Today Current Affairs: 26th March 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
187th Raising Day Of The Assam Rifles:

The 187th Raising Day of the Assam Rifles has been celebrated in Shillong.
- Assam Rifles is the watchdog of the North East and the oldest paramilitary force in the country.
- Assam Rifles is a Central Paramilitary Force under the Central Armed Police Forces.
- It came into being in 1835, as a militia called the ‘Cachar Levy’, to primarily protect British Tea estates and their settlements against tribal raids.
- It significantly contributed to the opening of Assam region to administration and commerce and over time it came to be known as the “right arm of the civil and left arm of the military”.
- Assam Rifles has two battalions stationed in Jammu and Kashmir and one National Disaster Relief Force battalion, which is playing its active role in case of natural calamities.
- Although India has been contributing to the UN peacekeeping for many years, the addition of the Riflewomen Team of the Assam Rifles adds another social and human dimension to our commitment to the community of nations.
Tax On Lotteries:

The Supreme Court has held that a lottery conducted by Government of India, states or authorised by a state or conducted by private entities is an activity falling within the nomenclature of ‘betting and gambling’.
- And hence, the State Legislature has the competence to tax lottery scheme which is gambling being conducted not only by the Government of India or the Government of any State or by any other agency or instrumentality of a particular State but also by a private entity within the State as gambling.
- Thus, the apex court allowed the appeals filed by Karnataka and Kerala governments and set aside the orders of Karnataka and Kerala High Courts which held that they lacked the legislative competence to levy tax on the lotteries.
- The tax sought to be imposed by the State Legislatures of Karnataka and Kerala by way of the impugned Acts, is traceable to the power conferred on the State Legislatures under Entry 62 of List II.
- The Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India defines and specifies allocation of powers and functions between Union & States. It contains three lists; i.e. 1) Union List, 2) State List and 3) Concurrent List.
- Originally there was 97 subjects in union list but now it is 100 subjects in union list.
Article 371 Of The Constitution:

Arunachal Pradesh Chief Minister Pema Khandu is planning to lead an all-party delegation to New Delhi soon to seek amendment of Article 371 (H) which has special provisions pertaining to the state in order to place it at par with special provisions meant for Nagaland enshrined in Article 371 (A) of the constitution.
- Other demands: The special provision with respect to the state should be further strengthened by amending Article 371(H) by inserting provisions for protection of religious or social practices of the tribes of the state, customary law and procedure of the state’s tribes, administration of civil and criminal justice involving decisions according to customary laws of the tribes and including provisos to protect local ownership and transfer of land and its resources.
- This is necessary to protect tribal rights and customary laws.
- Article 371 of the Constitution includes “special provisions” for 11 states, including six states of the Northeast.
- Articles 370 and 371 were part of the Constitution at the time of its commencement on January 26, 1950; Articles 371A through 371J were incorporated subsequently.
Article 355 Of The Constitution:

Citing post-poll violence in Birbhum district, West Bengal, many political leaders have urged the president to invoke Article 355 of the Constitution to ensure that the state government functions in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution.
- The petitioner has asked for imposition of Article 355 on account of breakdown of constitutional machinery.
- Article 355 refers to the provision in the Constitution that states that “It shall be the duty of the Union to protect every State against external aggression and internal disturbance and to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution”.
- The Article 355 is part of emergency provisions contained in Part XVIII of the Constitution of India, from Article 352 to 360.
- It is this duty in the performance of which the centre takes over the government of a state under Article 356 in case of failure or breakdown of constitutional machinery in a state.
- This is popularly known as ‘President’s Rule’.
- The president’s rule can be proclaimed under Article 356 on two grounds:
- Article 356 empowers the President to issue a proclamation if he is satisfied that a situation has arisen in which the government of a state cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of the constitution.
- Article 365 says that whenever a state fails to comply with or to give effect to any direction from the centre, it will be lawful for the President to hold that a situation has arisen in which the government of the state cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of the constitution.
- A proclamation imposing the president’s rule must be approved by both the houses of parliament within two months from the date of its issue.
- The President acquires the following extraordinary powers when the President’s rule is imposed in a state:
- He can take up the functions of the state government and powers vested in the governor or any other executive authority in the state.
- He can declare that the powers of the state legislature are to be exercised by the parliament.
- He can take all other necessary steps including the suspension of the constitutional provisions relating to any body or authority in the state.
- The 38th Amendment act of 1975 made the satisfaction of the President in invoking Article 356 final and conclusive which would not be challenged in any court on any ground.
- But, this provision was subsequently deleted by the 44th Amendment Act of 1978 implying that the satisfaction of the President is not beyond judicial review.
Lead Poisoning:
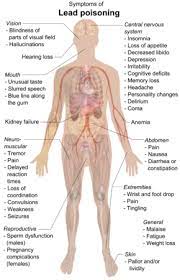
High levels of lead were found in the blood of thousands of children living around the Kabwe mine in Zambia.
- Lead poisoning or chronic intoxication is caused by the absorption of Lead in the system and is characterised especially by fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, anaemia, a dark line along the gums, and muscle paralysis or weakness of limbs.
- Children younger than 6 years are especially vulnerable to lead poisoning, which can severely affect mental and physical development.
- At very high levels, lead poisoning can be fatal.
- Lead exposure also causes anaemia, hypertension, renal impairment, immunotoxicity and toxicity to the reproductive organs.
- More than three quarters of global lead consumption is for the manufacture of lead-acid batteries for motor vehicles.
- People can become exposed to lead through occupational and environmental sources.
- This mainly results from:
- Inhalation of lead particles generated by burning materials containing lead, for example during smelting, recycling, stripping leaded paint and using leaded aviation fuel, and
- Ingestion of lead-contaminated dust, water (from leaded pipes) and food (from lead-glazed or lead-soldered containers).
Lead:
- Lead is a naturally occurring toxic metal found in the Earth’s crust.
- Lead in the body is distributed to the brain, liver, kidney and bones.
- It is stored in the teeth and bones, where it accumulates over time.
- Human exposure is usually assessed through the measurement of lead in blood.
- Lead in bone is released into blood during pregnancy and becomes a source of exposure to the developing foetus.
- There is no level of exposure to lead that is known to be without harmful effects.
- Lead exposure is preventable.
- According to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), in 2019, lead exposure accounted for 900 000 deaths and 21.7 million years of healthy life lost (Disability-Adjusted Life Years, or DALYs) worldwide due to long-term effects on health.
- The highest burden was in low- and middle-income countries.
GSAT-7B : Dedicated Satellite For The Indian Army

The Ministry of Defense has given the Acceptance of Necessity for the GSAT-7B satellite. This satellite will be a dedicated satellite for the Indian Army.
- The satellite would help the Indian Army enhance its surveillance in border areas.
- Currently, India has only two dedicated military satellites — the GSAT-7 (Rukmini) and GSAT-7A (Angry Bird) — used by the Indian Navy and Air Force respectively.
- Till date, the Indian Army has been dependent on GSAT-7A and other satellites, but with this new state-of-the-art technology, the Army will have new eyes in the sky.
- The military-grade satellite will be a force multiplier in providing fail-safe communication support.
- The GSAT 7B will primarily fulfil the communication needs of the Army.
- While many features of this satellite are still a closely guarded secret, it is expected that the state of the art, multi-band, military-grade satellite shall be a shot in the arm for the communication and surveillance needs of the Army.
- Such a satellite would be of utmost importance for the Indian Army as it currently faces a double threat of China and Pakistan lurking at its borders.
- The use of such a satellite would also mean that the Army’s vast array of radio communication equipment could come under a single platform.
Sujalam 2.0 Grey Water Recycling Project:

On the World Water Day (22nd March), the Ministry of Jal Shakti launched a countrywide project to reuse grey water, or run-offs from kitchens, bathing and laundry.
- The campaign would focus on the creation of institutional level greywater management assets in Panchayat Ghar, healthcare facilities, schools, Anganwadi Centres (AWCs), community centres and other government institutions.
- Creation of individual and community greywater management assets will be encouraged.
- With active participation from all States and local communities’ great success was achieved under the Sujlam 1.0 campaign which was started in August 2021.
- More than 1 million soak pits were built at household and community level across the country.
- The funds to execute the activities for greywater management will be sourced from Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen Phase-II or through 15th Finance Commission tied-grants or MGNREGS or through convergence of all.
- Grey water is defined as wastewater that is produced from household processes (e.g. washing dishes, laundry and bathing).
- Grey water can contain harmful bacteria and even faecal matter that contaminates soil and groundwater.
- So far, India does not have a focused policy framework for management and usage of grey water in urban and rural areas.
- However, some guidelines for treatment of wastewater do exist.
- For example, the Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organisation (CPHEEO) has specified permitted discharge standards for treated water; use of treated wastewater in agriculture and horticulture (MoHUA, 2012).
- The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB, 2000) directs that treated wastewater can be used as a source of artificial ground water recharge once it meets standards and is compatible with existing groundwater.
H2Ooooh! – Water Wise Program For The Children Of India:

On the occasion of World Water Day (22nd March), National Mission for Clean Ganga, UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) and other partners released three animation films under its initiative “H2Ooooh! – Water Wise program for the Children of India”.
- The films are based on the stories submitted by school students focusing on protection and conservation of Indian Rivers.
- It was launched by UNESCO in July 2021, jointly with the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) and others.
- H2Ooooh! is a unique program crafted for Indian school students from Standard 1-8.
- It aims to increase awareness about the limited availability of water, its sustainable use, its conservation, its exploitation and much more.
- It seeks to enable the students to share their own experiences and proposals for the protection of the environment.
- Divided in three phases, the project aims to spur creativity and raise awareness on water conservation and its sustainable use for students between the age of 6-14 years, by providing training and encouraging them to submit paintings and story ideas for the animated short films.
- Since its launch, nearly 31000 students from 53 schools in 18 Indian states have been engaged actively, with the support from over 400 teachers.
Reserve Bank Innovation Hub: Bengaluru

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor inaugurated the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH) in Bengaluru.
- It has been set up as a Section 8 company under the Companies Act, 2013 with an initial capital contribution of Rs. 100 crore.
- It is is a wholly owned subsidiary of the RBI.
- RBIH aims to create an ecosystem that focuses on promoting access to financial services and products for the low-income population in the country.
- This is in line with the objective behind establishment of RBIH i.e., to bring world-class innovation to the financial sector in India, coupled with the underlying theme of financial inclusion.
- The Hub is expected to build an ecosystem for development of prototypes, patents and proofs of concept and promote cross-thinking, spanning regulatory domains and national boundaries.
- It had plans to identify and mentor start-ups having maximum potential.
- It is also expected to collaborate with various government Ministries, Departments and academia to identify problem statements in different domains and explore potential solutions.
- RBI Innovation hub hosted Swanari TechSprint to create sustainable solutions for women-owned enterprises.
- TechSprint is aimed at advancing digital financial inclusion for women in India.




