Today’s Current Affairs: 8th December 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Directorate General of Civil Aviation:

The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) granted the Indigo airline a temporary one-time exemption from some Flight Duty Time Limitation (FDTL) norms for pilots.
- It is the regulatory body in the field of civil aviation primarily dealing with safety issues.
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- It is responsible for regulation of air transport services to/from/within India and for enforcement of civil air regulations, air safety and airworthiness standards.
- It also coordinates all regulatory functions with the International Civil Aviation Organisation.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- One of the main functions of the DGCA is to ensure the safety of passengers and crew members on all flights operating in India.
- It conducts regular safety inspections of all airlines and aircraft to meet the required safety standards.
- It also investigates any incidents or accidents that occur within the Indian airspace.
- It plays a crucial role in developing new airports and modernizing existing facilities to ensure that they can meet the growing demands of the aviation industry.
- It is responsible for the regulation of air traffic in India. It works closely with the Airports Authority of India (AAI) to ensure air traffic is managed safely and efficiently.
- The DGCA also plays a key role in developing new air traffic control systems and technologies to improve the overall efficiency of Indian airspace.
- It is also responsible for issuing licenses and certificates to pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers, and other aviation personnel.
Infrastructure Investment Trust : Update

National Highways Authority of India received the Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) in-principle approval for ‘Raajmarg Infra Investment Trust’ (RIIT) as an Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT).
- It is Collective Investment Scheme similar to a mutual fund, which enables direct investment of money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects
- These are like mutual funds in structure which can be established as a trust and registered with Sebi.
- Objective: To provide retail investors with access to investment opportunities in infrastructure projects, which were previously only available to large institutional investors.
- An InvIT has 4 parties namely; Trustee, Sponsor(s) and Investment Manager and Project Manager.
- INVITs are created by sponsors, who are typically infrastructure companies or private equity firms.
- The sponsor sets up the INVITs and transfers ownership of the underlying infrastructure assets to the trust.
- The trust then issues units to investors, which represent an ownership stake in the trust and thus the underlying assets.
- While the trustee (certified by Sebi) has the responsibility of inspecting the performance of an InvIT, sponsor(s) are promoters of the company that set up the InvIT.
- InvITs are regulated by the SEBI (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014.
Open Market Operations : RBI

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently said it will conduct Open Market Operation (OMO) purchases of government securities worth ₹1 trillion and a three-year dollar–rupee buy/sell swap of $5 billion to inject further durable liquidity into the financial system.
- OMOs refer to a central bank selling or purchasing securities in the open market in an effort to influence the money supply.
- In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses OMOs to manage liquidity and ensure financial stability.
- By influencing the availability of funds in the banking system, OMOs play a critical role in shaping interest rates and controlling inflation.
- When the RBI buys government securities, it injects money into the banking system, increasing liquidity and lowering interest rates.
- When the RBI sells government securities, it reduces liquidity by absorbing money, leading to higher interest rates.
- OMOs are used to:
- Control inflation: By selling government securities, the RBI reduces liquidity, causing interest rates to rise. This, in turn, helps control inflation by curbing excess demand.
- Boost economic growth: During economic slowdowns, the RBI can buy securities to inject liquidity into the system. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and investment, which can help stimulate growth.
- Manage exchange rates: OMOs can influence the exchange rate of the Indian Rupee by impacting the supply of money. This can be particularly relevant in maintaining stability amidst volatile foreign exchange markets.
Shani Shingnapur Temple:

The Ahilyanagar police cyber cell recently arrested two Shani Shingnapur Temple Trust employees for allegedly diverting over ₹50 lakh each into their personal accounts by manipulating online applications used for booking pooja services.
- It is a Hindu temple located in Maharashtra.
- It is dedicated to Lord Shanidev, the popular Hindu god associated with the planet Saturn.
- The deity here is a five-and-a-half-feet-high black rock standing on a platform and is believed to be swayambhu (self-emerged).
- Apart from the temple, Shingnapur is a small village which is also famous for the fact that in the whole village no house has doors, and despite this, no theft has been reported in the village.
- It has no roofs, doors, or walls around.
- The temple is unique, as it is the only one where Lord Shani is worshipped in an open-sky setting.
- The premises also contain a tomb of Saint Udasi Baba and a temple dedicated to Dattatreya.
Centre for Chronic Disease Control (CCDC):

A new study by the Centre for Chronic Disease Control (CCDC) for the first time concurrently estimated the daily salt and iodine consumption levels of the adult population in India and examined the effect of the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended salt intake levels on iodine levels.
- Established in 2000, CCDC is an independent, not-for-profit, biomedical research organization based in New Delhi.
- It aims to reduce the burden of chronic diseases in India and low- and middle-income countries through surveillance, capacity building, and translational research in cardio-metabolic diseases.
- It is a Scientific & Industrial Research Organization recognized by the Department of Scientific & Industrial Research, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India.
- It has been designated as a WHO Collaborating Centre for Surveillance, Capacity Building, and Translational Research in Cardio-Metabolic Diseases.
- Recently, CCDC received the recognition of a collaborating Centre of Excellence (CoE) by the Indian Council of Medical Research.
- It also holds registration under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 1976.
- CCDC undertakes clinical research with special emphasis on chronic non-communicable diseases (NCD).
- Within the spectrum of chronic diseases, CCDC’s main focus areas are: cardiology, diabetes and metabolic disease, vascular diseases, cancers, and mental health.
- In addition, basic science research in diet/nutrition and cardiac biochemistry are also carried out.
Dolomedes indicus:

In the evergreen rainforests of the Western Ghats, researchers recently identified a new species of spider named Dolomedes indicus.
- It is a new species of spider.
- It was discovered in the evergreen rainforests of the Western Ghats, in the Wayanad district of Kerala.
- It marks the first time a spider of the Dolomedes genus, commonly known as raft or fishing spiders, has been described in India.
- Unlike the common house spiders that wait passively in webs, Dolomedes indicus is an active, semi-aquatic predator that uses the water’s surface tension to its advantage.
- It appears to be highly sensitive to its environment, thriving only in pristine, cool waters under a forest canopy.
- It could serve as a vital indicator species, helping conservationists monitor the health of freshwater ecosystems.
Powai Lake:

Flagging a series of non-compliances by the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) in checking untreated sewage flowing into Powai Lake, a National Green Tribunal (NGT)-mandated committee recently recommended that the BMC face a penalty of Rs 5 lakh per month per inlet if the new action plan is violated.
- It is an artificial lake situated in the northern suburb of Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The lake was built by the British in 1890.
- The Padmavati Devi Temple, situated on the bank of the lake, dates back to the 10th century AD.
- The lake is surrounded by the Powai Bird Sanctuary.
- It is an important resting, feeding, and breeding site of several bird species, resident and migratory.
- Among some of the lake’s rare and distinguished residents and visitors are the Watercock, Pheasant-tailed Jacana, Slaty-legged Crake, Ruddy-breasted Crake, Woolly-necked Stork, Caspian Tern, and Peregrine Falcon.
- In recent times, 40% of the lake has disappeared. The lake has deteriorated due to accelerated growth of residential, commercial, and industrial areas around the lake.
Afar region : Prediction
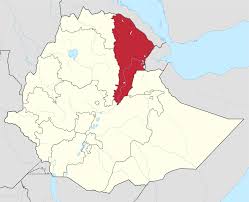
Scientists predict that Africa’s Afar region could become Earth’s next ocean basin.
- It is the northeastern part of Ethiopia, where the Red Sea meets the Gulf of Aden.
- The Afar depression, also known as the Danakil depression, forms the northern part of the region and is largely desert scrubland with shallow salty lakes and long chains of volcanoes.
- The Awash River valley forms the southern part of the area.
- It is situated at a unique triple junction where the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, and East African Rift converge.
- The region’s landscape is marked by deep rift valleys, volcanic plateaus, and extensive fissures, reflecting the dynamic forces reshaping the Earth’s crust.
- It is one of the hottest places on earth.
- It offers scientists a rare opportunity to observe the processes of continental break-up and ocean genesis in action.
- The region is well known for its early hominid fossil finds including ‘Lucy’, an Australopithecus afarensis, discovered in 1974.
Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe:

Foreign Minister of Ukraine said at the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe that Ukraine wants “real peace, not appeasement” with Russia.
- It is a dynamic organization that is dedicated to promoting peace, stability, and security throughout Europe and Central Asia.
- It is the world’s largest regional security organization.
- Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE), in 1994, was renamed the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE).
India is not a member country. - It works for stability, peace and democracy through political dialogue about shared values and through practical work that makes a lasting difference.
- Decision-making bodies of OSCE: There are four decision-making bodies with delineated, distinct mandates namely;
- Summits: It is the highest decision-making body of the OSCE
- Ministerial Councils: The OSCE’s central decision-making and governing body
- Permanent Council: It is responsible for the day-to-day business of the Organization
- Forum for Security Co-operation: It deals with the politico-military dimension of security
- Leadership: The OSCE’s leadership includes the Chairperson-in-Office, the Secretary General, and the heads of its institutions and field operations.
- Headquarter: Vienna.
Exercise Harimau Shakti 2025:

The Fifth edition of “Exercise Harimau Shakti -2025” commenced in Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan.
- It is a joint military exercise conducted between India and Malaysia.
- The Indian contingent is being represented mainly by troops from the DOGRA Regiment.
- The aim of the exercise is to jointly rehearse conduct of Sub Conventional Operations under Chapter VII of United Nations Mandate.
- Both sides will practice tactical actions such as cordon, search and destroy missions, heliborne operations, etc.
- In this exercise both sides will rehearse drills to secure helipads and undertake casualty evacuation during counter-terrorist operations.
- Both sides will exchange views and practices of joint drills on a wide spectrum of combat skills that will facilitate the participants to mutually learn from each other.
- Sharing of best practices will further enhance the level of defence cooperation between Indian Army and Royal Malaysian Army.
- The exercise will also foster strong bilateral relations between the two nations.
AstroSat:

The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) celebrated a decade of successful operation of the UltraViolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT) on AstroSat.
- It is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- The payloads cover the energy bands of Ultraviolet (Near and Far), limited optical and X-ray regime.
- It enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- Payloads of Astrosat: Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (UVIT), Large Area X-ray Proportional Counter (LAXPC), Cadmium–Zinc–Telluride Imager (CZTI), Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT) and Scanning Sky Monitor (SSM).
- UVIT consists of two telescopes: one dedicated to near-ultraviolet and visible wavelengths, and the other to far-ultraviolet observations.
- Objectives of AstroSat:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
- The spacecraft control centre at Mission Operations Complex (MOX) of ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru manages the satellite during its entire mission life.
INTERPOL Red Notice:

The Madhya Pradesh State Tiger Strike Force in a coordinated operation with the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has successfully apprehended an international wildlife offender wanted under an INTERPOL Red Notice (RN).
- A Red Notice is a request to law enforcement worldwide to locate and provisionally arrest a person pending extradition, surrender, or similar legal action.
- It is based on an arrest warrant or court order issued by the judicial authorities in the requesting country.
- Red Notices are issued for fugitives wanted either for prosecution or to serve a sentence in relation to serious ordinary law crimes such as murder, rape and fraud.
- Member countries apply their own laws in deciding whether to arrest a person.
- Purpose: International alert for a wanted person, but it is not an arrest warrant.
- It contains two main types of information:
- Information to identify the wanted person, such as their name, date of birth, nationality, hair and eye colour, photographs and fingerprints if available.
- Information related to the crime they are wanted for, which can typically be murder, rape, child abuse or armed robbery.
- Red Notices are published by INTERPOL at the request of a member country, and must comply with INTERPOL’s Constitution and Rules.
- Interpol cannot compel the law enforcements authorities in any of the countries to arrest someone who has a RN issued.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation is India’s National Central Bureau (NCB) for INTERPOL, handling Red Notices for all crimes, including wildlife offenses.
DRDO Transfers Seven Indigenous Technologies to Armed Forces:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) handed over seven home-grown technologies to the Indian Armed Forces on 2 December 2025. These technologies were developed under the Technology Development Fund (TDF) scheme, which promotes indigenous defence innovations by supporting Indian industry, particularly MSMEs and startups. The event also saw the approval of 12 new projects covering strategic, aerospace, naval, and electronic warfare (EW) domains — reflecting India’s growing commitment to defence self-reliance.The Technology Development Fund (TDF) is a scheme launched by the Ministry of Defence and implemented by DRDO to support indigenous development of defence technologies. The aim is to reduce India’s reliance on imported defence systems by enabling Indian companies to design, develop, and deliver critical technologies.
Dr Renuka Iyer Appointed Chief Medical Officer of NCCN:
Dr Renuka Iyer has been appointed as the new Chief Medical Officer (CMO) of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Her appointment, effective from 26 February 2026, marks a major leadership transition at the organisation known globally for its authoritative cancer treatment guidelines. Dr Iyer is a distinguished oncologist with over 20 years of experience in academic medicine, research, and clinical practice. She is renowned for her work in gastrointestinal cancers, especially rare tumours, and has contributed significantly to oncology guidelines and education.
Fino Payments Bank Becomes First to Receive RBI Nod to Transition into SFB:
Fino Payments Bank has become the first payments bank to receive the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) in-principle approval to convert into a Small Finance Bank (SFB). This move, announced on 5 December 2025, opens up new avenues for Fino to expand its operations beyond the limitations imposed on payments banks. The approval follows nearly two years after Fino submitted its application under the RBI’s ‘on tap’ licensing guidelines for SFBs.
Roman Gofman Appointed as Next Mossad Chief:
Major General Roman Gofman has been appointed as the next director of Mossad, set to take over in June 2026. The decision, announced on December 5, 2025, by Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, reflects a bold and rare move—placing a career military officer without a traditional intelligence background at the helm of Israel’s most secretive agency.In 2024, he was appointed as military secretary to Prime Minister Netanyahu, a role that placed him at the heart of Israel’s strategic and operational decision-making.




