Today’s Current Affairs: 6th February 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Delays In Implementing The National Policy For Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021:

Several rare disease patients across India, including many children, are facing a life-or-death struggle due to delays in implementing the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021, patient advocacy groups said recently.
- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) in March 2021.
- Currently, 63 rare diseases are included under the National Policy for Rare Diseases on the recommendation of the Central Technical Committee for Rare Diseases (CTCRD).
- The key features of NPRD, 2021, are as under:
- The rare diseases have been identified and categorized into 3 groups.
- Group 1: Disorders amenable to one-time curative treatment.
- Group 2: Diseases requiring long-term/lifelong treatment with relatively lower cost of treatment.
- Group 3: Diseases for which definitive treatment is available but challenges are to make optimal patient selection for benefit, very high cost, and lifelong therapy.
- The rare diseases have been identified and categorized into 3 groups.
- Financial support of up to Rs. 50 lakhs per patient is provided for the treatment at the notified Centres of Excellence (CoEs) for Rare Diseases.
- 12 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) have been identified so far, which are premier Government tertiary hospitals with facilities for diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of rare diseases.
- Treatment of patients starts immediately after registration with the CoEs.
- Nidan Kendras have been set up for genetic testing and counselling services.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has obtained exemption from the Goods & Services Tax (GST) and Basic Customs Duty on drugs imported for Rare Diseases for individual use and through CoE.
- As envisaged in the policy, the Department of Health Research has established the National Consortium for Research and Development on Therapeutics for Rare Diseases (NCRDTRD) for streamlining the research activities for rare diseases.
- It has provisions for the promotion of research and development for diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases; promotion of local development and manufacture of drugs; and creation of a conducive environment for indigenous manufacturing of drugs for rare diseases at affordable prices.
Extremely Large Telescope:

Lurking in the barren Atacama Desert, the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), a colossal machine nears completion
- It will be the world’s largest optical telescope, with a primary mirror.
- It is being built by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in Chile at a cost of 1.3 billion euros (around $1.4 billion).
- It will be capable of detecting—and possibly even imaging—terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of other stars.
- The ELT is under construction atop Cerro Armazones, which is a mountaintop in Chile’s Atacama Desert.
- The giant ELT dome will house the telescope and its interior structure, providing protection from the extreme environment of the Atacama Desert.
- The main structure of the telescope will hold its five mirrors and optics, including the enormous 39-metre primary mirror.
- The primary mirror, rather than being a single slab of glass, is made up of 798 hexagonal segments, each of which is 5 feet (1.5 m) across and 2 inches (5 cm) thick.
- European Southern Observatory (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy.
- It is supported by 16 European countries: Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland,
- Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Poland, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
- Chile has been its host and partner country for many decades.
- It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction, and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy to enable important scientific discoveries.
- ESO operates three unique, world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor.
- Headquarters: Garching, Germany
National Youth Parliament Scheme (NYPS) 2.0:

The Minister of State in the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs provided information about the National Youth Parliament Scheme 2.0 to the Rajya Sabha.
- Its key objectives are to strengthen the roots of democracy, inculcate healthy habits of discipline, and tolerance of the views of others and to enable the student community to know about practices and procedures of the Parliament and to enhance their knowledge of the functioning of the Government, Constitutional values and for living their life in a democratic way.
- The web-portal of NYPS 2.0 enables all the citizens of the country to participate in the Youth Parliament programme through 3 different ways:
- Institution Participation: All educational institution can participate in this category by organizing the Youth Parliament sittings as per the guidelines available on the portal.
- The students from classes VI to XII may be selected for the “Kishore Sabha” sub-category and Under Graduate and Post Graduate level students may be selected for the “Tarun Sabha” sub-category.
- Group Participation: A group of citizens can participate in this category by organizing the Youth Parliament sittings as per the guidelines available on the portal.
- Individual Participation: An individual citizen can participate in this category by attempting a quiz on the theme of ‘Bhartiya Democracy in Action’.
- The e-training material viz. Literature on Youth Parliament, Model Debate, Model Questions, Model List of Business, Model Scripts, Video Tutorials, etc. are available as training resources on the web-portal of NYPS 2.0.
Gaia Mission:

Astronomers have recently discovered a gigantic black hole named Gaia BH3 hiding close to the earth, the third of its kind using the European Space Agency’s Gaia telescope.Gaia, the Global Astrometric Interferometer for Astrophysics, is a European Space Agency (ESA)’s astronomical observatory mission.
- Its goal is to create the largest, most precise three-dimensional map of the Milky Way by surveying about 1% of the galaxy’s 100 billion stars.
- It was launched in 2013.
- Nestled at the Lagrange Point 2, some 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth, Gaia orbits the sun in sync with our planet.
- It is shielded by Earth from the sun’s glare and free from the distorting effects of Earth’s atmosphere, which plague ground-based telescopes’ observations.
- It scans the whole sky every two months.
- The 2.3 meters Gaia satellite is attached to a 10 meters circular sunshield and is fitted with two telescopes that sit 106 degrees apart.
- Gaia provides unprecedented positional and radial velocity measurements with the accuracies needed to produce a stereoscopic and kinematic census of about one billion stars in our Galaxy.
- Gaia also maps Solar System objects, primarily main belt asteroids circling the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- With its ability to detect faint and fast-moving objects, it is expected that Gaia will also detect several thousand Near-Earth Objects (NEOs).
International Big Cat Alliance:

In a major development, the Framework Agreement on establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) has officially come into force.
- It was established by Government of India, through the nodal organisation viz., National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- It was launched on 9th April 2023, during the event ‘Commemorating 50 years of Project Tiger’.
- It aims to conserve the seven big cats – Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar and Puma.
- It is open to 97 ‘range’ countries, which contain the natural habitat of these big cats, as well as other interested nations, international organizations, etc.
- Present Member countries: Nicaragua, Eswatini, India, Somalia and Liberia – have deposited the instruments of ratification under the Article VIII (1) of the Framework Agreement.
- Objective:
- To facilitate collaboration and synergy among stakeholders, consolidating successful conservation practices and expertise to achieve a common goal of conservation of big cats at global level.
- This unified approach, bolstered by financial support, aims to bolster the conservation agenda, halt the decline in big cat populations, and reverse current trends.
Dhimsa Dance:

Tribal families from Neelabandha, a hillptop hamlet in Anakapalli district of Andhra Pradesh received electricity for the first time after Independence and performed ‘Dhimsa’ in excitement.
- Dhimsa Dance is a popular tribal dance performed by tribes, including Bagata, Valmiki, Poraja, Khond, Gadaba, Kondadora, Mukadora, Kotia in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is performed during festivals, weddings and at the time of the “hunting festival” in April when men and women dance for hours together.
- There are 12 varieties of Dhimsa and its origin can be traced to the Koraput Area the home to Ghond Tribe.
- It is accompanied by wind and percussion instruments, the dance changes by the music, and a troupe comprises 20.
- Themes of dance: Various themes of the Dimsa, are woven around their mythologies, folktales, ethos, mores, economic activities and their kinship and marital life etc.
- Musical instruments like dappu, tudumu, mori, kidgi, gilka, and jodukommulu are used.
- Dhimsa dance is done in a circle with each other’s arms closed at each other’s back.
- This dance is mainly a movement of hands and legs. Dancers form small or big circles and perform together as a team.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
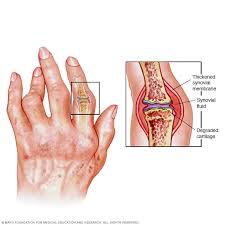
Researchers have developed an innovative “self-actuating” drug delivery system that could revolutionize the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by targeting inflammation directly within the joints so that therapeutic agents are released only when needed.
- Researchers have developed a smart system that responds directly to the biochemical signals in the inflamed synovial environment.
- The system uses specially designed microspheres loaded with methotrexate, a commonly used anti-rheumatic drug.
- The formulation consists of polymer-lipid hybrid micro-composites, where the lipid component (soya lecithin) ensures high drug encapsulation efficiency, and the polymer component (gelatin) provides responsiveness to Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP).
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- It is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, wherein the immune system attacks healthy cells in the body by mistake, and causing inflammation in the affected parts of the body. The specific causes of RA are unknown.
- It mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees.
Symptoms: In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. - This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness (lack of balance), and deformity (misshapenness).
- It can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
- Treatment: Its treatment usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Glacier Meltdown:

A recent study revealed that 110 glaciers in Arunachal Pradesh’s eastern Himalayas have disappeared over 32 years (1988-2020), with glacial cover shrinking by 309.85 sq. km.
- Glacial retreat occurs when glaciers melt faster than the accumulation of new ice and snow, leading to reduced ice cover and formation of glacial lakes.
- It is a key indicator of global climate change, affecting water resources, ecosystems, and disaster risks.
- Reasons Behind Glacier Meltdown:
- Rising Global Temperatures: The eastern Himalayas are warming faster than the global average (0.1°–0.8°C per decade).
- Increased Carbon Emissions: Accelerates atmospheric heating, leading to faster ice melting.
- Changing Precipitation Patterns: More rainfall instead of snowfall, disrupting glacial accumulation.
- Anthropogenic Activities: Deforestation, infrastructure projects, and tourism add to local warming.
- Black Carbon Deposits: From burning fossil fuels, reduces glacier reflectivity, increasing heat absorption.
State Emblem of India : Direction

The Union Home Ministry has directed states to prevent the improper depiction of the State Emblem of India, emphasizing the mandatory inclusion of the motto “Satyameva Jayate” in Devanagari script.
- Adopted as the State Emblem of India on January 26, 1950 from the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka.
- Features of the State Emblem:
- Three Visible Lions: The fourth lion is hidden from view.
- Dharma Chakra: Positioned at the center of the abacus.
- Bull (Right): Represents the zodiac sign Taurus, symbolizing Buddha’s birth.
- Horse (Left): Symbolizes Kanthaka, the horse Buddha rode while renouncing princely life.
- Elephant (East): Represents Queen Maya’s dream of a white elephant entering her womb.
- Lion (North): Symbolizes Buddha’s enlightenment and Dharma propagation.
- No Bell-shaped Lotus: Omitted in the official State Emblem.
- Motto ‘Satyameva Jayate’: Taken from the Mundaka Upanishad, meaning ‘Truth Alone Triumphs’, inscribed below the emblem in Devanagari script.
- Crowned by Dharma Chakra: Represents Buddha’s first sermon (Dharmachakra Pravartana).
- Legal Provisions:
- State Emblem of India (Prohibition of Improper Use) Act, 2005: Regulates authorized use of the emblem.
- State Emblem of India (Regulation of Use) Rules, 2007: Specifies the permitted authorities and usage rules.
Jevons Paradox:
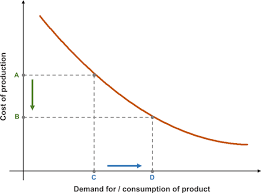
The Jevons Paradox has resurfaced in economic discussions after the DeepSeek AI launch led to a selloff in global tech stocks, raising concerns over AI chip demand.
- Jevons Paradox states that when a resource becomes more efficient and cheaper to use, overall consumption increases instead of decreasing.
- Proposed by William Stanley Jevons in 1865, observing that improved coal efficiency led to higher coal consumption instead of savings.
- Factors Influencing Jevons Paradox:
- Cost Reduction: Lower usage costs drive higher demand.
- Increased Accessibility: Efficiency makes resources more widespread.
- Economic Growth: Higher productivity spurs industrial expansion.
- Elastic Demand: When demand is highly responsive to price changes, consumption rises sharply.
Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
The Union Government has announced a shift from fiscal deficit to debt-to-GDP ratio as the primary fiscal anchor from FY 2026-27, targeting a 50±1% ratio by 2031. Debt-to-GDP Ratio represents the proportion of a country’s total debt to its GDP, indicating economic stability and repayment capacity.A higher ratio signals increased risk of default and financial instability. A lower ratio indicates better fiscal health and investor confidence. Debt sustainability depends on growth rates, fiscal deficit trends, and interest payments.
Santorini Island:
Santorini, a popular Greek island, has been placed on high alert after experiencing over 200 undersea earthquakes in four days, with magnitudes up to 4.6.Santorini Island Located in: Southern Aegean Sea, part of the Cyclades archipelago in Greece. Controlled by: Greece (part of the Thira regional unit).
Ujjivan Small Finance Bank Seeks Universal Banking Licence:
Ujjivan Small Finance Bank (USFB) has applied for a universal banking licence, a major milestone in its journey from a small finance bank to a full-fledged commercial bank. This move aligns with the bank’s strategy to expand its financial services, increase regulatory flexibility, and strengthen its position in the banking sector. The bank’s decision follows a growing trend of small finance banks transitioning to universal banks for broader operational capabilities.
First Black Mrs World:
Soweto-born Tshego Gaelae has made history by becoming the first Black woman to win the Mrs World 2025 title at the grand finale in Las Vegas. The 34-year-old attorney and 2024 Mrs South Africa Queen follows in the footsteps of Candice Abrahams, the only other South African to hold the title (2016). Gaelae’s victory is a milestone in the pageant’s 40-year history, and she plans to use this platform to champion women’s empowerment while representing South Africa on a global stage.
India’s economy is expected to grow at 6.5% in FY26 : CRISIL
India’s economy is projected to grow at a rate of 6.5% in FY26, slightly improving from the 6.4% growth forecasted for the current fiscal year (FY25). Crisil’s report highlights several factors driving this growth, including lower inflation, expected rate cuts by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and favorable conditions such as a normal monsoon and stable global crude oil prices.
Bart De Wever Sworn in as Belgium’s New Prime Minister:
Belgium saw a significant political shift as Bart De Wever, leader of the New Flemish Alliance (N-VA), was sworn in as the country’s new Prime Minister. This marks the first time a Flemish nationalist has ascended to the highest office in Belgium. After more than eight months of tough coalition talks, a new government was formed with five political parties: N-VA, Christian Democrats (CD&V), socialists (Vooruit), liberals (MR), and centrists (Les Engagés). This newly formed coalition, called “Arizona,” now holds a majority in Belgium’s 150-seat federal parliament.
Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso Break Ties with ECOWAS:
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) has formally acknowledged the departure of Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso. This move follows over a year of diplomatic strain, primarily caused by military coups and disagreements over ECOWAS’ approach to regional governance.




