Today’s Current Affairs: 18th July 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
PM SHRI (PM Schools for Rising India) Scheme : Oppose

After Punjab, West Bengal, and Delhi refused participation in the PM-SHRI scheme, the Education Ministry has stopped funds to the three states under the Centre’s flagship Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).
- PM SHRI Scheme is a centrally sponsored scheme by the Government of India.
- Its objective is to establish over 14,500 PM SHRI Schools, overseen by the Central Government, State/UT Governments, local bodies, as well as Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS) and Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti (NVS).
- These schools aim to create an inclusive and welcoming atmosphere for every student, ensuring their well-being and providing a secure and enriching learning environment.
- The goal is to offer a diverse range of learning experiences and ensure access to good physical infrastructure and appropriate resources for all students.
- The overarching purpose of PM SHRI School is to nurture students in a manner that transforms them into engaged, productive and contributing citizens.
- This aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy 2020, striving to build a society characterized by equity, inclusivity and pluralism.
- These schools will not only focus on enhancing cognitive development but also creating holistic and well-rounded individuals equipped with key 21st-century skills.
- The pedagogy adopted in these schools will be more experiential, holistic, integrated, play/toy-based (particularly in the foundational years), inquiry-driven, discovery-oriented, learner-centred, discussion-based, flexible, and enjoyable.
- The schools will be upgraded with labs, libraries, and art rooms.
- They will be developed as green schools with water conservation, waste recycling, energy-efficient infrastructure, and integration of the organic lifestyle as part of the curriculum.
- The focus will be on the learning outcomes of every child in every grade.
- Assessment at all levels will be based on conceptual understanding and application of knowledge to real-life situations and will be competency-based.
- A School Quality Assessment Framework (SQAF) is being developed, specifying the key performance indicators to measure outcomes. A quality evaluation of these schools at regular intervals will be undertaken to ensure the desired standards.
- The duration of the scheme is from 2022-23 to 2026-27, after which it shall be the responsibility of the States/UTs to continue to maintain the benchmarks achieved by these schools.
Jerdon’s Courser : Spotted

Jerdon’s Courser, a critically endangered species, has not been visually spotted in over a decade.
- Jerdon’s Courser is a nocturnal cursorial (adapted for walking and running) bird endemic to the Eastern Ghats of India.
- Scientific Name: Rhinoptilus bitorquatus
- It was considered to be extinct from the beginning of the 20th century until its rediscovery in 1986.
- It inhabits open patches within scrub forests.
- It is found only in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
Late Blight Disease:

The Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI) recently issued an advisory for potato farmers across the country, warning of a high risk of late blight disease in the crop due to changes in weather conditions.
- Late Blight Disease is one of the most serious fungal diseases that can affect tomatoes and potatoes
- It is spread from infected transplants, volunteer potato or tomato plants, and certain weeds botanically related to tomatoes.
- Spores of this fungus can be airborne and travel great distances in storms. Rain deposits spores on plants, causing infection.
- Late blight is favored by cool, wet weather and will cycle repeatedly if weather conditions are favorable
- When plants have become infected, lesions (round or irregularly shaped areas that range in color from dark green to purplish black and resemble frost injury) appear on the leaves, petioles and stems.
- A whitish growth of spore-producing structures may appear at the margin of the lesions on the under-leaf surfaces.
- Potato tubers develop rot up to 15 mm (0.6 inch) deep.
- Secondary fungi and bacteria(particularly Erwinia species) often invade potato tubers and produce rotting that results in great losses during storage, transit, and marketing.
- The disease can be managed with a timely application of fungicide, though epidemics can occur rapidly once crops are infected.
ASMITA Project:

The Ministry of Education and the University Grants Commission (UGC) recently unveiled the ASMITA Project, aimed at bolstering the availability of educational resources in Indian languages.
- ASMITA (Augmenting Study Materials in Indian Languages through Translation and Academic Writing) is an initiative to develop 22,000 books in Indian languages in the next five years.
- It is a collaborative effort of the UGC and the Bharatiya Bhasha Samiti, a high-powered committee under the Ministry of Education.
- The primary objective of this initiative is to promote and integrate Indian languages more deeply into the education system, thereby enriching the learning experience and making it more inclusive.
- This project is seen as part of a broader strategy to enhance the accessibility and quality of educational materials across various Indian languages.
- Thirteen nodal universities have been identified to lead the project, along with member universities from various regions.
- The UGC has also created a standard operating procedure (SOP) for the book-writing process in each assigned language.
- The SOP includes the identification of nodal officers and authors, allocation of title, subject, and programme, writing and editing, submission of the manuscript, review and plagiarism check, finalisation, designing, proofreading and e-publication.
Bhojshala Complex:

The existing structure at the Bhojshala complex constructed using remains of a temple that existed earlier at the site, said the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) in its scientific survey report.
- Bhojshala Complex is located in the Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh.
- It was built by Raja Bhoja (1000-1055 A.D.) in 1034 AD, who was the greatest monarch of the Paramara dynasty.
- It served as a university and many students used to come here to learn music, Sanskrit, astronomy, yoga, Ayurveda and philosophy.
- It was for the first time attacked by Alauddin Khilji.
- In 1514 AD, Mehmudshah Khilji IIattacked this complex and tried to convert it into a dargah. He encroached on land outside Saraswati Temple and built ‘Kamal Moulana’ Makbara.
- In the rocks of this complex, two hymns written in the Prakrit language of the Karmavatar or crocodile incarnation of Vishnu are engraved.
- Two Sarpabandha pillar inscriptions, one containing the Sanskrit alphabet and the main endings of nouns and verbs and the other containing the individual declensions of the ten tenses and moods of Sanskrit grammar.
- In 1951, the complex was declared as a monument of national importance under the Ancient and Historical Monument and Archaeological Sites and Remains (Declaration of National Importance) Act, 1951.
- It is currently protected by ASI under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
World Bank Group Guarantee Platform:

The World Bank Group (WBG) guarantee platform was opened for business.
- World Bank Group Guarantee Platform is housed at the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) and brings together products and experts from the World Bank, International Finance Corporation (IFC), and MIGA for simplicity, efficiency and speed.
- It aims to boost WBG annual guarantee issuance to $20 billion by 2030.
- WBG Guarantees will serve as a one-stop shop for all WBG guarantee businesses, providing the best guarantee solutions for clients to meet project needs and development priorities.
- WBG clients can now choose from a simplified market-friendly menu of guarantee options.
- The platform will provide three types of coverages:
- Credit guarantees for loans to the public or private sector;
- Trade finance guarantees for trade finance projects involving public entities;
- Political risk insurance against non-commercial risks for private sector projects or public-private partnerships.
Chandipura Virus Infection:
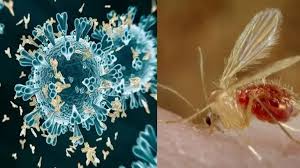
The Gujarat government said that six children have died of suspected Chandipura virus (CHPV) infection in the state since July 10.
- Chandipura Virus Infection is a virus of the Rhabdoviridae family, which also includes other members such as the lyssavirus that causes rabies.
- Several species of sandflies like Phlebotomine sandflies and Phlebotomus papatasi, and some mosquito species such as Aedes aegypti(which is also the vector for dengue) are considered vectors of CHPV.
- The virus resides in the salivary gland of these insects, and can be transmitted to humans or other vertebrates like domestic animals through bites.
- The infection caused by the virus can then reach the central nervous system which can lead to encephalitis — inflammation of the active tissues of the brain.
- Disease progression can be as rapid as a patient reporting high fever in the morning, and their kidneys or liver being affected by the evening.
- The CHPV infection presents initially with flu-like symptoms such as acute onset of fever, body ache and headache.
- It may then progress to altered sensorium or seizures and encephalitis.
- Respiratory distress, bleeding tendencies, or anaemia.
- The infection often progresses rapidly after encephalitis, which may then lead to mortality within 24-48 hours of hospitalization.
- This infection has largely remained limited to children below 15 years.
- The infection can only be symptomatically managed as currently there is no specific antiretroviral therapy or vaccine available for treatment.
What Are 15-minute Neighborhoods?

The 15-minute neighbourhood concept is an urban planning approach where all essential services and amenities—such as groceries, schools, healthcare, and recreational facilities—are accessible within a 15-minute walk or bike ride from residents’ homes.
- This model aims to reduce car reliance, improve environmental sustainability, and enhance community well-being by promoting walkability and local accessibility.
- The 15-minute neighborhood concept can help address Bengaluru’s urban challenges through:
- By promoting walking and cycling for short trips, it decreases the reliance on cars, alleviating road congestion.
- Less vehicle use leads to lower emissions, enhancing air quality.
- Close proximity to essential services fosters stronger social connections and a sense of community.
- Better infrastructure for non-motorized transport reduces accidents and improves public safety.
- Accessible services within walking distance benefit women, children, the elderly, and economically weaker sections.
- Encouraging active transport like walking and cycling boosts physical health and well-being.
Retreat Of The Foreign Ministers Of The Bay Of BIMSTEC:

The 2nd Retreat of the Foreign Ministers of the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) was held in New Delhi, taking on added significance amid escalating tensions and major developments in Myanmar.
- External Affairs Minister of India emphasised the need for BIMSTEC to address regional challenges internally, especially in light of recent setbacks faced by Myanmar’s military junta against various Ethnic Armed Organisations (EAOs).
Highlights of the BIMSTEC Foreign Ministers’ Retreat:
- The meeting underscored the urgency of addressing long-standing goals like capacity building and economic cooperation due to current global and regional challenges.
- Discussions centred on the impact of the Myanmar crisis on regional stability and developmental projects.
- The instability in Myanmar is a major concern for BIMSTEC as it has affected various developmental and connectivity projects aimed at strengthening ties among Nepal, Bhutan, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand.
- Conversations included the potential for humanitarian aid, though India’s current assistance has been limited to displaced populations and military personnel who have taken refuge in Mizoram.
- India maintains a cautious stance, particularly since Ethnic Armed Organizations (EAOs) have gained control over crucial trade routes and territories near international borders.
- India continues to cooperate on countering transnational crimes such as cybercrime, narcotics, and illegal arms.
World Day For International Justice 2024:

Every year on 17th July, the World Day for International Justice is observed to promote international criminal justice and honour the fight against impunity for serious crimes affecting the global community.
- Originated on 17th July 1998, with the adoption of the Rome Statute, establishing the International Criminal Court (ICC).
- The ICC is not part of the United Nations system and has a separate agreement governing its relationship with the UN.
- Currently, 124 countries are States Parties to the Rome Statute of the ICC, India is not a party to the Rome Statute/ICC.
- The ICC is the first permanent international court and has jurisdiction over crimes under international law including genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity and crimes of aggression committed on or after 1st July 2002.
- The Rome Statute marks a significant step in the fight against impunity for grave crimes, ensuring accountability for perpetrators.
- The day raises awareness about international justice mechanisms and their role in addressing impunity, and promoting global peace and security.




