Today Current Affairs: 16th December 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Linking Climate To Security:

India voted against a draft resolution at the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) linking climate to security, saying it was an attempt to shift climate talks from the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) to the Security Council and a “step backward” for collective action on the issue.
- The resolution was sponsored by Ireland and Niger, and it did not pass, with 12 UNSC members voting for it, India and Russia voting against it and China abstaining.
- Niger, which holds the UNSC presidency for December, organised a debate on December 9 titled ‘Maintenance of international peace and security: security in the context of terrorism and climate change.’
- One of the objectives of the debate was to examine how terrorism and security risks could be linked to climate change, as per a concept note circulated by Niger.
- India’s Permanent Representative and Ambassador to the U.N. T.S. Tirumurti said, the draft resolution, would undermine progress made at Glasgow, where the latest round of talks under the UNFCCC, the 26th Conference of the Parties (COP26), concluded in November.
- Tirumurti said the attempt to discuss climate action and climate justice issues at the UNSC was “motivated by a desire to evade responsibility in the appropriate forum.”
Central Vigilance Commission (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

Parliament has passed the Central Vigilance Commission (Amendment) Bill, 2021.
- The bill will replace the ordinance promulgated in this regard.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003.
- The Act provides for the constitution of a Central Vigilance Commission to conduct inquiries into offenses alleged to have been committed under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- Presently, the Director of Enforcement has a tenure of a minimum of two years.
- The Bill adds that the tenure of the Director may be extended by up to one year at a time, till the completion of five years from the initial appointment.
- Such extensions may be granted in the public interest, on the recommendation of the Committee.
- Under the 2003 Act, the Director of Enforcement is appointed by the central government, on the recommendation of a Committee.
- This Committee is chaired by the Central Vigilance Commissioner and includes the Secretaries from the Ministries of Home Affairs, Personnel, and the Revenue department.
Delhi Special Police Establishment (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

Parliament has passed the Delhi Special Police Establishment (Amendment) Bill, 2021.
- The Bill will replace the ordinance promulgated in this regard.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946. Under the Act, the minimum tenure of the Director of Central Bureau of Investigation is of two years.
- The Bill permits extension of the tenure of the CBI Director up to one year at a time, till the completion of five years from the initial date of appointment.
- Such extensions may be granted in the public interest, on the recommendation of the Committee.
- In several countries, the term of Director and Chief of premier investigation agency is in the range of 6 to 10 years, and in the case of CBI, the tenure of Director is fixed as a minimum of 2 years but how much beyond it, is not defined.
- He said, with a view to make the Agency more democratized and institutionalized, the amendment to the existing Act has been brought. He said, after two years the tenure of Director of CBI will be extended for one year at a time.
National Energy Conservation Day 2021:

The National Energy Conservation Day is observed on December 14th, every year by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- The day focuses on making people aware of global warming and climate change and promotes efforts towards saving energy resources.
- It also highlights the achievements of the country in the fields of energy efficiency and conservation.
- The Ministry of Power celebrated Energy Conservation Week (8-14 Dec) in 2021 under Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- As part of celebrations, the BEE under the Ministry of Power has organized various programs.
Energy Conservation:
- It refers to the efforts made to ensure that energy is used efficiently by either using less energy for a particular constant purpose – like switching off lights and fans when not being used – or reducing the use of a particular service that uses energy – like driving less and using public transport instead.
- Energy conservation is a conscious, individual effort, and at a macro level, it leads to energy efficiency.
- The end goal of energy conservation is to reach towards sustainable energy.
- It is different from the term ‘energy efficiency’, which is using technology that requires less energy to perform the same function.
Energy Conservation Act, 2001:
- The Act was enacted with the goal of reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy. It provides regulatory mandates for:
- Standards & labeling of equipment and appliances;
- Energy conservation building codes for commercial buildings; and
- Energy consumption norms for energy intensive industries.
Energy Conservation Week:
- The Ministry of Power is celebrating Energy Conservation Week under Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav from 8th to 14th December 2021.
- The BEE and the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) have together taken a number of initiatives to ensure the growth of this sector in an energy-efficient and environmentally-friendly way.
- To ensure synergy among various players in the MSME sector, BEE and the Ministry of MSME have also promoted a collaborative platform–“SAMEEEKSHA” (Small and Medium Enterprises Energy Efficiency Knowledge Sharing).
- The platform aims to pool the knowledge and synergise the efforts of various organisations for the promotion and adoption of clean, energy technologies and practices.
- The BEE has organized an Interactive Workshop on Outcomes of Energy and Resource Mapping of the MSMEs Clusters.
Pinaka Extended Range Rocket System:

The DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organization) successfully test fired the Pinaka Extended Range (Pinaka-ER) Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Earlier, the DRDO also launched the Supersonic Missile Assisted Torpedo System (SMART).
- The Pinaka, a Multi-Barrel Rocket-Launcher (MBRL) system named after Shiva’s bow, can fire a salvo of 12 rockets over a period of 44 seconds.
- The new version is equipped with advanced technology to enhance its strength. The metal weight is lesser compared to the earlier version.
- The newly tested system can achieve a range of up to 45km which is a big feat for the Indian Army.
- The existing Pinaka system, which is already in the Army, has a range of up to 35-37km.
- The new incarnation of pinaka represents one of the few examples of an evolutionary process being followed with an indigenous Indian weapon system.
- The development of the Pinaka multi-barrel rocket systems was started by the DRDO in the late 1980s, as an alternative to the Multi Barrel Rocket Launcher systems of Russian make called the ‘Grad’, which are still used by some regiments.
- After successful tests of Pinaka Mark-1 in the late 1990, it was first used successfully in the battlefield during the 1999 Kargil War. Subsequently, multiple regiments of the system came up over the 2000s.
- DRDO has also developed and successfully tested the Mk-II and guided variants of the Pinaka, which has a range of around 60 km, while the Guided Pinaka system has a range of 75 km and has integrated navigation, control and guidance system to improve the end accuracy and enhance the range.
- The navigation system of the Guided Pinaka missile is also aided by the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
- In 2020, an enhanced version of the Pinaka Mark (Mk)-1 missile was successfully flight-tested from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, off the coast of Odisha.
Deposit Insurance And Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Bill, 2021:

The Prime Minister said that Rs 1,300 crore had been paid to over 1 lakh depositors who could not access their money as their banks faced financial crises.
- The deposits worth Rs 76 lakh crore were insured under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act providing full coverage to around 98% of bank accounts.
- Earlier, the Union Cabinet cleared the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Bill, 2021.
- Deposit Insurance: It is a protection cover against losses accruing to bank deposits if a bank fails financially and has no money to pay its depositors and has to go in for liquidation.
- Credit Guarantee: It is the guarantee that often provides for a specific remedy to the creditor if his debtor does not return his debt.
- Limit for Deposit Insurance:
- Currently, a depositor has a claim to a maximum of Rs 5 lakh per account as insurance cover. This amount is termed ‘deposit insurance’
- The cover of Rs 5 lakh per depositor is provided by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC).
- Depositors having more than Rs 5 lakh in their account have no legal recourse to recover funds in case a bank collapses.
- Premium for the insurance has been raised from 10 paise for every Rs 100 deposit, to 12 paise and a limit of 15 paise has been imposed.
- The premium for this insurance is paid by banks to the DICGC, and not be passed on to depositors.
- The Insured banks pay advance insurance premiums to the corporation semi-annually within two months from the beginning of each financial half year, based on their deposits as at the end of previous half year.
- Coverage:
- Banks, including regional rural banks, local area banks, foreign banks with branches in India, and cooperative banks, are mandated to take deposit insurance cover with the DICGC.
- Types of Deposits Covered:
- DICGC insures all bank deposits, such as saving, fixed, current, recurring, etc. except the following types of deposits:
- Deposits of foreign Governments.
- Deposits of Central/State Governments.
- Inter-bank deposits.
- Deposits of the State Land Development Banks with the State co-operative banks.
- Any amount due on account of any deposit received outside India.
- Any amount which has been specifically exempted by the corporation with the previous approval of the RBI.
Char Dham:

The Supreme Court has allowed carriageways of three highways to be widened to 10m as part of the Char Dham roads project after modifying its earlier order limiting the width to 5.5m.
- A three-judge Supreme Court bench modified an earlier, September 2020 order by another three-judge bench directing that three highways being laid as part of a 899-km road network in Uttarakhand should stick to a width of 5.5 metres for the carriageway.
- Following a review sought by the Defence Ministry, the Supreme Court has now decreed that the width of the roads can be of 10m as sought by the Centre, paving the way for their double-laning.
- Acknowledging the strategic importance of the three highways — which act as feeder roads for connecting with the China border — the top court also noted the need for balancing such priorities with environmental concerns.
- It also ordered the setting up of an oversight committee led by former Supreme Court judge AK Sikri to ensure that the works were executed in an environmentally conscious manner, incorporating the recommendations of a high-powered committee in this regard.
- The foundation stone for the Char Dham road project was laid by PM Narendra Modi in December 2016.
- But the project was challenged on environmental grounds in courts with petitioners alleging irregularities vis-a-vis environmental clearances for the project and that it was being pursued in violation of existing norms.
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) cleared the project in September 2018, but its order was challenged for being passed by a bench different from the one that had heard the matter. Supreme Court stayed the NGT order in October 2018.
- In September 2020, it passed an order on a writ petition stating that highways for the Char Dham project should not exceed 5.5m in width as prescribed in a 2018 circular of the Union Road Transport Ministry.
- But the Defence Ministry had in December that year sought a modification in the order to allow the width to be of 10m.
- The top court then asked its high-powered committee (HPC) to look into the contentions raised by the Centre on the width of the highways.
Earthquake Struck Eastern Indonesia:

A 7.3-magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia.
- The epicentre was in the Flores Sea, north of East Nusa Tenggara province.
- Indonesia sit along the Ring of Fire region, an area where most of the world’s volcanic eruptions occur.
- The Ring of Fire has seen a large amount of activity in recent days, but Indonesia has been hit hard due to its position on a large grid of tectonic plates.
- Indonesia is at the meeting point of three major continental plates – the Pacific, the Eurasian and the Indo-Australian plates – and the much smaller Philippine plate.
- As a result, several volcanoes on the Indonesian islands are prone to erupting. Indonesia is home to roughly 400 volcanoes, out of which 127 are currently active, accounting for about a third of the world’s active volcanoes.
- The Ring of Fire is a Pacific region home to over 450 volcanoes, including three of the world’s four most active volcanoes – Mount St. Helens in the USA, Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines. It is also sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt.
- Around 90% of the world’s earthquakes occur in the Ring of Fire, and 80% of the world’s largest earthquakes.
- It stretches along the Pacific Ocean coastlines, where the Pacific Plate grinds against other, smaller tectonic plates that form the Earth’s crust – such as the Philippine Sea plate and the Cocos and Nazca Plates that line the edge of the Pacific Ocean.
- The 40,000 kilometre horse-shoe-shaped ring loops from New Zealand to Chile, passing through the coasts of Asia and the Americas on the way.
- The Ring of Fire is the result from subduction of oceanic tectonic plates beneath lighter continental plates. The area where these tectonic plates meet is called a subduction zone.
Public Accounts Committee:

The centennial celebrations of Parliament’s Public Accounts Committee was recently held.
- The PAC is formed every year with a strength of not more than 22 members of which 15 are from Lok Sabha and 7 from Rajya Sabha.
- The term of office of the members is one year.
- The Chairman is appointed by the Speaker of Lok Sabha. Since 1967, the chairman of the committee is selected from the opposition.
- Its chief function is to examine the audit report of Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) after it is laid in the Parliament.
Limitations of the Public Accounts Committee:
- Broadly, it cannot intervene in the questions of policy.
- It can keep a tab on the expenses only after they are incurred. It has no power to limit expenses.
- It cannot intervene in matters of day-to-day administration.
- Any recommendation that the committee makes is only advisory.
- They can be ignored by the ministries.
- It is not vested with the power of disallowance of expenditures by the departments.
- Being only an executive body; it cannot issue an order. Only the Parliament can take a final decision on its findings.
Konyak Nagas:

The Konyak Union (KU), the apex body of the Konyak Naga tribe that resides in Nagaland’s Mon district, Monday, has announced fresh regulations to continue its “non-cooperation” with the armed forces on Konyak soil — a decision took following the killing of 14 civilians in Oting village in a security ambush recently.
Konyak Nagas:
- They are the largest of the Naga tribes.
- In Nagaland, they inhabit the Mon District—also known as ‘The Land of The Anghs’.
- The Anghs/Wangs are their traditional chiefs whom they hold in high esteem.
- Facial tattoos were earned for taking an enemy’s head.
- Other unique traditional practices that set the Konyaks apart are: gunsmithing, iron-smelting, brass-works, and gunpowder-making. They are also adept in making ‘janglaü’ (machetes) and wooden sculptures.
- Festivals: Aoleng, a festival celebrated in the first week of April (1-6) to welcome the spring and also to invoke the Almighty’s (Kahwang) blessing upon the land before seed-sowing, is the biggest festival of the Konyaks. Another festival, ‘Lao Ong Mo’, is the traditional harvest festival celebrated in the months of August/September.
Wholesale Price Index:

Wholesale inflation, based on the Wholesale Price Index, jumped to 14.23 per cent in November from 12.54 per cent in October (on a year-on-year basis), data released by the Ministry of Commerce & Industry showed.
- It was primarily due to rise in food prices especially of vegetables, and minerals and petroleum products
- This is the highest level of wholesale inflation in the 2011-12 series and eighth consecutive month in which it has stayed at double-digit level.
- This comes after the retail inflation print for November, had shown a spike to a three-month high of 4.91 per cent despite a cut in excise duty on fuels.
- The wide gap between WPI and CPI inflation reflects the price pressures on the inputs side, which are expected to pass through to the retail level in the coming months.
- Despite not being a policy tool, the surge in the WPI is a cause of worry. While the CPI-based retail inflation — the more widely tracked policy tool — looks at the price at which the consumer buys goods, the WPI tracks prices at the wholesale, or factory gate/mandi levels.
- Between the wholesale price and the retail price, the difference essentially is the former only tracks basic prices devoid of transportation cost, taxes and the retail margin etc.
- And that WPI pertains to only goods, not services.
- So, the WPI basically captures the average movement of wholesale prices of goods and is primarily used as a GDP deflator (the ratio of the value of goods an economy produces in a particular year at current prices to that of prices that prevailed during the base year).
What Is Indo- Pacific?
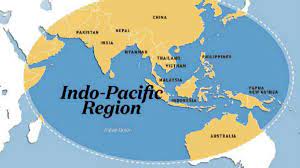
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken has said that the United States will expand its military and economic relationships with partners in Asia to push back against China’s increasing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific.
- The idea of the Indo-Pacific as a single strategic space is an outgrowth of China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean region.
- It signifies the interconnectedness of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, the importance of the oceans to security and commerce.
Importance of Indo-Pacific region:
- Maintaining regional stability.
- Strong ties with the US are seen as a vital tool for enhancing India’s strategic posture.
- For the long-term vision of national interest.
- China’s increasingly active presence in the Indian Ocean region as well as its efforts to expand geopolitical reach in Asia and beyond by the use of trade and military.
- For adhering to freedom of navigation, adherence to rules-based order and stable trade environment.
- For free sea and air lanes, connectivity and upholding international rules and norms.
Role and Implications for India in the Indo – pacific region:
- The Indo-Pacific, as described in the National security strategy, represents the most populous and economically dynamic part of the world and stretches from the west coast of India to the western shores of the United States.
- India has always been a country with great national ambitions and is one of the most important advocates of the concept of “Indo-Pacific Strategy”.
- With opening of economy, India has been connecting with its Indian Ocean neighbours and major maritime powers of the world.




