Today Current Affairs: 21st December 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
The Election Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

The Election Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2021 that seeks to link electoral rolls to Aadhaar number has been listed for introduction in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill allows electoral registration officers to ask for Aadhaar numbers of applicants wanting to register as voters to establish the identity of the applicant.
- It also seeks to allow the officers to ask for the number from “persons already included in the electoral roll for the purposes of authentication of entries in electoral roll, and to identify registration of name of the same person in the electoral roll of more than one constituency or more than once in the same constituency”.
- People who cannot furnish their Aadhaar numbers will be allowed to present other documents to establish identity.
- Various Sections of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 and 1951 will be amended.
- Section 23 of the RP Act, 1950 will be amended to allow linking of the roll data with the Aadhaar ecosystem “to curb the menace of multiple enrolment of the same person in different places”.
- Amendment to Section 14 of the RP Act, 1950 will allow to have four “qualifying” dates for eligible people to register as voters. As of now, January 1 of every year is the sole qualifying date.
- Now, “the January 1, April 1, July 1 and October 1 in a calendar year” will be the qualifying dates in relation to the preparation or revision of electoral rolls.
- Amendment to Section 20 of the RP Act, 1950 and Section 60 of the RP Act, 1951 will allow the elections become gender-neutral for service voters.
- It will also help replace the word “wife” with the word “spouse” making the statutes “gender neutral”.
Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI):

The Breastfeeding Promotion Network of India (BPNI), in collaboration with the Association of Healthcare Providers of India (AHPI), which comprises more than 12,000 private hospitals, has launched an accreditation programme that will enable hospitals to get a “breastfeeding-friendly” tag.
- This programme is called “Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI)”.
- The initiative is only for private hospitals and is based on the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s MAA programme for government hospitals launched in 2016.
- The certification process involves two stages — the first stage includes self-assessment by a hospital, followed by an external assessment by an authorised appraiser who interviews doctors, nurses and patients as well as reviews different practices and training of staff.
- The accreditation process costs ₹17,000 per hospital.
- The BFHI programme is a worldwide programme of the WHO and UNICEF. Though India adopted it in 1993, it fizzled out by 1998 and is now being revived after more than two decades.
- Chennai’s Bloom Healthcare has become the first hospital to be recognised as “breastfeeding-friendly” under this programme.
- Early initiation of breastfeeding continues to be low in the country.
- According to the National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-2021), while there were 88.6% institutional births, only 41.8% of infants were breastfed within the first one hour, which has improved only marginally from 41.6% during NFHS-4 (2015-2016).
- In fact, many States such as Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh have shown a decline in the proportion of children breastfed within the first hour.
Republic Of Cyprus:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has directed all engineering and technical colleges in the country to ensure their faculty members do not participate in conferences organised by countries which are not recognised by the Indian government.
- The stern directive by the technical education regulator came following an objection raised by the Cyprus government with the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) after some Indian academics participated in a conference organised in the occupied part of the Republic of Cyprus.
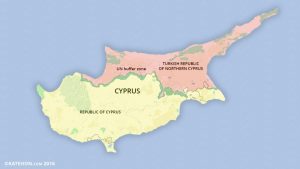
- Cyprus , officially called the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
- It is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean and is located south of Turkey; west of Syria; northwest of the Gaza Strip, Israel, and Lebanon; north of Egypt; and southeast of Greece.
- The country’s capital and largest city is Nicosia.
- However, the Republic of Cyprus is de facto partitioned into two main parts:
- the area under the effective control of the Republic, located in the south and west and comprising about 59% of the island’s area, and
- the north, administered by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, covering about 36% of the island’s area.
- Another nearly 4% of the island’s area is covered by the UN buffer zone.
Project 15B:

Mormugao, Indian Navy’s second indigenous stealth destroyer of the P15B class, planned to be commissioned in mid-2022, proceeded on her maiden sea sortie on 19th December, 2021.
- Mormugao is being built at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (MDSL) as part of the Project 15B destroyers.
- Mormugao will add significantly to the Indian Navy’s combat capabilities.
- With the recent commissioning in November 2021 of INS Visakhapatnam and the fourth P75 submarine INS Vela, commencement of sea trials of Mormugao is testimony to the cutting-edge capabilities of MDSL and the strong indigenous shipbuilding tradition of a modern and vibrant India.
P-15B:
- The Visakhapatnam-class destroyers or simply P-15B, is a class of guided-missile destroyers currently being built for the Indian Navy.
- Designed by the Directorate of Naval Design, a total of four ships are being built by Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL).
- The first vessel of the class, INS Visakhapatnam was commissioned on 21 November 2021.
Lokur Commission:

The Supreme Court on Friday stayed all proceedings before Justice Madan Lokur Commission, set up by the West Bengal government to inquire into the alleged interception of mobile phones using military grade spyware Pegasus, disapproving breach of undertaking by the state for halting the commission’s work when the SC was seized of the pan-India issue.
- The West Bengal government had, in July 2021, set up a Commission of Inquiry (Lokur Commission), under the 1952 Act, to look into the alleged surveillance of phones using the Pegasus spyware developed by the Israeli cyber-intelligence company NSO Group.
- The Commission will look into the alleged breach of privacy of several individuals.
- While both central and state governments can set up such Commissions of Inquiry, states are restricted by subject matters that they are empowered to legislate upon.
- If the central government set up the commission first, then states cannot set up a parallel commission on the same subject matter without the approval of the Centre.
- But if a state has appointed a Commission, then the Centre can appoint another on the same subject if it is of the opinion that the scope of the inquiry should be extended to two or more states.
- Under The Commissions of Inquiry Act, 1952, a Commission set up by the government shall have the powers of a civil court, while trying a suit under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- This means that the Commission has powers to summon and enforce the attendance of any person from any part of India and examine her on oath, and receive evidence.
- It can order requisition of any public record or copy from any court or office.
- Commissions set up by the central government can make an inquiry into any matter relatable to any of the entries in List I (Union List) or List II (State List) or List III (Concurrent List) in the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution, while Commissions set up by state governments can look into entries in List II or List III.
Poshan Tracker:

The Government of India has told in the Lok Sabha that the Data recorded in the Poshan (Nutrition) Tracker have not been made public in the interest of privacy of women and children.
- The objective is to honour the privacy of women and children who are serviced by the Government of India in collaboration with State Governments across the anganwadi systems in the country.
Poshan Tracker:
- The Poshan Tracker, known as the ICDS-CAS (Integrated Child Development Services-Common Application Software) in its earlier avatar, was set up with the aim of tracking and improving various services delivered at anganwadis and to ensure nutritional management of beneficiaries.
- This real-time monitoring system is one of the key pillars of Poshan Abhiyan or Nutrition Mission approved by the Union Cabinet in November 2017 with a financial outlay of ₹9,000 crore for three years.
- The Government has spent ₹1,053 crore to develop the tracker.
- The tracker is one of the important pillars of the Poshan Abhiyan and helps the Government monitor services delivered at 12.3 lakh anganwadi centres and record nutritional indicators of 9.8 lakh beneficiaries, including children in the age of six months to six years as well as pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Anganwadis provide six services, which include supplementary nutrition in the form of hot-cooked meals and take home ration, immunisation and pre-school education.
- The parliamentary committee in its report raised several questions on the effective use of the Poshan Tracker.
- It sought that key performance indicators be constantly monitored and uploaded on its website and a State-wise progress report be maintained “so that identification of those deprived of the benefits can be made on a real-time basis for timely remedial measures.”
- The committee also recommended that the Ministry put in place a monitoring mechanism to ensure there were no gaps in distribution of food packets to anganwadi beneficiaries.
About Poshan Abhiyaan:
- The programme seeks to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
Launched in 2018 with specific targets to be achieved by 2022. - It aims to reduce:
- Stunting and wasting by 2% a year (total 6% until 2022) among children.
- Anaemia by 3% a year (total 9%) among children, adolescent girls and pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- The target of the mission is to bring down stunting among children in the age group 0-6 years from 38.4% to 25% by 2022.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA):

The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has cancelled the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010 registration of various non-governmental organisations (NGOs).
- Suspension of FCRA licence means that the NGO can no longer receive fresh foreign funds from donors pending a probe by the Home Ministry. The FCRA is mandatory for associations and NGOs to receive foreign funds.
- The FCRA registration of Vadodara-based NGO is cancelled because it was accused of illegally converting members of the Hindu community, funding the anti-CAA protests and for criminal activities to strengthen Islam.
- The FCRA registration of two other Christian NGOs — the New Hope Foundation, based in Tamil Nadu, and Holy Spirit Ministries from Karnataka were also cancelled.
- The FCRA registration of AFMI Charitable Trust was cancelled by the MHA for violating the provisions of the Act.
Prior Reference Category:
- THe MHA had put 10 Australian, American and European donors on its watchlist.
- Following which the Reserve Bank of India wrote to all banks that any funds sent by the foreign donors should be brought to the notice of the Ministry and not cleared without its permission.
- All the donors that were placed on the watchlist or “prior reference category” work in the field of climate change, environment and child rights.
- Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010: Foreign funding of persons in India is regulated under FCRA act and is implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Individuals are permitted to accept foreign contributions without permission of MHA.
- However, the monetary limit for acceptance of such foreign contributions shall be less than Rs. 25,000.
- The Act ensures that the recipients of foreign contributions adhere to the stated purpose for which such contribution has been obtained.
- Under the Act, organisations are required to register themselves every five years.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Act, 2020:
- Prohibition to accept foreign contribution: The Act bars public servants from receiving foreign contributions.
- Public servant includes any person who is in service or paid by the government, or remunerated by the government for the performance of any public duty.
- Transfer of foreign contribution: The Act prohibits the transfer of foreign contribution to any other person not registered to accept foreign contributions.
- Aadhaar for registration: The Act makes Aadhaar number mandatory for all office bearers, directors or key functionaries of a person receiving foreign contribution, as an identification document.
- FCRA account: The Act states that foreign contributions must be received only in an account designated by the bank as FCRA account in such branches of the State Bank of India, New Delhi.
- Reduction in use of foreign contribution for administrative purposes: The Act proposes that not more than 20% of the total foreign funds received could be defrayed for administrative expenses. In FCRA 2010 the limit was 50%.
- Surrender of certificate: The Act allows the central government to permit a person to surrender their registration certificate.
Goa Liberation Day:

60th Goa Liberation Day was celebrated on 19th December, 2021 in commemoration of the Indian armed forces freeing Goa from Portuguese colonial rule.
- Although India attained independence from British rule back in 1947, it would still take Goa – which was a Portuguese colony at the time – 14 more years to be liberated from foreign control. Finally, on December 19, 1961, Indian armed personnel managed to wrest control of Goa from the Portuguese, ending around 450 years of colonial rule.
About Operation Vijay:
- Portuguese were the first ones to colonize parts of India and were the last to leave.
- The Portuguese invaded Goa in the year 1510.
- Operation Vijay began on December 17, 1961, when the then Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru ordered the invasion.
- With a force of almost 30,000, the Indian attack overpowered the ill-prepared Portuguese 3,000 member army.
- With minimal blood shed, the attack was successful and was carried forward to retrieve the other Portuguese-controlled areas, Daman and Diu.
- At this point on December 18, the Portuguese Governor General Vassalo da Silva gave up control of the Union Territory of Goa, Daman and Diu.
Mediation Bill,2021:

The Centre will table the much awaited Mediation Bill in the Rajya Sabha.
- The Bill provides for establishment of the Mediation Council of India and for community mediation. The Bill intends to institutionalise the process of mediation by strengthening the Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanisms.
- The Bill safeguards the interest of the litigants to approach the competent adjudicatory forums/ courts in case urgent relief is sought.
- The successful outcome of mediation in the form of a Mediation Settlement Agreement (MSA) has been made enforceable by law.
- Since the Mediation Settlement Agreement is out of the consensual agreement between the parties, the challenge to the same has been permitted on limited grounds.
- According to the Bill, the mediation process protects the confidentiality of the mediation undertaken and provides for immunity in certain cases against its disclosure.
- The registration of Mediation Settlement Agreement has also been provided for with State/ District/ Taluk Legal Authorities within 90 days to ensure maintenance of authenticated records of the settlement so arrived.
Agni-P Missile:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully test-fired the new generation nuclear-capable ballistic missile ‘Agni Prime’.
- This is the second test of the missile, the first test took place in June 2021.
- The Agni-P missile aims to further strengthen India’s credible deterrence capabilities.
- Agni-P is a two-stage canisterised solid propellant missile with dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
- It has been termed as a new generation advanced variant of Agni class of missiles with improved parameters, including manoeuvring and accuracy.
- Canisterisation of missiles reduces the time required to launch the missile while improving the storage and ease of handling.
- The surface-to-surface ballistic missile has a range of 1,000 to 2,000 km.
Agni Class of Missiles:
- Agni class of missiles are the mainstay of India’s nuclear launch capability, which also includes the Prithvi short-range ballistic missiles, submarine launched ballistic missiles and fighter aircraft.
- Agni-V, an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km, had been tested several times and validated for induction.
- The Agni-P and Agni-5 ballistic missiles trace their origins back to the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP), which was spearheaded by former DRDO chief and ex-Indian president Dr APJ Abdul Kalam in the early 1980s.
Other Ranges of Agni Missiles:
- Agni I: Range of 700-800 km.
- Agni II: Range more than 2000 km.
- Agni III: Range of more than 2,500 Km
- Agni IV: Range is more than 3,500 km and can fire from a road mobile launcher.
- Agni-V: The longest of the Agni series, an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km.
What Is Parvovirus?
Nearly 2,000 pet and stray dogs in Amravati city were affected by canine parvovirus virus last month with veterinarians cautioning pet owners against a severe outbreak.
What is Parvovirus?
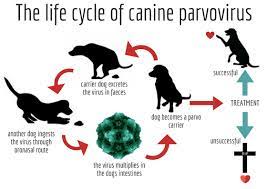
- It is a highly contagious viral disease affecting puppies and dogs.
- It affects the intestinal tract of canines with puppies being more susceptible.
- Bloody diarrhoea, vomiting, drastic weight loss, dehydration and lethargy are some of the symptoms.
- The virus has reported a 90 per cent mortality rate.
- This virus was discovered in 1967 and has rapidly become a serious threat to canine health. This is primarily due to the fact that the virus is hard to kill, can live for a long time in the environment, and is shed in large quantities by infected dogs.
How does the virus spread in dogs?
- Through direct contact with an infected dog or by indirect contact with a contaminated object, including the hands and clothing of people who handle infected dogs.
The recent rise in cases of Parvovirus in pets is due to the Covid-19 pandemic that compelled many pet owners to avoid timely vaccination of their dogs.
- Also, due to the non-implementation of the animal birth control programme, dog vaccination and rabies in the last three years has led to rising parvovirus cases in street dogs in the city.
- Parvovirus has no cure and inoculating a puppy or a dog gives them a fighting chance against the infection.
Minerals (Evidence of Mineral Contents) Second Amendment Rules, 2021 and the Mineral (Auction) Fourth Amendment Rules, 2021:

The Minerals (Evidence of Mineral Contents) Second Amendment Rules, 2021 and the Mineral (Auction) Fourth Amendment Rules, 2021 have been notified.
- These two rules will amend the Minerals (Evidence of Mineral Contents) Rules, 2015 [MEMC Rules] and the Mineral (Auction) Rules, 2015 [Auction Rules], respectively.
- Earlier, Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha both cleared the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Amendment Bill, 2021.
Minerals (Evidence of Mineral Contents) Second Amendment Rules, 2021:
- It will enable any person (who is intending to participate in auction) to propose suitable blocks for auction for composite licence where mineral potentiality of the blocks has been identified based on the available geoscience data.
- A committee constituted by the State Government shall assess the mineral potentiality of the blocks so proposed and recommend the block for auction.
Mineral (Auction) Fourth Amendment Rules, 2021:
- It would provide that in case the blocks proposed by any person are notified for auction, the said person would be provided incentive of depositing only half of the bid security amount in auction of the blocks proposed by him.
- Part surrender of mining lease area has been allowed in all cases.
- Till now, part surrender was allowed only in case of non-grant of forest clearance.
- Provisions have also been added to allow disposal of overburden/ waste rock/ mineral below the threshold value, which is generated during the course of mining or beneficiation of the mineral.
- Minimum area for grant of mining lease has been revised from 5 ha. (hectares) to 4 ha. For certain specific deposits, minimum 2 ha. is provided.




