Today’s Current Affairs: 19th April 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
International Big Cat Alliance : Establishing India As The Headquarters Of The Alliance

The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) signed an official agreement with the Government of India, formally establishing India as the headquarters and secretariat of the alliance.
- International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in April 2023 during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger. Formally approved by the Union Cabinet in February 2024.
- The IBCA is implemented through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective is to conserve seven major big cat species across the world: Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah.
- Current ratifying members: India, Nicaragua, Eswatini, Somalia, Liberia are the initial countries that ratified the IBCA Framework Agreement.
- Membership is open to all UN Member States, including:
- Range countries, where big cats naturally occur.
- Non-range countries that are interested in supporting global conservation of big cats.
- India formally joined the IBCA in September 2023, after ratifying the framework agreement.
- The IBCA became a treaty-based intergovernmental organisation after five countries ratified the framework agreement. These include India, Nicaragua, Eswatini, Somalia, and Liberia.
- Institutional Support and Funding: India has committed ₹150 crore for the period 2023–2028
Operation ATALANTA:

The European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) under Operation ATALANTA has proposed a joint naval exercise with the Indian Navy.
- EUNAVFOR Operation ATALANTA, which operates in the Western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, has proposed a joint maritime exercise with the Indian Navy to be conducted around the end of May 2025.
- The primary goal of the proposal is to enhance coordination and maritime cooperation between European naval forces and the Indian Navy, particularly in the face of resurgent piracy threats and geopolitical instability in the Red Sea region.
- The proposed drill will go beyond the usual Passage Exercises (PASSEX) and will include advanced tactical manoeuvres, counter-piracy operations, and inter-naval communications training, if approved.
- The Horn of Africa region, once again experiencing piracy amidst Houthi rebel activity in the Red Sea, has prompted a need for enhanced maritime coordination, even though incidents have decreased recently.
- Operation ATALANTA launched in 2008, Operation ATALANTA is the EU’s counter-piracy mission in the Western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, initially targeting piracy off the Somali coast.
Gita and Natyashastra added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register:

The manuscripts of the Bhagavad Gita and Bharat Muni’s Natyashastra were added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register.
- An international initiative by UNESCO to preserve humanity’s valuable documentary heritage and safeguard it against neglect, decay, and destruction.
- Established In: 1992.
- Objective is to protect archival holdings, manuscripts, rare collections, and promote broader accessibility and awareness.
Bhagavad Gita:
- Name: Bhagavad Gita (The Song of the Lord).
- Attributed to: Sage Vyasa.
- Features: A 700-verse dialogue between Krishna and Arjuna, expounding profound spiritual, ethical, and philosophical principles central to Hindu thought.
Natyashastra:
- Name: Natyashastra (Treatise on Performing Arts).
- Author: Bharat Muni.
- Features: A foundational text detailing Indian classical dance, drama, music, and stagecraft; establishes concepts like Rasa (aesthetic flavor) that continue to influence Indian arts.
James Webb Space Telescope : Evidence Of Extraterrestrial Life On a Distant Exoplanet

Scientists have found tentative but strong evidence of possible extraterrestrial life on a distant exoplanet named K2-18b, located 124 light years away from Earth in the Leo constellation.
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched in December 2021, is the largest and most powerful space observatory built through a collaboration between NASA, European Space Agency (ESA), and Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
- JWST orbits the L2 Lagrange Point, about 5 million km beyond Earth, enabling a stable position for deep-space observation.
- The telescope operates primarily in the infrared spectrum and is equipped with components such as:
- Optical Telescope Element (OTE) – collects light from distant objects.
- Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) – houses all cameras and instruments.
- Sunshield – protects sensitive instruments from solar radiation.
- Spacecraft Bus – provides necessary operational support.
- The Cambridge University research team, led by Nikku Madhusudhan, studied the planet’s atmosphere and detected chemical signatures of gases like dimethyl sulphide (DMS) and dimethyl disulphide (DMDS).
- On Earth, these gases are known to be produced only by marine phytoplankton and certain bacteria, raising the possibility of biological activity on K2-18b.
NASA’s Curiosity Rover : Discovered Carbon-Bearing Minerals On Mars

NASA’s Curiosity Rover has discovered carbon-bearing minerals on Mars, marking the first solid evidence of a carbon cycle on the Red Planet.
- The discovery was made during the rover’s exploration of an 89-meter stretch of terrain in an ancient lakebed in the Gale Crater, where it drilled into different types of rocks.
- The Curiosity rover identified a carbonate mineral called siderite, which contains carbon and oxygen, in the sulfate-rich layers of Martian rocks. This is the first time this mineral has been found on Mars.
- The rocks containing 5–10% siderite by weight suggest that a significant portion of Mars’ past CO₂ may be trapped in the planet’s crust, rather than having escaped into space.
- The rocks also showed the presence of iron oxyhydroxides, indicating that siderite may have dissolved in acidic water, releasing some CO₂ back into the atmosphere. This points to a limited and slow carbon cycle.
- NASA’s Curiosity Rover is a S. robotic rover launched on November 26, 2011, aboard an Atlas V rocket and landed on Mars on August 5, 2012.
- It is part of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission and was the first to use a sky crane landing system to reach the Martian surface.
- The rover runs on a thermoelectric power generator, which utilizes the radioactive decay of plutonium instead of solar panels.
- Its four primary scientific goals are:
- Determine whether life ever existed on Mars.
- Characterize Mars’ past and present climate.
- Understand the geology of Mars.
- Prepare for future human exploration.
- The rover is approximately 3 meters long, weighs around 900 kilograms, and is equipped with an onboard chemistry lab for analyzing rock samples.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology:
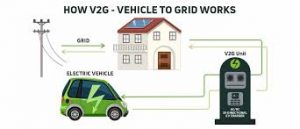
The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB), in partnership with IIT Bombay, has launched a pilot V2G project to test its feasibility in the state.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) is a set of technologies that enable Electric Vehicles (EVs) to send stored electricity back to the power grid when they are not in use.
- When an EV is idle and connected via a bi-directional charger, it can act as a decentralised battery energy storage system, contributing electricity to the grid.
- V2G supports both charging (Grid to Vehicle – G2V) and discharging (Vehicle to Grid – V2G) of EV batteries, creating a two-way energy flow.
- During charging, EV batteries act as a load on the grid, which can be managed using tools like Time of Use (ToU) tariffs and smart charging to reduce stress during peak hours.
- During discharging, EV batteries serve as distributed energy sources, providing electricity during peak demand periods or when renewable energy (RE) is low.
- V2G is part of a broader framework including Vehicle to Home (V2H) and Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) applications, but V2G is the most widely explored use case
PETA : In News

The Trump administration’s recent policy changes to end animal testing are garnering support from animal rights groups like PETA.
- People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) is a nongovernmental organization (NGO) committed to ending abusive treatment of animals in business and society and promoting consideration of animal interests in everyday decision-making and general policies and practices.
- It is the largest animal rights organization in the world.
- It is based in Norfolk, Virginia, United States, with entities worldwide.
- PETA was founded in 1980 by Ingrid Newkirk and Alex Pacheco, who were influenced by Australian ethicist Peter Singer’s book Animal Liberation (1975).
- Initially recognized for exposing cruelty in research laboratories, PETA has grown into a global entity with over nine million members and considerable annual expenditures.
- PETA opposes speciesism, a human-supremacist worldview, and focuses on the four areas in which the largest numbers of animals suffer the most intensely for the longest periods of time: in laboratories, in the food industry, in the clothing trade, and in the entertainment business.
- PETA also works on a variety of other issues, including the cruel killing of rodents, birds, and other animals who are often considered “pests” and cruelty to domesticated animals.
- PETA works through public education, investigations, research, animal rescue, legislation, protests, and negotiations with companies and regulatory agencies.
Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025:

The World Trade Organization’s (WTO) Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025 reveals that global merchandise trade is projected to decline by 0.2% in 2025.
- The WTO’s revised forecast for global merchandise trade shows a 0.2% decline in 2025.
- If trade tensions escalate further, especially with new tariff measures, the decline could deepen to 1.5%. This marks a sharp contrast from the 2.9% growth in 2024.
- The reactivation of US reciprocal tariffs could cut global trade growth by 0.6% points, while ongoing US-China tariff escalation in 2025 may reduce trade by an additional 0.8% points.
- Despite the challenges in merchandise trade, the global services trade is projected to grow by 4.0% in 2025, slower than expected due to tariff-induced disruptions.
- The decline in goods trade impacts services like transport and travel, while broader uncertainty dampens investment-related services.
- North America is expected to face a sharp 12.6% decline in exports, significantly affecting global trade.
- Asia and Europe are projected to see modest trade growth, with Asia’s exports growing by 1.6%, and Europe’s exports growing by 1.0%.
- Least-developed countries (LDCs), heavily reliant on a narrow range of exports, are particularly vulnerable to the downturn in global trade.
- US-China trade disruption may drive significant trade diversion, with Chinese exports projected to rise by 4%-9% in regions outside North America.
- Meanwhile, US imports from China are expected to fall, creating opportunities for other suppliers, including LDCs, to fill the gap.
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) forecasts global growth to slow to 2.3% in 2025, signaling a potential shift toward recession, with developing countries being particularly vulnerable.
- As the risks of economic fragmentation and geo-economic confrontation rise, UNCTAD urges increased regional and international policy coordination to strengthen global economic resilience.
- In 2024, India’s rank among leading merchandise exporters (excluding intra-EU trade) dropped to 14th, while its share of global merchandise trade remained steady at 2.2%.
- Similarly, India’s rank among major merchandise importers (excluding intra-EU trade) fell to 7th, with its share unchanged at 3.4%.
- As for commercial services (excluding intra-EU trade), India’s rank as an exporter declined to 6th, with a slight drop in share from 5.4% to 5.3%. In terms of imports, India’s rank remained at 6th, although its share fell slightly from 4.2% to 4.1%.
Shinkansen Trains and Bullet Train Project:

Japan is set to provide India with two Shinkansen train sets (E5 and E3 series) at no cost in 2026.
- Shinkansen Trains (E5 Series): It has been operational since 2011. With a speed of 320 km/h, it was initially chosen for India’s first bullet train line.
- Known for its aerodynamic design, advanced safety systems, and smooth ride quality, it represents the cutting edge of high-speed rail technology.
- Shinkansen Trains (E3 Series) a slightly slow and older model primarily used for mini-shinkansen services, it shares similar features to the E5 series, such as safety mechanisms.
- Bullet Train Project (Mumbai-Ahemdabad) implemented by the National High-Speed Rail Corporation Ltd. (NHSRCL), the project incorporates Japanese Shinkansen technology.
- The project is funded by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), covering about 80% of the costs.
- The Project was initially scheduled for completion by 2022, but the revised deadline is now 2028.
- The Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor is part of India’s National Rail Plan (NRP) 2030.
World Heritage Day 2025:

World Heritage Day 2025, themed “Heritage under Threat from Disasters and Conflicts: Preparedness and Learning from 60 years of ICOMOS Actions,” is being celebrated globally, reaffirming the need to protect cultural and natural legacies.
- Heritage Sites are locations officially recognized by UNESCO for possessing outstanding cultural, natural, or mixed universal value.
- They represent humanity’s shared legacy, preserving achievements in history, architecture, biodiversity, and culture for future generations.
- As of 2024, India proudly holds 43 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, showcasing its rich and diverse civilizational history.
India’s journey began in 1983 with the listing of Agra Fort, Taj Mahal, Ajanta Caves, and Ellora Caves as the first recognized sites. - Categories of Sites in India: Cultural Sites (e.g., Taj Mahal, Hampi): Reflecting India’s monumental architecture, spirituality, and artistic excellence. Natural Sites (e.g., Western Ghats, Sundarbans): Celebrating India’s ecological richness and biodiversity. Mixed Sites (e.g., Khangchendzonga National Park): Having both cultural and natural significance.
IT adoption in Aquaculture:
India’s aquaculture sector is witnessing a transformation through digital and IT-driven innovations, as highlighted by investments like the $4.5 million infusion into aquaculture tech platforms.Aquaculture refers to the controlled farming of aquatic organisms like fish, shrimp, and mollusks in freshwater or marine environments, aimed at boosting food production and exports.
Crowdfunded Bridge on Magai River:
Villagers of Kyampur Chhavni in Ghazipur, Uttar Pradesh, crowdfunded and began building a bridge across the Magai River after waiting 58 years for government action. The residents of Kyampur Chhavni pooled money and resources to construct a 105 ft bridge after decades of administrative delays. Ravindra Yadav, a retired Army engineer, contributed ₹10 lakh from his retirement funds and provided technical expertise. Contributions ranged from ₹100 cash donations to providing cement, steel, sand, and manual labor after daily work. Magai River flows through Azamgarh, Mau, and Ghazipur districts in Eastern Uttar Pradesh. Origin Village Dubawan, Azamgarh district, Uttar Pradesh.
DPS Wetland : Declared a Flamingo Conservation Reserve
The DPS Wetland in Navi Mumbai has been officially declared a Flamingo Conservation Reserve by the Maharashtra State Wildlife Board. Situated in Seawoods, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra. Spread over 30 acres, adjacent to the Thane Creek Ramsar site. DPS Lake forms part of the Thane Creek ecosystem, a tidal waterbody fed by numerous freshwater sources and marine influences. Supports migratory birds on the Central Asian Flyway.
Taurus Missiles:
Russia warned Germany that any Ukrainian strikes using Taurus missiles would be considered direct participation in the ongoing conflict.The Taurus KEPD-350 is a long-range, air-launched cruise missile capable of precision strikes on fortified and high-value targets. Developed by jointly developed by the European missile manufacturer MBDA and Saab Bofors Dynamics (Germany and Sweden partnership). Aim is to esigned for deep penetration strikes against heavily fortified structures such as bunkers, bridges, and command centres.
Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD):
A study commissioned by the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser has recommended rolling back the 2015 order mandating Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) installation across all coal plants. FGD installation should be mandated only for plants burning imported or high-sulphur coal (>0.5% sulfur content), not for all coal plants.
Findings:
- 92% of Indian coal is low-sulphur (0.3–0.5%).
- Stack heights and climatic conditions in India naturally disperse SO₂ emissions, limiting local air quality threats.
- Full FGD rollout would consume significant freshwater and add 69 million tonnes of CO₂ emissions by 2030 while marginally reducing SO₂.
- Acid rain is not a major environmental issue in India as per IIT Delhi’s 2024 study
2-day Conclave on Buddhism in Arunachal Pradesh:
A two-day conclave titled ‘Buddha Dhamma and the Culture of Northeast India’ will be held in Namsai, Arunachal Pradesh, starting from April 21, 2025. This event is significant as it aims to highlight the impact and spread of Buddhism in the Northeast region of India, emphasizing its role in preserving and propagating various Buddhist traditions, including Theravāda, Mahāyāna, and Vajrayāna. The conclave is being organized by the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC) in collaboration with the Ministry of Culture. The event will include panel discussions, cultural performances, and practices related to Vipassana meditation, focusing on the Buddhist influence on the region’s art, culture, and global peace.
India’s Economy to Grow by 6.5% in 2025 : UNCTAD Forecast
India is set to maintain its position as the fastest-growing major economy in 2025 with an impressive 6.5% GDP growth, according to the latest “Trade and Development Foresights 2025” report released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). While global economic momentum shows signs of slowing, India stands out for its resilience, fueled by increased public spending and proactive monetary policies.
India Set to Become Fastest-Growing Major Aviation Market by 2026:
India is poised to become the world’s fastest-growing large aviation market by 2026, according to Airports Council International (ACI). While China remains significantly ahead in overall aviation market size, India’s growth is being fuelled by increasing demand for air travel among its vast population, where per capita air travel remains low. The rapid pace of infrastructure development, policy reforms, and growing middle-class aspirations are contributing factors.
Government Clarifies No GST on UPI Transactions Above ₹2,000:
The Finance Ministry of India has categorically denied any plans to impose Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Unified Payments Interface (UPI) transactions over ₹2,000. The Ministry termed such claims as false, baseless, and misleading. Reinforcing the government’s commitment to promoting digital payments, the clarification emphasizes that no MDR (Merchant Discount Rate) is charged on person-to-merchant (P2M) UPI transactions, and thus no GST applies to such transactions either
Pilot Program of ANPR-FASTag-based Barrier-Less Tolling System:
Satellite-based Tolling System will be launched from 1st May 2025 to replace the current FASTag-based toll collection, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) and the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) have officially denied any such decision. Instead, the government has announced a pilot implementation of a more advanced ANPR-FASTag-based Barrier-Less Tolling System at selected toll plazas.




