Today’s Current Affairs: 5th Jun 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Petroleum Coke : For Lithium-Ion Batteries

The Union government of India permitted the import of pet coke for making graphite anode material for lithium-ion batteries.
- Petroleum Coke is a final carbon-rich solid material and residual waste material extracted from oil refining.
- It is a spongy, solid residue from oil distillation that can be burned for fuel similar to coal.
- It is a byproduct created when bitumen is found in tar sands.
- Bitumen contains a higher number of carbon atoms than regular oil and it’s these atoms, extracted from large hydrocarbon molecules using heat, that go on to form petcoke.
- It is high in calorific value and easy to transport and store.
- It releases toxic gases like carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, mercury, arsenic, chromium, nickel, and hydrogen chloride after burning.
- There are two distinctive grades of Petroleum Coke viz. Calcinable or Green Petcoke and Fuel Grade Petcoke.
- It is widely used by power stations and several manufacturing industries including cement, steel and textile plants in India.
Salt Cavern Based Oil Reserves:
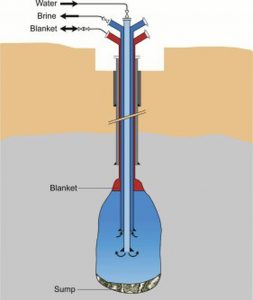
Government-owned engineering consultancy firm Engineers India (EIL) is studying the prospects and feasibility of developing salt cavern-based strategic oil reserves in Rajasthan.
- Salt caverns are developed by the process of solution mining, which involves pumping water into geological formations with large salt deposits to dissolve the salt.
- After water with dissolved salt is pumped out of the formation, the space can be used to store crude oil.
- The process is simpler, faster, and less cost-intensive than developing excavated rock caverns.
- Salt cavern-based oil storage facilities are also naturally well-sealed, and engineered for rapid injection and extraction of oil.
- The salt that lines the inside of these caverns has extremely low oil absorbency, which creates a natural impermeable barrier against liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons, making the caverns apt for storage.
- Rajasthan, which has the bulk of requisite salt formations in India, is seen as the most conducive for developing salt cavern-based strategic storage facilities.
UNRWA : Towards Financial Collapse

United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres recently announced that the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) is “on the verge of financial collapse,”
- United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) is a UN agency that supports the relief and human development of Palestinian refugees.
- It was established in 1949 when nearly three-quarters of a million Palestinians became refugees in the aftermath of the 1948 Arab- Israeli war.
- It is To support Palestinian refugees and their patrilineal descendants who fled or were expelled from their homes during the 1948 Palestine War and 1967 Six-Day War.
- UNRWA was originally designed as a temporary agency, though its mandate has been continuously renewed every three years by the General Assembly.
- It’s services encompass education, health care, relief and social services, camp infrastructure and improvement, microfinance and emergency assistance, including in times of armed conflict.
- It provides services in its five fields of operations: Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Gaza Strip and West Bank, including East of Jerusalem.
- UNRWA is unique in that it delivers services directly to its beneficiaries.
- It is funded almost entirely by voluntary contributions from UN Member States. It also receives some funding from the Regular Budget of the United Nations.
- It reports only to the UN General Assembly.
- It was originally headquartered in Beirut, Lebanon, but was moved to Vienna, Austria, in 1978.
- In 1996 the General Assembly moved the agency to the Gaza Strip to demonstrate the Assembly’s commitment to the Arab-Israeli peace process.
Kavach System : Railway

The railways recently confirmed that there was no ‘Kavach’ system installed on the trains involved in the accident in Odisha’s Balasore district.
- It is an indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system.
- Kavach was developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) under Indian Railway (IR) in collaboration with Medha Servo Drives Pvt Ltd, HBL Power Systems Ltd and Kernex Microsystems.
- It is a set of electronic devices and Radio Frequency Identification devices installed in locomotives, in the signalling system as well the tracks, that talk to each other using ultra-high radio frequencies to control the brakes of trains and also alert drivers, all based on the logic programmed into them.
- Since 2016, the railways have been carrying out field tests for Kavach on passenger trains.
- It has been designed to assist locomotive pilots in avoiding Signal Passing At Danger (SPAD) and overspeeding.
- The system can alert the loco pilot, take control of the brakes and bring the train to a halt automatically when it notices another train on the same line within a prescribed distance.
- The device also continuously relays the signals ahead to the locomotive, making it useful for loco pilots in low visibility.
- It also controls the speed of the train by an automatic application of brakes in case the loco pilot fails to do so.
- It helps the loco pilot in running the train during inclement weather conditions such as dense fog.
GAGAN Satellite Technology:

The Prime Minister of India lauded Asia’s first demonstration of Performance-Based Navigation for helicopters for a flight from Juhu to Pune using GAGAN satellite technology.
- GAGAN satellite technology is the acronym for GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation.
- It is jointly developed by ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- It uses a system of ground stations to provide necessary augmentations to the GPS standard positioning service (SPS) navigation signal.
- It is designed to provide the additional accuracy, availability, and integrity necessary to enable users to rely on GPS for all phases of flight.
- It also provides the capability for increased accuracy in position reporting, allowing for more uniform and high-quality Air Traffic Management (ATM).
- In addition, GAGAN will provide benefits beyond aviation to all modes of transportation, including maritime, highways, and railroads.
- There are only four Space-Based augmentation systems available in the world namely India (GAGAN), US (WAAS,) Europe(EGNOS) and Japan (MSAS).
Da Vinci Robotic Surgical System:
Apollo Hospitals, Ahmedabad, a pioneer in healthcare innovation, recently launched the Da Vinci Xi Robotic Surgical System.
- Da Vinci Robotic Surgical System is a tool that helps surgeons perform a variety of surgeries including gynecological surgeries, urological, head and neck, thoracic, colorectal, cardiac and general surgeries.
- The da Vinci only uses small cuts, it’s less traumatic on your body, resulting in less pain, fewer complications and a shorter recovery time.
- It can be used in the field of colorectal surgeries, urology, oncology, gynaecology thoracic, cardiology, paediatric and gastro-intestinal surgeries, kidney transplants and in liver transplantation.
- The machine is made up of three different parts:
- The console/control center: The surgeon operates while seated at a console unit, using hand and foot controls and with a magnified, 3D, high-definition view.
- The patient cart: The cart holds surgical instruments and the camera.
- The vision cart: This cart has a video screen so that the healthcare providers in the room can see what’s happening during the surgery.
- A Da Vinci surgery is when your surgery is performed using the da Vinci Surgical System, a machine that uses four thin robotic arms.
- The robotic instruments have a wider range of motion than the human hand. Surgeons can use the surgical system for a variety of procedures.
Second Meeting Of The Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-2):

The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has gathered in Paris, France, for the second meeting of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-2).
- The first session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-1) concluded in Uruguay in 2022.
- INC-2 aimed to set the stage for negotiations on the substance of a global deal to end plastic pollution to edge closer to protecting ecosystems, species and humanity from the grave impacts of the linear plastics economy.
Highlights of INC-2 Meeting:
- The primary agenda of INC-2 was to adopt the rules of procedure. The rules govern various aspects such as the negotiation process, decision-making procedures (consensus or voting), and the entities authorized to make decisions.
- During the previous INC-1 meeting, a part of Rule 37, stating “each member shall have one vote,” was kept in brackets, indicating unresolved disagreement.
- The bracketed part now includes provisions from the Minamata Convention, allowing regional economic integration organizations (such as the European Union) to vote on behalf of their member states. However, the member states must be present during voting or as part of the committee.
- India has consistently insisted on bracketing Rule 38, which states, “The Committee shall make every effort to reach agreement on all matters of substance by consensus.
- If all efforts to reach consensus have been exhausted and no agreement has been reached, the decision shall, as a last resort, be taken by a two-thirds majority of the representatives of Members who are present and voting.”
- The formation of the OEWG (Open-Ended Working Group) has delayed the start of discussions in the contact groups on substantive matters.
- In UNEA resolution 5/14, the assembly mandated an ad hoc open-ended working group (OEWG) to lay the groundwork for negotiations.
INC :
- It was established in February 2022, at the 5th session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA-5.2).
- A historic resolution (5/14) was adopted to develop an international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, including in the marine environment with the ambition to complete the negotiations by the end of 2024.
Sedition Law : Recommendation Of Law Commission

The Law Commission of India recently recommended retention of the sedition law and enhancement of the minimum punishment to seven years in jail from the current three years.
Recommendations – Amend Section 124A of the IPC:
- To bring about more clarity in the interpretation, understanding, and usage of the provision and to align it with the SC’s 1962 verdict.
- To replace mere inclination to incite violence or cause public disorder with proof of actual violence or imminent threat to violence.
- To enhance the alternative punishment to “7 years”, giving the courts greater room to award punishment in accordance with the gravity of the act.
- Procedural safeguards to minimise the abuse i.e Section 154 of the CrPC could be amended to hold that a FIR under Section 124A would be registered only after a police officer conducts a preliminary inquiry.
The Sedition Law in India:
Section 124A of the IPC:
- It states, “Whoever, words, either spoken or written, or by signs, or by visible representation, or otherwise, brings or attempts to bring into hatred or contempt , or excites or attempts to excite disaffection towards the Government established by law in India shall be punished with imprisonment for life, to which fine may be added, , or with imprisonment which may extend to three years, which fine may be added, or with fine.”
- This means anyone who attempts to create hatred, contempt, or disaffection towards the government can be punished under the sedition law.
- Punishment:
- Sedition is a non-bailable offence.
- Punishment under the law varies from imprisonment up to three years to a life term and fine.
- A person charged under this law can’t apply for a government job.
- They have to live without their passport and must present themselves in the court as and when required.
ILO Monitor On The World Of Work : 11th edition

The ILO Monitor on the World of Work database provides access to several of the indicators related to the labour market.
Highlights of the ILO Monitor (11th edition):
- In 2023, the global jobs gap i.e periods during one’s professional career when s/he did not have secure, formal employment is projected to stand at 453 million people (11.7%), more than double the level of unemployment.
- Low-income countries in debt distress face a jobs gap of 25.7% in 2023.
- Some countries are facing complex and cascading crises, like natural disasters (e.g. the earthquakes in Türkiye and Syrian Arab Republic), which interact with broader global challenges and exacerbate labour market impacts.
- Significant social protection policy gaps remain in developing countries, especially in low-income countries, including in regard to old-age pensions.
- Only 38.6% of older persons in lower middle-income countries receive an old-age pension.
Recommendations:
- Building a national social protection floor: For example, by expanding basic old-age pensions in developing countries.
- This will act as a catalyst for inclusive sustainable development and decent jobs.
- Policies and financial support: To build resilience and overcome the global employment divide.
- Build global financial resources: The UN Global Accelerator on Jobs and Social Protection, and the Global Coalition for Social Justice can play a positive role here.
Li-ion Battery Recycling Technology:

The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in India has transferred cost-effective lithium-ion battery recycling technology to nine recycling industries and start-ups as part of the Mission LiFE under the “Promote circularity campaign.”
- This indigenous technology can process various types of discarded lithium-ion batteries, recovering over 95% of lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel contents in the form of corresponding oxides/carbonates with a purity of about 98%.
- The recycling process of lithium-ion batteries involves several steps.
- First, the batteries are collected, sorted and disassembled
- Next, the electrodes, which contain valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel, are extracted, through a process called leaching, where the electrodes are submerged in a liquid that dissolves these metals.
- After that, the metals are purified to remove impurities, resulting in high-purity lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel compounds.
- Aim is to recover valuable materials from lithium-ion batteries, reducing the need for mining and minimizing environmental impact.
- It helps conserve resources and promotes sustainable practices in battery manufacturing.
- Developed by the technology was developed at the Centre of Excellence on E-waste Management, in collaboration with the Government of Telangana and industry partner.
What Are Earth System boundaries?

Reports suggest that seven of eight Earth system boundaries (ESBs) that are critical for the stability of the planet’s health and survival of species have already been crossed.
- Earth System Boundaries (ESBs) are scientifically measured limits for climate, freshwater, biodiversity and different kinds of pollution.
- Operating within these limits, can help maintain a stable and resilient planet.
- These are hard limits and even temporary overshooting of some of the boundaries can permanently damage the planet’s critical systems.
Findings of the Report:
- Two or more ESBs have already transgressed 52% of the world’s land surface, affecting 86% of the global population.
- India, along with other parts of South Asia, Europe, and parts of Africa is an ESB transgression hotspot.
- Himalayan foothills have recorded at least 5 ESB transgressions.
- The seven ESBs that have been crossed are:-
- Climate, functional integrity, and levels of surface water, groundwater, nitrogen, phosphorus and aerosols.
- The eighth, which has not been crossed, is. 5 degrees C warming
- The global annual mean interhemispheric aerosol optical depth (AOD) difference, which measures the degree of air pollution globally has also not been crossed.
Galleri Test : Identifies The Original Site Of Cancer
A blood test capable of detecting over 50 types of cancer has shown remarkable potential in a major trial conducted by the NHS.
- Galleri test, has demonstrated high accuracy rates and the ability to identify the original site of cancer in a significant percentage of positive cases.
- It aims to revolutionize cancer detection by identifying treatable cancer at an early stage, thus offering a chance to save lives.
- In the trial, two-thirds (66.6%) of the cancers among the 5,000 participants with suspected symptoms were accurately identified through this blood test.
- Remarkably, in 85% of these positive cases, the Galleri test successfully pinpointed the original site of the cancer.
- Traditional methods, such as scans and biopsies, subsequently diagnosed over 350 participants with cancer in the study.
- Among those who tested positive on the blood test, an impressive 75% were confirmed to have cancer through traditional methods.
- Even among those who initially tested negative, 2.5% were later diagnosed with cancer.
- Although not infallible, the Galleri test exhibited an 85% accuracy rate in detecting the source of cancer.




