Today’s Current Affairs: 19th Jul 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Alzheimer’s Disease : New Criteria For Detecting

New criteria for detecting Alzheimer’s disease created by physicians and researchers from around the world were recently presented at the International Alzheimer’s Congress (AAIC) in Amsterdam.
- Alzheimer’s Disease is a progressive and degenerative neurological disorder that affects the brain, leading to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioural changes.
- It slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks.
- It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of all dementia cases.
- The condition primarily affects older adults, typically starting after the age of 65, though early-onset forms can occur in individuals younger than 65.
- The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Early signs may include mild memory loss, difficulty finding words, misplacing items, and trouble with problem-solving.
- As the disease advances, individuals may experience more severe memory impairment, confusion, mood swings, changes in behaviour, disorientation, and difficulty with basic tasks like dressing and eating.
- There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, and the available treatments mainly focus on managing symptoms and slowing down its progression.
- Medications may be prescribed to enhance cognitive function or manage behavioural and psychological symptoms.
BIMSTEC : Meeting

The first-ever Foreign Ministers’ meeting of the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) recently began in Bangkok
- BIMSTEC is a regional organization comprising seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- It came into being on 6 June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- It constitutes seven Member States: five deriving from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- Permanent Secretariat of BIMSTEC is operational since September 2014 in Dhaka.
- There are 14 priority areas 1) Counter terrorism and transnational crime, 2) Transport & Communication, 3)Tourism, 4) Environment and Disaster Management, 5)Trade and Investment, 6) Cultural Cooperation, 7) Energy, 8) Agriculture, 9 )Poverty Alleviation, 10) Technology, 11) Fisheries, 12) Public Health, 13) People-to-People contact 14) Climate Change.
- Each country takes lead in specific areas.
- India is the Lead Country in four areas, viz Counter-Terrorism and Transnational Crime, Transport & Communication, Tourism, and Environment and Disaster Management.
Advance Authorisation Scheme: Implementation

The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) implemented the Advance Authorisation Scheme under the Foreign Trade Policy, which allows duty-free import of inputs for export purposes.
- Advance Authorisation Scheme allows duty free import of inputs, which are physically incorporated in an export product.
- In addition to any inputs, packaging material, fuel, oil, catalyst which is consumed / utilized in the process of production of export product, is also be allowed.
- They are not allowed to sell the products in the domestic market.
- The Advance Authorization is valid for 12 months from the date of issue of such Authorization.
- This scheme is available to either a manufacturer exporter directly or a merchant exporter tied with a supporting manufacturer.
- It includes physical exports, intermediate supply, supplies made to specified categories of deemed exports.
- The inputs imported are exempt from duties like Basic Customs Duty, Additional Customs Duty, Education Cess, Anti-dumping duty, Safeguard Duty and Transition Product-Specific Safeguard duty, Integrated tax, and Compensation Cess, wherever applicable, subject to certain conditions.
National Multidimensional Poverty Index:

According to the ‘National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023, India has registered a significant decline of 9.89 percentage points in the number of multidimensionally poor, from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-2021,
- It claims that about 13.5 crore people came out of multidimensional poverty during the period, assessed by identifying.
- It said that rural areas witnessed the fastest decline in poverty from 32.59% to 19.28%, primarily due to decrease in the number of multidimensionally poor in States such as Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan. Delhi, Kerala, Goa and Tamil Nadu have the least number of people facing multidimensional poverty
- Along with the Union Territories. Bihar, Jharkhand, Meghalaya, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh top the chart where the percentage of total population who are multidimensionally poor is high.
- Multidimensional poverty in urban areas, during the same period, saw a decrease from 8.65% to 5.27%.
- Uttar Pradesh registered the largest decline in number of poor with 3.43 crore people escaping multidimensional poverty.
- Between 2015-16 and 2019-21, the MPI value has nearly halved from 0.117 to 0.066 and the intensity of poverty has reduced from 47% to 44%.
National Multidimensional Poverty Index:
- It is prepared based on the latest National Family Heath Survey of 2019-21 and is the second edition of the National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
- Totally 12 parameters of health, education and standard of living are examined in the report.
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever:

As Europe reels under a heat wave and wildfires, the rising temperatures have also raised fears of spread of viral haemorrhagic fever generally not found in colder climates.
- Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever is a viral haemorrhagic fever usually transmitted by ticks.
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues (animal tissue where the virus has entered the bloodstream) during and immediately post-slaughter of animals.
- The disease was first detected among soldiers in the Crimean Peninsula (near the Black Sea) in 1944.
- In 1969, it was found that an ailment identified in the Congo Basin was caused by the same pathogen. Thus, the disease was named the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.
- Its outbreak constitute a threat to public health services as the virus can lead to epidemics, has a high case fatality ratio (10–40%).
- Animals such as cattle, goats, sheep and hares serve as amplifying hosts for the virus.
- Transmission to humans occurs through contact with infected ticks or animal blood.
- It can be transmitted from one infected human to another by contact with infectious blood or body fluids”, such as sweat and saliva.
- The ticks can also be hosted by migratory birds.
- Symptoms include fever, muscle ache, dizziness, neck pain, backache, headache, sore eyes and sensitivity to light.
- After 2–4 days the agitation may be replaced by sleepiness, depression and lassitude
- There is no vaccine for the virus in either humans or animals, and treatment generally consists of managing symptoms.
- According to the WHO, “the antiviral drug ribavirin has been used to treat CCHF infection with apparent benefit.”
Gambusia Fish : To Combat Mosquito-Borne Diseases

The Andhra Pradesh government has released approximately 10 million Gambusia fish into the state’s water bodies to combat mosquito-borne diseases like Malaria and Dengue.
- The release of these invasive alien fish species has raised concerns about the potential harm that will be sustained by native species that abound in the state’s freshwater bodies.
- Gambusia Fish is also known as mosquito fish, is widely used as a biological agent for controlling mosquito larvae.
- It is native to the waters of the south-eastern United States.
- It has been a part of mosquito-control strategies for over a century in various parts of the world, including India.
- A single full-grown fish eats about 100 to 300 mosquito larvae per day.
- Also, it has been part of various malaria control strategies in India since 1928, including the Urban Malaria Scheme.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature declare Gambusia one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world.
Entamoeba Moshkovskii : Leading Pathogen Causing Diarrhoea Outbreaks
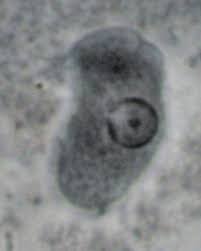
The recent three-year surveillance study by the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (ICMR-NICED) reveals the emergence of Entamoeba moshkovskii (E. Moshkovskii) as a leading pathogen causing diarrhoea outbreaks in the Kolkata region.
- The previously non-pathogenic amoeba, Entamoeba moshkovskii, has now become the primary cause of amoebic infections, surpassing the once dominant pathogen, E. histolytica.
- The study found that over 3% of patients with diarrhoea were infected with E. moshkovskii, making it the leading cause of amoebic infections in humans in Kolkata.
- Infections caused by E. histolytica, the previous predominant amoeba pathogen, were decreasing, while E. moshkovskii was taking its place.
- Unlike E. histolytica, which usually peaked during the wet season and decreased during the dry season, E. moshkovskii infections in Kolkata exhibited two distinct infection peaks coinciding with the summer and post-fall seasons.
- E. moshkovskii infections were most prevalent in children aged 5-12 years.
- The study indicated that E. moshkovskii may act as a “potential” pathogen, causing diarrhoea and gastrointestinal disorders, rather than solely being a commensal of the human gut.
Entamoeba moshkovskii:
- It belongs to the same genus as E. histolytica but has distinct genetic and biochemical traits.
- Originally isolated from sewage in Moscow in 1941.
- Found in soil, water, and animals.
- Symptoms:
- Causes problems like diarrhea, tummy pain, fever, and dehydration.
- It can damage the intestines, leading to ulcers, bleeding, or even serious issues like infections in the liver.
Perovskite Solar Cells:
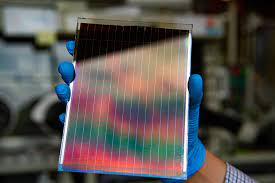
Indian scientists at the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI), Hyderabad, have developed highly stable, low-cost Carbon-based perovskite solar cells (CPSCs).
- These solar cells overcome the challenges of degradation during operation, making them suitable for large-scale commercialization.
- Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are a type of solar cell that utilizes perovskite materials as the light-harvesting active layer to convert sunlight into electricity.
- The most commonly used perovskite material in solar cells is methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3).
- Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) face stability issues when exposed to heat, moisture, and other environmental factors.
Wimbledon Title : Carlos Alcaraz

Carlos Alcaraz defeated Novak Djokovic in a thrilling five-set final to win his first Wimbledon title.
- Wimbledon is one of the four major tennis tournaments known as Grand Slam events. It is held annually in London, England, and is the oldest tennis tournament in the world.
- The other three Grand Slam tournaments are the Australian Open, the French Open, and the US Open.
- They feature singles, doubles, and mixed doubles matches, and determine the champions in each category.
- Grand Slam refers to the accomplishment of winning all four major championships of Australia, France, Britain (Wimbledon), and the United States in the same calendar season
- The result sparks speculation about a potential generational shift in men’s tennis.
Chachin Grazing Festival:

The Chachin Grazing Festival recently took place in the Tawang region.
- This two-day event held at Chachin brought together local graziers from all over the region to celebrate their traditional occupation and honor their cultural heritage.
- The Monpa lifestyle, deeply rooted in the region, revolves around nomadic herding.
- The graziers depend on this primitive form of subsistence farming to sustain their livelihoods.
- Throughout history, the Chachin and adjacent grazing regions in close proximity to Bumla Pass have played a crucial role in supporting and sustaining the traditional way of life of the local Monpa community.
- During the festival, several initiatives were undertaken to support the local graziers.
- A medical camp was set up to provide essential healthcare services to the graziers, who often reside in remote areas lacking access to urban medical facilities.
- A veterinary camp was organized to ensure the well-being of the yaks, the livestock of the graziers.
- A lecture on animal health aimed to equip the graziers with knowledge for better livestock care.
Global Food Regulators Summit 2023:

Delhi is all set to host the Global Food Regulators Summit 2023
- First time this prestigious event will take place in the Indian capital.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is at the helm of organizing this significant gathering.
- Scheduled for July 20-21, 2023, the summit aims to bring together food regulators from over 40 countries and representatives from 30 international organizations.
- The Global Food Regulators Summit 2023 will serve as a platform for food regulators from various countries to come together, share knowledge, and exchange best practices.
- With participation from over 40 countries, the summit promises to foster collaborative efforts in enhancing food safety standards worldwide.
- A Global Theme : The theme of the summit, “One Earth, One Family, One Future,” aligns perfectly with India’s G20 Presidency.
- This theme highlights the importance of global unity and cooperation in addressing the challenges and opportunities surrounding food safety.
- Initiative that will be introduced at the summit is the SaNGRAH platform (Safe food for Nations: Global Food Regulatory Authorities Handbook).
- The summit will also witness the launch of a Common Digital Dashboard, a unified IT portal that will provide comprehensive information on food safety standards, regulations, notifications, advisories, guidelines, contamination limits, and the latest developments by Food Regulators in India.




