Today Current Affairs: 16th March 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Guru Chemancheri Kunhiraman Nair:

Guru Chemancheri Kunhiraman Nair, a recipient of Padma Shri, died at the age of 104.
- Chemancheri Kunhiraman Nair, also known as Guru Chemancheri (1916 – 2021) was a noted Indian Kathakali actor.
- Kathakali is a major form of classical Indian dance from Kerala.
- He also played a significant role in making Bharatanatyam popular in north Kerala.
- He established an institution named Bharateeya Natya Kalalayam at Kannur in 1945. Later, he established another school, Cheliya Kathakali Vidyalayam, in 1983, in Cheliya.
- Awards:
- 1999 Kerala Sangeeta Nataka Akademi Fellowship of the Academy
- 2017 Padma Shri awarded by the Government of India
- Sangeet Natak Academi Tagore Award for contributions to Kathakali
Kenya-Somalia Dispute:
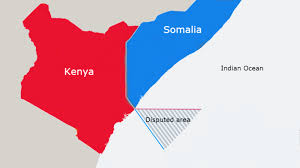
Kenya has declined to take part in proceedings of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) over its maritime border dispute with neighbouring Somalia.
Direction of Maritime Boundary:
- The main point of disagreement between the two neighbors is the direction in which their maritime boundary in the Indian Ocean should extend.
Somalia’s Stand:
- The sea border should be an extension of the same direction in which their land border runs as it approaches the Indian Ocean, i.e. towards the southeast.
Kenya’s Stand:
- The maritime border should run parallel to the equator.
Importance of Disputed Area:
- The triangular area thus created by the dispute is around 1.6 lakh sq. km. large, and boasts of rich marine reserves.
- It is also believed to have oil and gas deposits.
International Court of Justice:
- ICJ was established in 1945 by the United Nations charter and started working in April 1946.
- It is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations, situated at the Peace Palace in The Hague (Netherlands).
- It settles legal disputes between States and gives advisory opinions in accordance with international law, on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
- Its rulings are binding, though the court has no enforcement powers and countries have been known to ignore its verdicts.
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) For The Month Of February 2021:

The Office of the Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade has released the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) for the month of February 2021.
Wholesale Price-Inflation:
- It increased for the second consecutive month to 4.17%.
- This is the highest since November 2018, when wholesale inflation was at 4.47%.
- The WPI inflation was 2.03% in January 2021 and 2.26% in February 2020.
Reason:
- An increase in inflation in food articles, fuel & power has led to this surge.
- Food Inflation: The food articles in February saw 1.36% inflation which in January stood at (-) 2.80%.
- Retail inflation: Based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), it was at 5.03% in February.
Wholesale Price Index
- It measures the changes in the prices of goods sold and traded in bulk by wholesale businesses to other businesses.
Published by the Office of Economic Adviser, Ministry of Commerce and Industry. - It is the most widely used inflation indicator in India.
- The major criticism for this index is that the general public does not buy products at wholesale prices.
- The base year of All-India WPI has been revised from 2004-05 to 2011-12 in 2017.
National Institutes Of Food Technology Entrepreneurship And Management Bill, 2019:

The Rajya Sabha passed the National Institutes of Food Technology Entrepreneurship and Management Bill, 2019.
- The Bill declares certain institutes of food technology, entrepreneurship, and management as institutions of national importance.
- These institutes are the
- National Institute of Food Technology Entrepreneurship and Management Kundli, in Haryana
- Indian Institute of Food Processing Technology, Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu.
- The Bill declares these institutes as National Institutes of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship, and Management.
Project RE-HAB (Reducing Elephant-Human Attacks Using Bees):

A pilot project launched in Kodagu, Karnataka entails installing bee boxes along the periphery of the forest and the villages with the belief that the elephants will not venture anywhere close to the bees and thus avoid transgressing into the human landscape.
- This idea stems from the elephants’ proven fear of the bees.
- An initiative of the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), Project RE-HAB (Reducing Elephant-Human Attacks using Bees) intends to create “bee fences” to thwart elephant attacks in human habitations using honeybees.
- The pilot project was launched at four locations around Chelur village in the Kodagu district by KVIC. These spots are located on the periphery of the Nagarahole National Park and Tiger Reserve, a known conflict zone.
- Project RE-HAB is a sub-mission of the KVIC’s National Honey Mission.
- Between 2015 and 2020, nearly 2,500 people have lost their lives in elephant attacks across India, of which 170 human fatalities have been reported in Karnataka alone, says the KVIC.
NOTA (None Of The Above):

The Supreme Court asked the Centre and the Election Commission of India to respond to a plea that fresh elections should be conducted in constituencies where the highest number of votes polled are NOTA (None Of The Above).
- The petition said candidates ‘rejected’ by voters should not be fielded again in the fresh polls.
- Chief Justice of India Sharad A. Bobde expressed doubts initially about the feasibility of the petition to arm the electorate with the “right to reject” and nudge political parties to present voters with a better choice of candidates to pick from.
- Chief Justice Bobde said if voters kept rejecting candidates, Parliament/Assembly seats would continue to remain vacant, affecting legislative functioning.
- But the petition argued that “if voters are given the power to reject, political parties will take care to field worthy candidates in the first place.”
None of the Above (NOTA):
- Supreme Court, in the PUCL v Union of India (2013) directed the ECI to introduce NOTA indirect elections to allow voters to register their protest if none of the candidates is acceptable to them.
- NOTA has only symbolic value in a direct election. Regardless of NOTA numbers, the candidate polling most votes is elected.
- However, it is a step towards encouraging political parties to field candidates with integrity.
Great Indian Bustards:

The Supreme Court intervened on behalf of the critically endangered Great Indian Bustards over the birds falling dead after colliding with power lines running through their dwindling natural habitats in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Scientific Name: Ardeotis nigriceps.
- Physical description: Black crown on the forehead contrasting with the pale neck and head. The body is brownish and the wings are marked with black, brown and grey.
- They feed on grass seeds, insects like grasshoppers and beetles, and sometimes even small rodents and reptiles.
- Distribution: India, effectively the only home of the bustards, now harbours less than 150 individuals in five States.
- Today, its population is confined mostly to Rajasthan and Gujarat. Small population also occur in Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is the state bird of Rajasthan.
- Bustards generally favor flat open landscapes with minimal visual obstruction and disturbance, therefore adapt well in grasslands.
- They avoid grasses taller than themselves and dense scrub-like thickets.
- Listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection )Act, 1972,
- Listed in Appendix I of CITES,
- Listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- A Bench led by Chief Justice of India Sharad A. Bobde will examine on a priority basis whether overhead power cables can be replaced with underground ones to save one of the heaviest flying birds on the planet.
- The court found further that an alternative mechanism — to install flight bird diverters — to guide the birds away from the power lines would be expensive.
National Capital Territory Of Delhi:

The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) moved a Bill in the Lok Sabha in which it proposed that the “government” in the National Capital Territory of Delhi meant the Lieutenant-Governor of Delhi.
- The Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Bill, 2021 proposes to amend Sections 21, 24, 33, and 44 of the 1991 Act.
- Section 44 of the 1991 Act says that all executive actions of the L-G, whether taken on the advice of his Ministers or otherwise, shall be expressed to be taken in the name of the L-G.
- The Bill gives discretionary powers to the L-G even in matters where the Legislative Assembly of Delhi is empowered to make laws.
- The proposed legislation also seeks to ensure that the L-G is “necessarily granted an opportunity” to give her or his opinion before any decision taken by the Council of Ministers (or the Delhi Cabinet) is implemented.
- Delhi is a Union Territory with a legislature and it came into being in 1991 under Article 239AA of the Constitution inserted by the Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991.
- As per the existing Act, the Legislative Assembly has the power to make laws in all matters except public order, police, and land.
Changes In Hong Kong’s Electoral system:

China has made changes in Hong Kong’s electoral system.
- The measures are part of China’s efforts to consolidate its authoritarian grip over the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) following the imposition of national security law in June 2020.
The New Electoral System:
- Increased Membership of the Legislative Council:
- The number of Hong Kong’s Legislative Council (HKLC) members will be increased to 90, with the additional members also nominated, thereby reducing the share of elected representatives.
- Currently, only half of the 70 members of HKLC are directly elected and the rest are nominated.
- Expansion of Election Committee:
- The Election Committee (Hong Kong electoral college) has been expanded to include Beijing-nominated members.
- The Election Committee, as previously, will be responsible for electing the Chief Executive, and will also choose some of the members of HKLC.
- New Candidate Qualification:
- The selection of “patriots” will be ensured by the setting up of a new candidate qualification review committee.
- Implications:
- The change will give Beijing-appointed politicians a greater say in running the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR), marking the biggest change since the handover in 1997.
- An increased number of pro-Beijing officials would weaken the power of the opposition to influence the city’s leadership.
- It will erode the political freedoms that distinguished Hong Kong from the mainland under the “one country, two systems” model.
- The implication for India:
- Hong Kong is a destination for the re-export of Indian goods to the global market.
- Hong Kong is the fourth largest export market for India.
- India is of the view that Hong Kong can play an important role in strengthening ties with China, as it is considered a gateway to China.
- Thus, global tensions due to political unrest in Hong Kong carry consequences for India’s trade with the rest of the world, as well as with China.
Report By Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI):

According to a recent report by Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) India’s arms imports came down by a third (about 33%) between 2011-2015 and 2016-2020.
India Specific Findings:
- India remains the second-highest importer, only behind Saudi Arabia.
- Russia is the largest arms supplier to India in both periods (2011-2015 and 2016-2020). However, Russia’s share of Indian arms imports fell from 70% to 49%.
- France and Israel were the second and third largest arms suppliers in 2016–20. India’s arms imports from France increased by 709% while those from Israel rose by 82%.
- The USA became the fourth largest supplier for the period 2016-20.
- It was the second-largest arms supplier to India in 2011–15.
- India accounted for 0.2% of the share of global arms exports during 2016-20, making the country the world’s 24th largest exporter of major arms.
- This represents an increase of more than 200% over India’s export share (0.1%) during the previous five-year period of 2011-15.
- Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Mauritius were the top recipients of Indian military hardware.




