Today Current Affairs: 16th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
The Southern Ocean As The World’s Fifth Ocean:

The National Geographic magazine has recognized the ‘Southern Ocean’ as the world’s fifth ocean.
- The Southern Ocean is the only ocean ‘to touch three other oceans and to completely embrace a continent rather than being embraced by them’.
- Its northern limit is a latitude of 60 degrees south.
- It is also defined by its Antarctic Circumpolar Current that was formed 34 million years ago. The current flows from west to east around Antarctica.
- The International Hydrographic Organization too had recognized the term in 1937 before repealing it in 1953.
Policy For Declassification Of War History:

The Union Defence Minister has approved a policy on archiving, declassification, compilation and publication of war and operations histories by the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- Timely publication of war histories would give people an accurate account of the events, provide authentic material for academic research and counter the unfounded rumours.
- The requirement of having war histories written with a clear cut policy on declassification was recommended by the Kargil Review Committee, 2019 headed by K Subrahmanyam to analyse the lessons learnt and prevent future mistakes.
- Post Kargil conflict, a Group of Ministers (GoM) recommendations on national security, 2001 also mentioned the desirability of authoritative war history.
Provisions of Policy:
- Transfer of Record: Each organisation under the MoD such as Services (Army, Airforce and Navy), Integrated Defence Staff, Assam Rifles and Coast Guard, will transfer the records, including war diaries, letters of proceedings and operational record books, etc., to the history division of MoD for proper upkeep, archival and writing the histories.
- The History Division will be responsible for coordination with various departments while compiling, seeking approval and publishing of war and operations histories.
- Constitution of a Committee: For compilation of war and operations histories, the policy mandates the constitution of a committee headed by Joint Secretary, MoD and composed of representatives of the Services, Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) and other organisations and prominent military historians, if required.
- Timeline: The policy sets clear timelines with regard to the compilation and publication of war and operations histories.
- The committee should be formed within two years of completion of war and operations.
- Thereafter, the collection of records and compilation should be completed in three years and disseminated to all concerned.
- The records should ordinarily be declassified (i.e. no more secret) in 25 years.
- Records older than 25 years should be appraised by archival experts and transferred to the National Archives of India once the war/operations histories have been compiled.
- Responsibility for Declassification of Records: This rests with the respective organisations as specified in the Public Record Act 1993 and the Public Record Rules 1997.
- For Internal Consumption First: The compiled history on wars and operations, within five years, will be for internal consumption first, and later the committee may decide to publicly release whole or parts of it, considering the sensitivity of the subject.
Unlawful Activities Prevention Act, 1967:

The Delhi High Court granted bail to student activists in an Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967 case.
- While delivering the judgment, the court redefined the boundaries of the otherwise “vague” Section 15 of the UAPA.
High Court’s Ruling:
- Terrorist activity cannot be broadly defined to include ordinary penal offences.
- By doing so, it raised the bar for the State to book an individual for terrorism under the UAPA.
- The extent and reach of terrorist activity must travel beyond the effect of an ordinary crime and must not arise merely by causing disturbance of law and order or even public order.
- It must be such that it travels beyond the capacity of the ordinary law enforcement agencies to deal with it under the ordinary penal law.
Unlawful Activities Prevention Act, 1967
- UAPA was passed in 1967. It aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- Unlawful activity refers to any action taken by an individual or association intended to disrupt the territorial integrity and sovereignty of India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may, by way of an Official Gazette, declare it so.
- It has the death penalty and life imprisonment as the highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged.
- It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if the crime is committed in a foreign land, outside India.
- Under the UAPA, the investigating agency can file a charge sheet in maximum of 180 days after the arrests and the duration can be extended further after intimating the court.
- The 2004 amendment added the “terrorist act” to the list of offences to ban organisations for terrorist activities, under which 34 outfits were banned.
- Till 2004, “unlawful” activities referred to actions related to secession and cession of territory.
- In August, Parliament cleared the Unlawful Activities (Prevention), Amendment Bill, 2019 to designate individuals as terrorists on certain grounds provided in the Act.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan – II:

The Minister of Jal Shakti has urged all MPs to support the ongoing “Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch The Rain” campaign in their respective constituencies and states.
- Such interventions would ensure water source sustainability in rural areas and would strengthen the ongoing Jal Jeevan Mission being implemented by the Ministry.
- The Abhiyan with the theme- “Catch the Rain where it falls, when it falls’ was launched on the occasion of world water day (22nd March 2021).
- It covers all rural and urban areas of all districts of the country.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan-I of 2019, covered only 1592 water-stressed blocks out of 2836 blocks in 256 districts of the country.
- National Water Mission, under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, is the nodal agency for its implementation.
- A total of almost Rs. 14,000 Cr worth of water conservation-related work is completed/ongoing under the MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme) of the Dept of Rural Development.
- The campaign aims at tapping rainwater by constructing artificial recharge structures, revitalizing existing ponds and water bodies, creating new water bodies, provisioning check dams, rejuvenating wetlands and rivers before the onset of the monsoon.
- It is also planned to create a database of all water bodies in the country by geo-tagging them and using this data to create scientific and data-based district-level water conservation plans.
MoU For Seaplane Services In India:

The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways and the Ministry of Civil Aviation signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for Development of Seaplane Services in India.
- India’s first seaplane service started operation between Kevadia and Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad in October 2020, under Sagarmala Seaplane Services.
- This MoU envisages developing non-scheduled and scheduled operation of seaplane services within the territorial jurisdiction of India.
- Seaplane services will be developed as a part of the RCS-UDAN (Regional Connectivity Scheme-Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) initiative of the Civil Aviation Ministry.
- The Shipping Ministry would identify and develop waterfront aerodromes and other required infrastructure.
- The Civil Aviation Ministry will select potential airline operators through a bidding process. It will also incorporate the location and routes as identified by the Shipping Ministry.
- This MoU will help in expediting the development of new water aerodromes and also operationalization of new seaplane routes in India.
- It will not only enhance seamless connectivity across the nation by promoting eco-friendly transportation through seaplanes but also give a boost to the tourism industry.
- It will lead to an increase in tourism and hotel business at the local level. It will also serve employment to local people.
- The establishment of water airports will contribute to an increase in the level of current social infrastructural facilities (healthcare, education, community housing, etc.) at the proposed sites.
Indo-Thai CORPAT:

The 31st edition of India-Thailand Coordinated Patrol (Indo-Thai CORPAT) between the Indian Navy and the Royal Thai Navy was conducted in the Andaman sea close to the Strait of Malacca.
Naval Exercise:
- India and Thailand have been carrying out CORPAT along their International Maritime Boundary Line twice a year since 2005.
- Indian Naval Ship (INS) Saryu, an indigenously built Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel and Thailand’s Ship HTMS-Krabi, an Offshore Patrol Vessel, along with Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft from both navies participated in the CORPAT 31st edition.
- Aims:
- To keep part of the Indian Ocean safe and secure for commercial shipping and international trade.
- To ensure effective implementation of the United Nations Conventions on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- UNCLOS specifies regulations regarding protection and conservation of natural resources, conservation of the marine environment, prevention and suppression of illegal, unregulated fishing activity, drug trafficking, piracy, exchange of information in the prevention of smuggling, illegal immigration, and conduct of search and rescue operations at sea
World Giving Index 2021 Report:
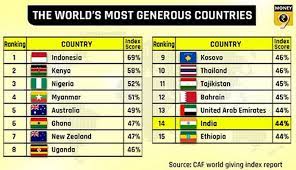
The Charities Aid Foundation (CAF) released the World Giving Index 2021 report. The Charities Aid Foundation (CAF) is a leading international charity registered in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1974.
World Giving Index (WGI):
- The World Giving Index (WGI) is an annual report published by the Charities Aid Foundation and ranks over 140 countries in the world according to how charitable they are.
- The first edition was released in September 2010.
- The WGI is a global survey, which asks people three questions: In the last month have you…
- Helped a stranger, or someone you didn’t know who needed help?
- Donated money to a charity?
- Volunteered your time to an organisation?
- The index measures countries by the proportion of population giving rather than how much they give.
Rankings:
- The most generous country in the world is Indonesia.
- Australia and New Zealand the only high-income countries to remain in this year’s Top 10.
- India is 14th most charitable country.
- Scores for India rapidly improved between 2017 and 2019, and this improvement was maintained during 2020.
- The improvement in India is seen across all the age groups and amongst both men and women.
- 61 percent of Indians helped strangers; 34 percent volunteered; 36 per cent donated money.
Treaty On The Prohibition Of Nuclear Weapons:

The entry into force of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in early 2021 highlights the growing divide between the nuclear-armed states and other countries that are impatient to see progress on nuclear disarmament promised by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
- The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) is also known as the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty.
- It is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons, with the goal of leading towards their total elimination.
- It was adopted in July 2017 and came into force in January 2021.
- As of March 2021, 54 states have ratified or acceded to the treaty, most recently Comoros in February 2021.
- Strategy:
- For those nations that are party to it, the treaty prohibits the development, testing, production, stockpiling, stationing, transfer, use, and threat of use of nuclear weapons, as well as assistance and encouragement to the prohibited activities.
- For nuclear-armed states joining the treaty, it provides for a time-bound framework for negotiations leading to the verified and irreversible elimination of its nuclear weapons program.
- The Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968 contains only partial prohibitions, and nuclear-weapon-free zone treaties prohibit nuclear weapons only within certain geographical regions.
United Nations Convention To Combat Desertification (UNCCD):

PM Modi delivered the keynote address at the UN ‘high-level dialogue on desertification, land degradation and drought’.
- He spoke at the Opening Segment in his capacity as the President of the 14th Session of the Conference of Parties (COP) of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
Key highlights of his address:
- In last 10 years, around 3 million hectares of forest cover added in India, enhancing the combined forest cover to almost one-fourth of the country’s total area.
- India is on track to achieve its national commitment of Land degradation neutrality.
- India is also working towards restoring 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030. This will achieve an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tons of carbon dioxide equivalent.
- He gave an example of the Banni region in Rann of Kutch in Gujarat to illustrate how restoration of land can start a virtuous cycle of good soil health, increased land productivity, food security and improved livelihoods.
United Nations convention to combat desertification (UNCCD):
- It is the first and only internationally legally binding framework set up to address the problem of desertification.
- Its secretariat has been located in Bonn, Germany.
Italian Marines Case Update:

The Supreme Court has closed a criminal case initiated against two Italian marines who killed two fishermen off the Kerala coast, setting the stage for the Italian government to try them in their own country as per an international tribunal award.
- It has also accepted the additional compensation of Rupees 10 crores offered by the Republic of Italy to the victims of the 2012 sea-firing incident which took place near the Kerala coast.
- The Government of India urged the Court to invoke the extraordinary power under Article 142 of the Constitution to quash the criminal cases against Marines, as the international tribunal under the United Nations Convention on Law of Seas had ruled that India lacks the jurisdiction to criminally prosecute them.
- In a close 3:2 vote, the tribunal ruled that the Italian marines enjoyed diplomatic immunity as Italian state officials under the United Nations Convention on the Law of Sea.
- Taking note of the “commitment expressed by Italy” to resume its criminal investigation into the incident, the tribunal said India must cease to exercise its jurisdiction.
The 42nd Session Of The Food And Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) Conference:

The 42nd session of the Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) Conference was held recently.
- For the first time ever, the FAO Conference is held in virtual mode.
- The conferenc takes place every two years and is FAO’s supreme governing body.
- It determines the policies of the Organization, approves the budget, and makes recommendations to Members on food and agriculture issues.
- FAO Strategic Framework 2022-2031.
- In this year’s Conference, FAO Members will adopt the Strategic Framework 2022-2031.
- The Framework aims to support the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development through the transformation to MORE efficient, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable agri-food systems for Better Production, Better Nutrition, a Better Environment, and a Better Life, leaving no one behind.
- The “Four Betters” represent an organizing principle for how FAO intends to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 1 (no poverty), SDG 2 (zero hunger), and SDG 10 (reduced inequalities).
About FAO:
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- Headquarters: Rome, Italy.
- Founded: 16 October 1945.
- Their goal is to achieve food security for all and make sure that people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active, healthy lives.




