that is the second-largest contributor to warming the planet behind carbon dioxide (CO2).
Union Vs Central Government:

In Tamil Nadu, however, a controversy erupted earlier this month over the new DMK government referring to the government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi as the ‘union government’ (ondriya arasu) instead of ‘central government’ (madhiya arasu).
- In common parlance, the terms “union government” and “central government” are used interchangeably in India.
- However, Article 1(1) of the Constitution of India says “India, that is Bharat, shall be a Union of States.”
- Scholars of India’s constitutional system have described it as being “basically federal, with striking unitary features” (D D Basu).
- While submitting the draft Constitution in 1948, Dr B R Ambedkar, chairman of the drafting committee, had said that the committee had used the world ‘Union’ because
- the Indian federation was not the result of an agreement by the units, and
- the component units had no freedom to secede from the federation.
Kuvempu Award 2020:

Odia poet Dr. Rajendra Kishore Panda has been selected for the Kuvempu Rashtriya Puraskar (award) 2020.
- Dr. Panda, born in 1944, is a poet and novelist from Odisha. He has published 16 poetry collections and a novel.
- He was presented the Gangadhar National Award in 2010, and the Sahitya Akademi Award in 1985.
- It is a national award instituted in memory of the late poet laureate Kuvempu.
- The award is given annually to a writer who has contributed in any of the languages recognised by the Constitution of India.
- The award carries a cash award of Rs. 5 lakh, a silver medal and a citation.
Kuvempu:
- Kuppali Venkatappa Puttappa, popularly known by his pen name Kuvempu, was an Indian poet, playwright, novelist and critic.
- He is widely regarded as the greatest Kannada poet of the 20th century.
- He was the first Kannada writer to be decorated with the Jnanpith Award for his version of the Ramayana titled ‘Sri Ramayana Darshanam.’
Taal Volcano: Philippines

The Philippines increased the alert level on Taal Volcano to level 3 on a five-level scale after a Phreatomagmatic Eruption (PE) occurred that generated a dark grayish plume, one kilometer high.
- Alert Level 3 means there is magmatic unrest, or movement of magma that may further drive succeeding eruptions.
- Situated on the island of Luzon, 50 km from Manila, Philippines.
- The Philippines is situated at the boundaries of two tectonic plates – the Philippines Sea Plate and the Eurasian plate – thus susceptible to earthquakes and volcanism.
- Taal is one of the most active volcanoes in the Philippines due to its location on the Pacific “Ring of Fire” – a zone of intense seismic activity.
- Phreatomagmatic Eruption: An eruption resulting from the interaction of new magma or lava with water and can be very explosive.
- The water can be from groundwater, hydrothermal systems, surface runoff, a lake or the sea.
- Other Types of Eruptions are: Icelandic, Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, Pelean and Plinian.
- Possible hazards of pyroclastic density currents (clouds of hot gas, ash, and other volcanic debris) and volcanic tsunami.
- Complex Volcano: It is classified as a “complex” volcano by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS).
- A complex volcano, also called a compound volcano, is defined as one that doesn’t have just one main vent or cone but several eruption points. Another such example is Mount Vesuvius on the west coast of Italy.
- Unpredictable: Taal has erupted more than 30 times in the last few centuries, the most recent was in 2020.
LEAF (Lowering Emissions by Accelerating Forest Finance) Coalition:

LEAF (Lowering Emissions by Accelerating Forest Finance) Coalition was announced at the Leaders Summit on Climate, 2021.
- LEAF coalition will be one of the largest ever public-private efforts to protect tropical forests and intend to mobilize at least USD 1 billion in financing to countries committed to protecting their tropical forests.
About LEAF Coalition:
- It is a collective of the governments of the USA, United Kingdom and Norway.
- As it is a public-private effort, thus also supported by transnational corporations (TNCs) like Unilever plc, Amazon.com, Nestle, Airbnb etc.
- A country willing to participate would need to fulfil certain predetermined conditions laid down by the Coalition.
- The results-based financing model will be used in LEAF.
- The model weighs on work by the Environmental Defense Fund over two decades, in collaboration with Indigenous communities, forest peoples, Brazilian and US NGOs, and other partners, to protect the Amazon and tropical forests globally.
- Performance will be measured against the TREES Standard (The REDD+ Environmental Excellence Standard)
Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation
- REDD+ aims to achieve climate change mitigation by incentivizing forest conservation.
- It monetises the value of carbon locked up in the tropical forests of most developing countries, thereby propelling these countries to help mitigate climate change.
- REDD+ was created by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Six Years Of Digital India Programme:

The Prime Minister of India addressed a virtual event to mark the completion of six years of Digital Indian programme.
- India’s Techade: The data and demographic dividend combined with India’s proven tech prowess presents massive opportunity for the country, and this decade will be ‘India’s techade’.
Highlighted Various Schemes of Digital India programme:
- Diksha: It stands for Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing. It serves as National Digital Infrastructure for Teachers. All teachers across the nation will be equipped with advanced digital technology.
- eNAM: It was launched on 14th April 2016 as a pan-India electronic trade portal linking Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMCs) across the States.
- eSanjeevani: It is a telemedicine service platform of the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- DigiBunai: DigiBunai aids the weavers to create digital artwork and translate the saree design to be loaded to the looms. DigiBunai™ is a first of its kind Open Source software for Jacquard and dobby weaving.
- PM SVANidhi scheme: The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has launched Pradhan Mantri Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi), for providing affordable loans to street vendors. It incentivises digital transactions by the street vendors.
- Digital solutions during Covid-19: Contact tracing app, Aarogya Setu.
- Digital India Programme: It was launched in 2015. The programme has been enabled for several important Government schemes, such as BharatNet, Make in India, Startup India and Standup India, industrial corridors, etc.
Glacial Lake Atlas Of Ganga Basin.:

The Secretary, Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR) released the Glacial Lake Atlas of Ganga Basin.
- The present glacial lake atlas is based on the inventoried glacial lakes in part of Ganga River basin from its origin to foothills of Himalayas covering a catchment area of 2,47,109 sq. km.
- The study portion of Ganga River basin covers part of India and transboundary region.
- The Atlas is available on Bhuvan portal of NRSC, ISRO, India WRIS Portal and National Hydrology Project (NHP) web site of DoWR, RD & GR.
- The atlas provides a comprehensive and systematic glacial lake database for Ganga River basin with size > 0.25 ha
- In the context of climate change impact analysis, the atlas can be used as reference data for carrying out change analysis, both with respect to historical and future time periods
- The atlas also provides authentic database for regular or periodic monitoring changes in spatial extent (expansion/shrinkage), and formation of new lakes
- The atlas can also be used in conjunction with glacier information for their retreat and climate impact studies.
The 7th edition Of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS):
The 7th edition of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS), a biennial event, was hosted by the French Navy at La Réunion from 28 June to 01 July 2021.
- Admiral Karambir Singh, Chief of the Naval Staff, Indian Navy, participated virtually in the inaugural session of the event and provided his congratulatory remarks to the Outgoing and Incoming Chairmen.
- IONS, conceived by the Indian Navy in 2008, seeks to enhance maritime cooperation among Navies of the littoral states of the IOR by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues that would lead to common understanding on the way ahead.
- The chairmanship of IONS has been held by India (2008-10), UAE (2010-12), South Africa (2012-14), Australia (2014-16), Bangladesh (2016-18) and Islamic Republic of Iran (2018-21).
- France has assumed the Chairmanship on 29 Jun 21 for a two-year tenure.
- IONS Conclave of Chiefs (CoC) is the decision-making body at the level of Chiefs of Navies, which meets biennially. 6th IONS and CoC was conducted by Iran Navy in April 2018 at Tehran. Owing to the pandemic, the CoC 2021, will be hosted by French Navy later this year.
Education Plus (UDISE+) 2019-20:

Union Education Minister released the Report on United Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) 2019-20 for School Education in India.
Key Highlights of Report:
- In 2019-20, total students in school education from pre-primary to higher secondary have crossed 26.45 crore. This is higher by 42.3 lakh compared to 2018-19.
- Gross Enrolment Ratio at all levels of school education has improved in 2019-20 compared to 2018-19. Gross Enrolment Ratio increased to 89.7% (from 87.7%) at Upper Primary level, 97.8% (from 96.1%) at Elementary Level, 77.9% (from 76.9%) at Secondary Level and 51.4% (from 50.1%) at Higher Secondary Level in 2019-20 (from 2018-19).
- In 2019-20, 96.87 lakh teachers have been engaged in school education. This is higher by about 2.57 lakh compared to 2018-19.
- The Pupil Teacher Ratio (PTR) has improved at all levels of school education. In 2019-20, the PTR for primary has become 26.5, PTR for upper primary and secondary has become 18.5 and PTR for higher secondary has become 26.1.
- Enrolment of Divyang students has increased by 6.52% over 2018-19.
- Gross Enrolment Ratio of girls has increased to 90.5% (from 88.5%) at Upper Primary level, 98.7% (from 96.7%) at Elementary Level, 77.8% (from 76.9%) at Secondary Level and 52.4% (from 50.8%) at Higher Secondary Level in 2019-20 (from 2018-19).
- More than 80% schools in India in 2019-20 had functional electricity.
- This is an improvement by more than 6% over the previous year 2018-19.
- Number of schools having functional computers increased to 5.2 lakh in 2019-20 from 4.7 lakh in 2018-19.
- Number of schools having internet facility increased to 3.36 lakh in 2019-20 from 2.9 lakh in 2018-19.
- More than 90% schools in India had handwash facility in 2019-20.
- This is a major improvement, as this percentage was only 36.3% in 2012-13.
Heat Dome Effect:
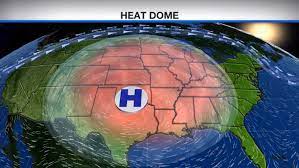
Canada is reeling under a severe heat wave. The weather experts have blamed the heat dome effect for the sudden rise in temperature.
- A heat dome occurs when the atmosphere traps hot ocean air like a lid or cap.
- The phenomenon begins when there is a strong change (or gradient) in ocean temperatures.
- In the process known as convection, the gradient causes more warm air, heated by the ocean surface, to rise over the ocean surface.
- As prevailing winds move the hot air east, the northern shifts of the jet stream trap the air and move it toward land, where it sinks, resulting in heat waves.
- A heat dome typically lasts a week.
Effects of heat domes:
- Those living without an air conditioner see the temperatures of their homes rising to unbearably high, leading to sudden fatalities.
- The trapping of heat can also damage crops, dry out vegetation and result in droughts.




