Today Current Affairs: 29th January 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Elephant Corridor Case:

The Supreme Court has appointed conservationist Nandita Hazarika as Member of a Technical Committee constituted by it on October 14 last year to hear complaints by landowners against the action taken by the Nilgris Collector, which included the sealing of their buildings and allegations about the “arbitrary variance in the acreage of the elephant corridor.”
- On October 14, the court upheld the Tamil Nadu government’s authority to notify an ‘elephant corridor’ and protect the migratory path of the animals through the Nilgiri biosphere reserve.
- The court had said it was the State’s duty to protect a “keystone species” such as elephants, immensely important to the environment.
- The corridor is situated in the ecologically fragile Sigur plateau, which connects the Western and the Eastern Ghats and sustains elephant populations and their genetic diversity.
- It has the Nilgiri Hills on its southwestern side and the Moyar River Valley on its north-eastern side. The elephants cross the plateau in search of food and water.
Elephant Corridors:
- Elephant corridors are narrow strips of land that connect two large habitats of elephants.
- Elephant corridors are crucial to reduce animal fatalities due to accidents and other reasons.
- So fragmentation of forests makes it all the more important to preserve migratory corridors.
The movement of elephants is essential to ensure that their populations are genetically viable. It also helps to regenerate forests on which other species, including tigers, depend.
- Nearly 40% of elephant reserves are vulnerable, as they are not within protected parks and sanctuaries. Also, the migration corridors have no specific legal protection.
- Forests that have turned into farms and unchecked tourism are blocking animals’ paths. Animals are thus forced to seek alternative routes resulting in increased elephant-human conflict.
- Weak regulation of ecotourism is severely impacting important habitats. It particularly affects animals that have large home ranges, like elephants.
‘Gaj Yatra’, a nationwide campaign to protect elephants, was launched on the occasion of World Elephant Day in 2017.
- The campaign is planned to cover 12 elephant range states.
- The campaign aims to create awareness about elephant corridors to encourage free movement in their habitat.
India Justice Report 2020:
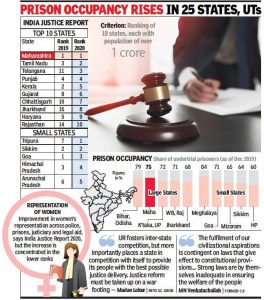
The India Justice Report (2020) prepared by the Tata Trusts in collaboration with the Centre for Social Justice, Common Cause, DAKSH, Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy and the Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative has been released recently.
- The Report assesses the capacity of various states to deliver justice.
About the Report:
- The report analysed expenditure, vacancies, representation of women, human resources, infrastructure, workload, diversity across 18 large and medium-sized states with a population of over 1 crore and 7 small states.
Overall Ranking:
- The overall ranking is a result of a state’s ranking across the four pillars of justice delivery system – Judiciary, Police, Prisons and Legal aid.
- Maharashtra was ranked topmost among 18 states for the second time in a row, followed by Tamil Nadu and Telangana. Uttar Pradesh remains last.
- Amongst the smaller states, Goa remained at the top and Arunachal Pradesh at the bottom.
Women Ratio in Police Force:
- Bihar leads the list of 25 states for employing most women in its police force which is 25.3%.
- It is the only state to have more than 20% women in the police force. However, women account for only 6.1% in the officer category.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest percentage of women police officers (24.8%), followed by Mizoram (20.1%).
Women Ratio in Judiciary:
- Overall, only 29% judges in High Courts across the country are women, but no state except Sikkim has over 20% women judges.
- Four states – Bihar, Uttarakhand, Tripura and Meghalaya have no woman judges in high courts.
Social Justice:
- Karnataka is the only state to meet its quotas for SC, ST and OBC in both officer cadre and constabulary.
- Chhattisgarh being the only other state that meets the diversity requirements for constabulary.
In the last 25 years, only 1.5 crore people have received legal aid with the Centre spending Rs. 1.05 per capita in 2019-20.
High Proportion of Undertrials:
- Two-thirds of all prisoners are undertrials awaiting a conviction.
- A person who is being held in custody awaiting trial for a crime.
Short Squeeze:
There are dozens of ways to pick stocks, but few have been as unconventional — or as successful — as the coordinated short-squeeze being deployed by Reddit’s army of day traders. Now, Wall Street is scanning the matter.
- A short squeeze is a term used by market participants to refer to a phenomenon where short-sellers in a stock who have placed their bets on a stock’s fall, rush to hedge their positions or buy the stock in the event of an adverse price movement, in order to cover their losses.
- This leads to a sharp rise in demand for the share and a huge rally in share prices.
- In order to cover his loss, the trader who was initially short on the stock starts buying the stock, which leads to a sharp rise in the share price of the stock.
- This phenomenon, where the short seller is buying the stock to cover her loss, is referred to as a short squeeze in market parlance.
- It leads to a dramatic rise in share price, far beyond its fundamentals.
Complaints have been filed with the Mumbai Commissioner of Police demanding action against Republic TV Editor-in-Chief Arnab Goswami under the Official Secrets Act:

Maharashtra Congress demanded for the arrest of Republic TV’s editor-in-chief Arnab Goswami by registering cases for sedition for leak of sensitive information related to national security through WhatsApp chat.
About the Official Secrets Act:
- Originally enacted during the time of Lord Curzon, Viceroy of India from 1899 to 1905.
- One of the main purposes of the Act was to muzzle the voice of nationalist publications.
- The Act replaced the earlier Act, and was extended to all matters of secrecy and confidentiality in governance in the country.
- It broadly deals with two aspects:
- Spying or espionage, covered under Section 3.
- Disclosure of other secret information of the government, under Section 5.
The Act does not say what a “secret” document is
- It is the government’s discretion to decide what falls under the ambit of a “secret” document.
Patharughat:

Twenty-five years before the Jallianwallah Bagh massacre, more than a hundred peasants fell to the bullets of the British on January 28, 1894 in Patharughat, a small village in Assam’s Darrang district.
- The unarmed peasants were protesting against the increase in land revenue levied by the colonial administration, when the military opened fire.
- On January 28, 1894, many local peasants gathered in a protest meeting at Patharughat (also known as Patharighat), condemning the increasing land tax levied by the British.
- As a result, a rebellion brewed in the hearts of the peasants against the British.
- After much discussion amongst themselves, it was decided that no taxes would be paid to the British, until a proper solution was found to the problem. They were even willing to revolt against the British for the cause.
- While the protest meeting was going on, Deputy Commissioner of Darrang district, JD Anderson, Mr Barrington, SP and Mr Remington, SDO, arrived at the venue along with full police force.
- On the orders of Barrington, the police opened fire on the gathering present there. hundreds of people were injured and around 140 of them were killed on spot.
- Every year on January 28, the government and local people pay respects to the martyrs of the incident (Krishak Swahid Diwas).
Lala Lajpat Rai:

The Prime Minister paid tribute to Lala Lajpat Rai on his Jayanti.
- Lala Lajpat Rai’s birth anniversary is celebrated on the 28th of January every year
- Lala Lajpat Rai was one of the greatest freedom fighters of India.
- He was also called ‘Punjab Kesari’ and ‘Lion of Punjab’.
- He studied law at the Government College, Lahore.
- Was influenced by Swami Dayananda Saraswati and joined the Arya Samaj in Lahore.
- He believed that the ideals in Hinduism combined with nationalism will lead to the establishment of a secular state.
- Along with Bipin Chandra Pal and Bal Gangadhar Tilak, he formed the Lal-Bal-Pal trio of extremist leaders.
- He was also involved with the Hindu Mahasabha.
- He fought against untouchability.
- Birth: He was born on 28th January, 1865 in a small village named Dhudike in Punjab’s Ferozepur district.
Contributions:
Political:
- He joined the Indian National Congress (INC) and participated in many political agitations in Punjab.
- For his political agitation, he was deported to Burma without trial in 1907 but returned after a few months because of lack of evidence.
- He was opposed to the partition of Bengal.
- He founded the Home Rule League of America in 1917 in New York. In the USA, he worked to get moral support for the Indian independence movement from the international community.
- He was also elected President of the All India Trade Union Congress.
- He supported the non-cooperation movement of Gandhi at the Nagpur session of the Congress in 1920.
- He protested against the Rowlatt Act and the Jallianwala Bagh massacre that followed.
- He was elected deputy leader of the Central Legislative Assembly in 1926.
- In 1928, he moved a resolution in the assembly refusing cooperation with the Simon Commission since the Commission had no Indian members.
Social:
- He founded the Hindu Relief movement in 1897 to provide help to the famine -stricken people and thus preventing them falling into the clutches of the missionaries.
- He founded the Servants of People Society in 1921.
Literary:
- His important literary works include Young India, England’s Debt to India, Evolution of Japan, India’s Will to Freedom, Message of the Bhagavad Gita, Political Future of India, Problem of National Education in India, The Depressed Glasses, and the travelogue ‘United States of America’.
Institutional:
- He founded several institutions and organizations such as Hisar Bar Council, Hisar Arya Samaj, Hisar Congress, National DAV Managing Committee.
- He was the editor of the Arya Gazette, which he had founded.
- He co-founded the Punjab National Bank in 1894.
Death:
- In 1928, he was leading a silent protest against the Simon Commission in Lahore when he was brutally lathi-charged by Superintendent of Police, James Scott. He died of injuries sustained a few weeks later.
Pakistan received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag for its Basmati rice under its Geographical Indications Act 2020:

Pakistan is fighting a case in the European Union (EU) against India’s move to get Basmati Rice as its product.
India-Pakistan on Basmati Rice:
- The issue of protecting Basmati rice as a product of Pakistan came to the forefront after India submitted an application to the European Union (EU) claiming sole ownership of the commodity in September 2019.
- India also claimed that the region producing basmati is a part of northern India, below the foothills of the Himalayas forming part of the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- The Indian claim to the EU was challenged in December 2019 and the main argument by Pakistan was that Basmati rice was a joint product of India and Pakistan.
- International laws require that before applying for registration of any product in the international market it has to be protected under the geographical indication laws of that country.
- Pakistan enacted the Geographical Indications (Registration and Protection) Act in March 2020, which gives it the right to oppose Indian application for registration of Basmati rice exclusive rights.
Significance of Pakistan’s GI tag for its Basmati:
- A GI tag would strengthen Pakistan’s case in the EU.
- Pakistan exported 5,00,000-7,00,000 tonnes of Basmati rice annually to different parts of the world out of which 2,00,000 tonnes to 2,50,000 tonnes is being shipped to EU countries.
Effect on India:
- Basmati rice was a joint heritage of India and Pakistan and Pakistan is as entitled to secure its Basmati rice trade as India.
- However, Pakistan securing the GI tag for its basmati rice would, in no way, affect India’s Basmati exports.
- Since Basmati rice fetches higher prices in the international markets, India had attempted to block Pakistan’s trade in the EU by declaring that its Basmati was the geographically original one.
GI tag for Basmati Rice in India:
- India is a producer of premium Basmati and it has been grown from time immemorial in the Indo-Gangetic Plains (IGP) area of India and 18 districts of Pakistan’s Punjab.
- It had been a tough battle for the country to protect Basmati’s name from the encroachment of various nations which all came out with their own versions of Basmati.
- Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) got GI tag for the region located in IGP below the foothills of the Himalayas, spread across seven states (Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Western Uttar Pradesh (26 districts) and Delhi) in May 2010.
Gold Schemes In India:

The government is planning to bring changes in the existing gold deposit and gold metal loan schemes to gradually stop investors from excessive investment in physical gold.
- Despite the government’s emphasis on gold monetisation over the last few years, including issuing gold bonds as part of its borrowing programmes, investment in physical gold and purchases of jewellery continues to outpace investment through financial channels.
- A number of amendments have been finalised in the existing revamped Gold Deposit Scheme, revamped Gold Metal Loan Scheme and India Gold Coin Scheme.
- The existing scheme will be made far from attractive from investment convenience and taxation aspects.
Gold Schemes:
Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS):
- GMS, which modified the then existing ‘Gold Deposit Scheme’ (GDS) and ‘Gold Metal Loan Scheme (GML), was launched in 2015 to mobilize gold held by households and institutions of the country and facilitate its use for productive purposes, and in the long run, to reduce country’s reliance on the import of gold.
Revamped Gold Deposit Scheme (R-GDS):
- Deposit limit: The minimum deposit at any one time shall be raw gold (bars, coins, jewellery excluding stones and other metals) equivalent to 30 grams of gold. There is no maximum limit for deposit under the scheme.
- Proposed Changes in the existing scheme: The minimum requirement of 30 grams could be reduced to 1 gram. Interest earnings and capital gains under the scheme will continue to be exempt from capital gains tax, wealth tax and income tax.
- Time period: The designated banks can accept gold deposits under the Short Term (1-3 years) Bank Deposit (STBD) as well as medium (5-7 years) and long (12-15 years) term government deposit schemes.
- Implementing agency: All scheduled commercial banks are allowed to implement this scheme and are also free to fix interest rates.
- Premature Withdrawal: Depositors can also make premature withdrawal of their deposits. It will be subject to a minimum lock-in period and penalty to be determined by individual banks.
Revamped Gold Metal Loan Scheme (GML):
- It is a mechanism under which a jewellery manufacturer borrows gold metal instead of rupees and settles the GML with the sale proceeds obtained.
- GML can be availed for 180 days in case of domestic jewellery manufacturers and for 270 days in case of exports.
- Amendments are also being planned in the GML scheme.
- Issue of Liquidity: According to the Scheme, the banks can lend or sell gold to jewellers or other banks that are part of the Scheme.
- However, a cash deposit can be given to anybody. But a gold deposit can only go to those looking specifically for gold.
- Thus, there is a chance of banks finding it difficult to match gold borrowers with gold depositors.
Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme:
- Aim: It seeks to encourage people to buy gold bonds instead of actual gold.
- Issuer: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues these bonds on behalf of the central government.
- Features: The gold bonds will be denominated in multiples of gram (s) of gold with a basic unit of one gram while the minimum investment limit is two grams. The maximum subscription is 500 grams per person per fiscal (April-March) and for joint holders, the limit will be applied on the first holder.
- The gold bonds will be sold only to resident Indian entities including individuals, Hindu undivided families, trusts, universities, and charitable institutions.
- The bond tenure is eight years with exit option beginning the fifth year onwards. They will also be tradable.
These bonds can also be used as collateral for loans.
The Gold Coin and Bullion Scheme:
- The government issues gold coins, which have the Ashok Chakra engraved on them
Kala Utsav 2020:

An annual function to promote arts in education, was organised by the Ministry of Education.
- Kala Utsav is an initiative of the Ministry of Education (MoE) to promote arts in education.
- This programme was initiated under Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), which has now been merged with other schemes under ‘Samagra Shiksha – an integrated scheme for school education’.
- Aim: Kala Utsav aims at nurturing and showcasing the artistic talent of school students at the secondary stage in the country.
- District/State/National Level Utsav is structured as an art festival that includes performances and display of exhibits.
- In the context of education of Arts (Music, Theatre, Dance, Visual Arts and Crafts), the initiative is guided by the recommendations of the National Curriculum Framework 2005 (NCF-2005).
- Importance: Introduction of Indigenous Toys and Games segment in Kala Utsav 2020 supported the ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative.
- It is in sync with the recommendations of National Education Policy 2020 which emphasizes the promotion of arts and culture through education.
- It complements the Samagra Shiksha Scheme by enhancing aesthetics and artistic experiences for secondary-level students, which play a major role in creating awareness of India’s rich cultural heritage and its vibrant diversity in line with ‘Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat’.
- It enhances the students’ reasoning, comprehensibility, problem-solving, cognitive and decisive abilities, which are helpful in the all-round development of the student.
AXIOM MISSION 1 (AX 1):

A former Israeli fighter pilot, an American technology entrepreneur, and a Canadian investor will be part of the crew of the first entirely-private orbital space mission.
- The three men are paying $55 million each to fly aboard a SpaceX rocket for an eight-day visit to the International Space Station, organized by Houston-based spaceflight firm Axiom.
- The Axiom Mission 1 (AX 1) flight is being arranged under a commercial agreement with NASA.
- The mission will be led by former NASA astronaut Michael Lopez-Alegria, who now works for Axiom space.
- While private citizens have traveled to space before, the AX 1 mission will be the first to use a commercially built spacecraft, the SpaceX Dragon 2, best known for flying its first two crews to the ISS late last year.
- Private civilians have travelled to the space station beforealso.
- Since 2001, Russia has been selling rides to the ISS to wealthy businessmen around the world.
- They traveled onboard the Russian Soyuz aircraft along with professional cosmonauts and NASA astronauts.
Common Trust Network:
![]()
Dr. Harsh Vardhan, Union Minister of Health & Family Welfare addressed the event on Restoring Cross Border Mobility by World Economic Forum’s Common Trust Network through Video Conference.
- As countries around the world work to overcome the COVID-19 pandemic and restart their economies, they all face the challenge of how to reopen their borders and allow travel and commerce to resume while protecting their populations’ health.
- To address this challenge, The Commons Project Foundation and the World Economic Forum have launched the Common Trust Network in collaboration with a broad voluntary network of public and private stakeholders.
The Common Trust Network is designed to
- empower individuals with digital access to their health information,
- make it easier for individuals to understand and comply with each destination’s requirements, and
- help ensure that only verifiable lab results and vaccination records from trusted sources are presented for the purposes of cross-border travel and commerce.
The Common Trust Registry: The Common Trust Network is enabled by a global registry of trusted laboratory and vaccination data sources, standard formats for lab results and vaccination records, and standard tools to make those results and records digitally accessible.
Union Minister for Environment and French Minister for Ecological Transition launched the Indo-French Year of the Environment:

The basic objective is to strengthen Indo-French cooperation in sustainable development, increase the effectiveness of actions in favor of global environment protection and give them greater visibility.
- The Indo-French Year of the Environment over the period 2021-2022 would be based on five main themes: environmental protection, climate change, biodiversity conservation, sustainable urban development, and the development of renewable energies and energy efficiency.
- It is also a platform for engaging in discussions on critical areas of collaboration relating to environment and allied areas.
- From the Indian side, it will be coordinated by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) along with the Ministry of External Affairs, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy and other concerned Ministries/Departments/Organisations.
- A joint screening committee will also be set up to finalise the calendar of the events for the Indo-French Year of the Environment.
- India-France alliance is the main pillar of the International Solar Alliance launched by PM Narendra Modi.
‘Marine Mega Fauna Stranding Guidelines’ and ‘National Marine Turtle Action Plan’.:

The Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has released ‘Marine Mega Fauna Stranding Guidelines’ and ‘National Marine Turtle Action Plan’.
- The documents contain ways and means to guide improved coordination amongst the government, civil society, and all relevant stakeholders on the response to cases of stranding, entanglement, injury or mortality of marine mammals and also conservation of marine turtles.
- These two documents highlight
- actions to be taken for handling stranded animals on shore, stranded or entangled animals in the sea or on a boat,
- management actions for improved coordination,
- reducing threats to marine species and their habitats,
- rehabilitation of degraded habitats,
- enhancing people’s participation,
- advance scientific research and exchange of information on marine mammals and marine turtles and their habitats.




