Today’s Current Affairs: 21st November 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
YUVA AI for ALL Initiative:

The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launched the YUVA AI for ALL Initiative to help everyone understand Artificial Intelligence.
- YUVA AI for ALL Initiative is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), under the IndiaAI Mission.
- It is a first-of-its-kind free course that introduces the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to all Indians, especially the youth.
- It consists of 5-hour self-paced course designed to make students, professionals and other curious learners comfortable with the basics of Artificial intelligence.
- Aim is to empower 1 crore (10 million) citizens with foundational AI skills.
- YUVA AI for ALL Initiative is simple, practical, and filled with real-life Indian examples to make learning relatable and fun.
- It is available for free on leading learning platforms – Future Skills Prime, iGOT Karmayogi, and other popular ed-tech portals.
- Every learner who completes the course will get an official certificate from the Government of India.
- It’s 100% free and open to everyone.
- It allows learning at one’s own pace — anytime, anywhere.
- IndiaAI Mission was initially launched as a joint initiative between the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Nasscom in 2023.
- The mission’s key goals are:
- “Making AI in India” – Encouraging domestic AI development.
- “Making AI Work for India” – Ensuring AI benefits various sectors in the country.
Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary:

A wild tiger has made a return to Gujarat after several decades, establishing a permanent presence in Dahod’s Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the state of Gujarat.
- The sanctuary falls on the border of Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh.
- It was declared as a wildlife sanctuary in March 1982.
- It is also known as “Ratanmahal Sloth Bear Sanctuary,” due to its highest population of sloth bears in the Gujarat state.
- It form the catchment of river Panam- a major river of Central Gujarat.
- It consists of dry teak forests at the foothills and mixed deciduous forests with dry bamboo brakes on the periphery.
- It consists of a high population of ‘Mahudo’ trees intermixed with pure patches of ‘Sadad’ and ‘Timru’ forest on plateaus of the hills.
- Flora: Teak, dudhlo, sadad, timru, amla, bamboo, dhavdo, kakadiyo, mahuda, tanach, charoli, ber, jamun, khakhro etc.
- Fauna: Leopard, Palm civet, Indian civet, Four-horned antelope, Loten’s sunbird, Large green barbet, yellow checked tit.
Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2026:

India slipped 13 ranks to figure at the 23rd position in the latest Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2026.
Highlights of the Climate Change Performance Index 2026:
- Denmark, the UK and Morocco took the lead in this year’s CCPI .
- China (54th), Russia (64th), the US (65th) and Saudi Arabia (67th) are the G20’s worst-performing countries, receiving an overall very low score.
- India fell 13 places from its previous ranking of 10th to stand at 23rd in the latest global climate change performance with a score of 61.31.
- It also labelled India among the biggest producers of oil, gas, and coal worldwide, leading it to fall from a ‘high performer’ to a ‘medium’ one in this year’s CCPI.
- India also scored medium in GHG emissions, climate policy, and energy use, and low in renewable energy.
Tier II Bonds:

Several banks are actively issuing Tier II bonds to bolster their capital adequacy ratios (CAR) as required under Basel III norms, with total issuances expected to reach Rs 25,000 crore in FY 2025–26.
- Tier II bonds are subordinated debt instruments banks issue to boost capital and support operations. They count as Tier II (supplementary) capital under Basel-III and help improve the CAR.
- CAR indicates a bank’s financial strength, with a higher ratio providing a stronger buffer against distress. CAR = (Eligible Capital ÷ Risk-Weighted Assets) × 100%.
- Tier II Bonds are different from Tier I Bonds as they strengthen a bank’s supplementary capital, whereas Tier I (AT1) Bonds strengthen its core capital (equity and retained earnings).
- Key Features of Tier II Bonds:
- Maturity: They are typically long-term instruments with original maturities of at least 5 years.
- Subordination: Tier II bondholders are paid after all depositors, senior debt holders, and general creditors in the event of a liquidation.
- Coupon Payments: They pay regular interest (coupons) and generally offer higher coupon rates than senior bonds due to higher risk.
- Call Options: Most Tier II bonds include a call option, allowing the bank to redeem the bonds after a specified period (e.g., 5 or 10 years).
- Loss Absorbency (Gone-Concern Capital): Tier I capital is considered “gone-concern” capital, meaning it is intended to absorb losses if a bank fails and is in the process of being wound up.
Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA):

The United States has officially designated Saudi Arabia as a Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA), signalling a major upgrade in defence ties after Trump’s meeting with Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman.
- MNNA is a special U.S. strategic designation that grants close defence partners military, financial, and technological privileges—without offering formal NATO-style security guarantees.
- Created under U.S. law in the 1980s.
- Intended to strengthen America’s global alliance network outside NATO.
- Aim is To promote defence collaboration, advanced weapons access, joint training, and security coordination, is to reinforce U.S. strategic partnerships in geopolitically sensitive regions.
- Current MNNA Countries:
- 20 nations across Asia, Africa, South America, and Oceania.
- Argentina, Australia, Bahrain, Brazil, Colombia, Egypt, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kenya, Kuwait, Morocco, New Zealand, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, South Korea, Thailand, Tunisia, and now Saudi Arabia.
New Initiatives to Improve the Public Distribution System:

The Union Food and Public Distribution Ministry recently launched several digital initiatives aimed at modernising warehousing operations, improving supply chain efficiency, and enhancing transparency across the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- It is an AI-based platform that allows Public Distribution System (PDS) beneficiaries to share their feedback on ration distribution through AI-enabled calls in their preferred language.
- It was introduced by the Department of Food and Public Distribution.
- The platform runs at a cost of ₹5 lakh.
- ASHA reaches 20 lakh beneficiaries monthly across India, developed in partnership with the Wadhwani Foundation and backed by the India AI mission via Bhashini’s multilingual AI infrastructure.
- Through ASHA, beneficiaries can report whether they received their full entitlement, the quality of foodgrains, and any difficulty faced at Fair Price Shops.
- The system uses multilingual translation, sentiment analysis, automated grievance categorisation, and real-time dashboards for administrators.
- Bhandaran 360 is the Central Warehousing Corporation’s new Enterprise Resource Planning platform.
- Implemented ahead of schedule, the system integrates 41 modules covering HR, finance, marketing, warehouse management, contract management, project monitoring, and other core functions.
- It is also linked with 35 external systems, including ICEGATE, port systems, FCI, NAFED, NCCF, and WDRA, enabling seamless digital connectivity across the food storage and movement ecosystem.
Raulane Festival:

Bright, colourful, and quite fascinating photos of the Raulane festival from Himachal Pradesh recently went viral on social media, with users discussing the unique ritual and culture of a centuries-old tradition.
- It is a traditional festival celebrated in Kalpa, Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh, in winter or early spring.
- It is believed to be around 5,000 years old.
- This ancient festival honours celestial fairies, known as Saunis, said to be radiant and gentle beings.
- Locals believe that the Saunis protect villagers during harsh winters by offering warmth and guidance.
- During the festival, two men symbolically “marry” and become vessels for the Saunis, embodying a divine couple, the Raula (groom) and the Raulane (bride).
- They get dressed in heavy woollen robes, ornaments and unique face masks.
- They also perform a slow, meditative dance at the Nagin Narayan Temple, and the whole community joins in.
- The Raulane festival preserves ancient Himalayan culture and traditions, with villagers coming together to honour their protectors.
17 Nation Join Blue NDC Challenge:
17 countries including France, Brazil, Belgium, Canada, and Singapore—have joined the Blue NDC Challenge at COP30, signalling a major global push to embed ocean-based climate solutions into national climate plans.
- A global initiative encouraging countries to integrate ocean-based climate actions into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement.
- It seeks to close the “ocean opportunity gap,” as oceans contribute only a small share of global climate finance and mitigation plans despite their massive potential.
Key Features:
- Expanded Membership: 17 countries now onboard, including new entrants like Belgium, Canada, Indonesia, and Singapore.
- Ocean Taskforce: Supported by France and Brazil to help governments embed ocean solutions into updated 2030 climate plans.
- Blue Package: A coordinated plan across five Ocean Breakthrough sectors—marine conservation, ocean food systems, offshore renewable energy, shipping decarbonisation, and coastal tourism.
- Focus on Mitigation & Adaptation: Recognises oceans’ potential to deliver up to 35% of global emission reductions needed for the 1.5°C target.
- Finance Mobilisation: Seeks to address chronic underfunding—ocean climate finance is <1% of global climate finance.
- Support for Blue Carbon Pathways: Mangroves, seagrasses, salt marshes integrated into national mitigation and adaptation strategies.
India Re-Elected to Codex Executive Committee:

India was unanimously re-elected to the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC) at 48th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC48) securing its seat for Asia until CAC50 in 2027, strengthening its role in setting global food safety and quality standards.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was created in 1963 by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO), sets global food safety and quality standards to protect consumers and ensure fair food trade. It has 189 members, and India joined in 1964.
- CAC is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- CCEXEC oversees the management of the CAC, guides strategic planning, and manages standards development.
- India is a member of CCEXEC in its capacity as the Regional Coordinator for Asia (CCASIA).
- The Codex Alimentarius, or “Food Code”, adopted by CAC is a collection of international standards, guidelines, and codes covering food hygiene, additives, pesticide residues, contaminants, labelling, and inspection.
- The Agreement on Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) of the World Trade Organization (WTO) recognizes Codex standards, guidelines and recommendations as reference standards for international trade and trade dispute settlement
- India has been chairing the Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH) since its inception in 2014, with the Spices Board of India serving as the secretariat.
- India actively engaged in discussions around the Codex Strategic Plan 2026–2031, advocating for SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) Key Performance Indicators.
UNSC Approves Trump’s Plan for Gaza:

The UN Security Council (UNSC) adopted Resolution 2803, endorsing the Trump Gaza Peace Plan and authorizing the establishment of an International Stabilization Force (ISF) in Gaza.
- The resolution passed with 13 votes in favor and none against, although China and Russia abstained.
- Trump Gaza Plan announced in September 2025, aims to transform Gaza from a conflict zone to a peaceful region. It outlines a phased approach:
- Phase 1: Ceasefire, hostages’ release, and partial Israeli troop withdrawal.
- Subsequent Phases: Demilitarization, transitional governance, and reconstruction, with the goal of creating a “deradicalized, terror-free zone.”
- BoP & International Stabilization Force (ISF): A Board of Peace (BoP), chaired by President Trump, will oversee Gaza’s transition, reconstruction, and governance reforms until December 2027, after which control will transfer to a reformed Palestinian Authority.
- The BoP is authorized to establish the International Stabilization Force (ISF), responsible for securing Gaza’s borders, supporting demilitarization, protecting civilians, and facilitating humanitarian aid.
Leadership Group for Industry Transition:

The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change addressed the Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT) Industry Leaders’ Roundtable, during UNFCCC CoP30 at Belém, Brazil.
- It was jointly launched by the governments of Sweden and India at the UN Climate Action Summit in September 2019.
- It is supported by the World Economic Forum.
- It was the first global high level initiative aimed at reaching net zero emissions from heavy industry.
- It gathers countries and companies that are committed to reaching net-zero carbon emissions from industry by 2050.
- LeadIT fosters public and private partnerships to enable the necessary policy environment, finance flows, and exchange of best practice for a just and inclusive industry transition.
- LeadIT 2.0 was initiated for the period 2024-26, at COP-28 in Dubai which focus on;
- Inclusive & Just Industry Transition
- Co-development & transfer of low-carbon technology
- Financial support to emerging economies for Industry Transition
- LeadIT’s three-year Mission Statement, adopted at the annual LeadIT Summit at COP28.
- Secretariat: It is hosted by the Stockholm Environment Institute.
- Member countries: 18 countries and 27 companies.
Tetrachloroethylene:
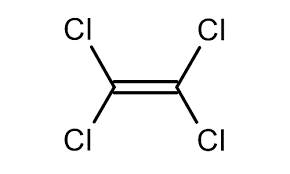
Researchers have identified Tetrachloroethylene commonly used in dry cleaning and household items that could lead to increased risk of liver diseases.
- It appears as a clear colorless volatile liquid having an ether-like odor.
- It is noncombustible and insoluble in water.
- Other names for tetrachloroethylene include perchloroethylene, PCE, perc, tetrachloroethene, and perchlor
- It breaks down very slowly in the air and so it can be transported long distances in the air.
- It evaporates quickly from water into air. It is generally slow to break down in water.
- It is generally slow to break down in soil.
- It can also seep into soil and groundwater through factory waste or improper disposal, making drinking water another potential source of exposure.
- Exposure to very high concentrations of tetrachloroethylene can cause dizziness headaches, sleepiness, incoordination confusion, nausea, unconsciousness, and even death.
- It is used to remove grease in industrial and household settings.
- It is widely used for dry cleaning of fabrics
- It is also used to make other chemicals and is used in some consumer products.
Viscose Staple Fibre:

The Central Government has revoked the Quality Control Order (QCO) requirement for Viscose Staple Fibre (VSF) with immediate effect.
- It is a natural and biodegradable fiber which has characteristics that are similar to cotton.
- It is produced by regenerating natural materials, such as cotton linter or wood pulp.
- It is made by processing cellulose xanthate, (main constituent of plant cell walls) which is extracted from wood and plant fibres into a viscous liquid.
- It is then subjected to a series of chemical processes to make a fibre.
- It is used as a substitute for cotton or polyester due to its favorable properties, such as good breathability, high moisture absorbency, and comfort.
- It is a versatile fibre which blends very well with other fibres.
- It has excellent colour retention capacity and is relatively light.
- Chemically, viscose resembles cotton, but it can also take on many different qualities depending on its manufacture.
- It is a highly versatile material that is widely adopted in the fashion & apparel industry.
- It is widely used for home textiles, dress materials, knitted wear and non-woven applications.
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012:

The Supreme Court issued notice in a case where a woman is accused of ‘penetrative sexual assault’ on a minor boy under Section 3 of the POCSO Act, 2012.
- The case has renewed debate on the Act’s gender neutrality, especially whether it covers female perpetrators of child sexual abuse.
- POCSO Act, 2012 was enacted by the Ministry of Women and Child Development to address the heinous crimes of sexual abuse and exploitation of children.
- It was amended in 2019 that increased punishments, including the death penalty for aggravated penetrative sexual assault of a child.
- The Act is gender-neutral and safeguards all children, irrespective of gender.
- It defines a child as any person below 18 years of age.
- The Act covers penetrative and non-penetrative assault, sexual harassment, and pornography. Offences are aggravated if committed by someone in trust or authority or against a mentally ill child, and child trafficking for sexual purposes is also punishable.
- Punishments range from 10 years to life imprisonment for penetrative sexual assault and 20 years to life for aggravated cases, with stricter terms if the child is under 16.
- Use, possession, attempt, and abetment of offences, including child pornography, are also punishable, with fines or imprisonment up to 7 years depending on severity and intent.
- The Act requires Special Courts to try offences. It ensures that the evidence of the child is recorded within 30 days, and the trial is completed within 1 year, wherever possible.
- The POCSO Act has an overriding effect over other laws if there is inconsistency.
- It applies only to child survivors and adult offenders, while cases of child-on-child offences or child-on-adult offences are governed by the Juvenile Justice Act, 2000.
Ginkgo-Toothed Beaked Whale:

A team of scientists has spotted the rare ginkgo-toothed beaked whales (Mesoplodon ginkgodens) for the first time in the wild along the coast of Baja California in Mexico.
- It is one of 24 species of beaked whales, which are the second most diverse group of cetaceans after dolphins.
- It resides in tropical and temperate waters throughout the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- It has a robust body and is less heavily scarred than other beaked whales.
- The flippers are small, pointed and narrow.
- It has a pair of distinguishing ginkgo-shaped teeth, one on each side of the lower jaw towards the middle of the beak.
- These beaked whales are the deepest-diving mammals on Earth.
- They spend most of their lives in the oceans, only coming to the surface for air for a few minutes at a time, usually far away from coastlines.
- They are very shy and easily frightened when approached by a boat.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Data Deficient
- CITES: Appendix II.
Trade Intelligence and Analytics Portal:

The Union Minister of Commerce and Industry launched the Trade Intelligence & Analytics (TIA) Portal in New Delhi.
- It is a one-stop trade intelligence and analytics platform that integrates multiple global and national databases.
- It is developed by the Department of Commerce.
- It serves as a centralized digital hub that consolidates diverse trade databases—both global and bilateral—into a single integrated system.
- It offers more than 270 interactive visualisations across over 28 dashboards.
- It provides real-time, interactive insights on India and global trade, commodities and sectoral analytics and market intelligence.
- It also includes automated trade reports and tracking of trade trends for the production-linked incentive (PLI) sectors and critical minerals.
- It also provides tools to compare and contrast macroeconomic, trade and investment indicators across countries.
- It incorporates trade indices such as:
- It assesses alignment between India’s export profile and partner countries’ import needs.
- It highlights products where India holds a competitive edge.
- It measures the strength of bilateral trade relationships relative to global flows.
- Its new and more exhaustive capabilities of the TIA Portal significantly improve accessibility and usability of trade data at one place.
Towards Long-Term Clean-Air Strategy:

The Supreme Court India told the Centre that enforcing a perennial Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) across the year is not practical for the National Capital Region (NCR) air pollution and stressed the need for a long-term pollution strategy.
- At the same time, China’s offer to sahare its urban pollution control experience has renewed the discussion on lessons India could adopt from international best practices.
- GRAP offers a structured, graded system of interventions when Air Quality Index (AQI) breaches specific thresholds. This helps authorities react quickly when pollution spikes.
- Restrictions on construction, traffic, truck entry, and industrial activity temporarily lower particulate emissions during severe pollution episodes.
- By reducing physical classes, outdoor work, and vehicle movement during hazardous AQI levels, GRAP offers temporary relief to vulnerable groups.
- GRAP is reactive and episodic; it only activates after pollution crosses set limits, not before.
- It does not comprehensively prevent long-term sources like stubble burning, vehicular growth, or construction dust.
- Frequent bans on construction, restrictions on transport, and shutdowns disproportionately affect daily-wage earners, migrant labourers and small businesses, making perennial enforcement impractical.
- Pollution arriving from Punjab-Haryana stubble burning, dust storms, and neighbouring industrial belts cannot be solved by Delhi-centric restrictions.
- Once GRAP restrictions are lifted, pollution levels tend to rebound quickly because systemic reforms in transport, waste, agriculture, and industry remain incomplete.
UNESCO’s Neurotechnology Ethics Framework:
UNESCO issued the first global normative framework on the ethics of neurotechnology, aiming to balance innovation with human rights by protecting the brain and neural data from misuse.The move comes as neurotech rapidly expands, offering major medical benefits but also raising concerns about privacy, autonomy, and manipulation. Neurotechnology refers to devices and procedures that access, assess, and act on neural systems, especially the human brain. It works by recording brain signals or stimulating specific brain regions to improve function, restore abilities, or enable brain–machine communication. Neurotechnology is used in medicine, assistive devices, research, wellness tech, and emerging commercial applications.Neurotechnology involves tools such as EEG (Electroencephalography), and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and other techniques that allow scientists and doctors to visualize brain activity in real-time, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like tumors, strokes, or epilepsy. It uses electrical or magnetic methods such as DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) and TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation) to activate specific brain regions, helping treat conditions like Parkinson’s disease by delivering targeted electrical impulses. Neuromodulation alters nerve activity by delivering targeted electrical, electromagnetic, or chemical stimulation to the nervous system, helping treat neurological and psychiatric disorders by correcting abnormal neural circuits.Neurofeedbac is Training the brain by giving real-time feedback on its electrical activity.
108th Birth Anniversary of Indira Gandhi:
India paid tributes to former Prime Minister late Indira Gandhi at Shakti Sthal, her memorial site in New Delhi on the occasion of her 108th birth anniversary. Born on 19th November 1917 in Allahabad to Jawaharlal Nehru and Kamala Nehru, Indira Gandhi became India’s first and only woman Prime Minister, serving from 1966–1977 and again from 1980 -1984. Role in the Freedom Struggle: In her childhood, she founded the ‘Bal Charkha Sangh’ and in 1930, the ‘Vanar Sena’ of children to help the Congress party during the Non-Cooperation Movement.She was imprisoned during the Quit India Movement in 1942.Indira Gandhi nationalised 14 major banks to expand credit access, support rural development and align banking with social welfare goals.During Fourth Five-Year Plan (1969–1974), she promoted High Yielding Variety seeds, fertiliser and irrigation subsidies aimed at boosting foodgrain production and helping India achieve food self-sufficiency.Led India’s decisive intervention supporting Mukti Bahini, resulting in the creation of Bangladesh and showcasing India’s geopolitical strength. Indira Gandhi’s tenure saw the imposition of National Emergency citing “internal disturbances,” during which civil liberties were suspended and the press was censored.
The Meerut Bugle:
The Meerut bugle, traditionally used in India’s military parades, ceremonies, and regimental bands, has received a Geographical Indication (GI) tag.The Meerut bugle is a brass wind instrument used in military drills, parades, ceremonies, and signals across the Army, paramilitary forces, and police units in India.It is known for its commanding sound and cultural association with Indian military tradition. Meerut’s bugle-making tradition dates back to the late 19th century, during the British era, when the instrument became integral to battlefield communication. Over time, the craft evolved into a specialised local industry, making Meerut one of India’s main centres for handmade bugles.A Geographical Indication (GI) tag is a legal certification identifying goods that originate from a specific region and possess qualities, characteristics, or reputation attributable to that place.
India’s First Tesla Centre to Open in Gurugram:
India is set to mark a new chapter in its electric mobility journey with the launch of its first-ever Tesla Centre on November 26, 2025, at Orchid Business Park, Gurugram. This major development comes just months after the global EV pioneer officially debuted in the Indian market with its Model Y variants and follows the opening of Tesla Experience Centres in Mumbai and New Delhi’s Aerocity. With this launch, India becomes the 50th global market for Tesla, underlining the company’s cautious but strategic approach to entering one of the world’s most promising automotive frontiers
HDFC Bank Reclaims Top Spot as India’s Most Valuable Brand in 2025:
HDFC Bank has once again claimed the title of India’s most valuable brand, overtaking Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), according to the 2025 Kantar BrandZ Most Valuable Indian Brands Report. With a brand value of $44.9 billion, HDFC Bank tops a list that reflects both long-term equity and fresh brand momentum in India’s rapidly evolving consumer landscape. This report also crowns Zomato as the fastest-rising brand for the second consecutive year, as it continues to expand beyond its food delivery roots.




