Today’s Current Affairs: 29th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Article 329(b) Of The Indian Constitution:

The Election Commission (EC) recently invoked Article 329(b) of the Constitution, which prohibits judicial intervention in the working of the commission in the middle of the election process.
- Article 329(b) enshrined in Part XV of the Constitution, articles 324-329 specifically discuss elections.
- While Article 324 gives the poll panel powers to direct and control elections, Article 329, which has two clauses, concerns itself with the role of the judiciary in electoral matters.
- Article 329(a) says the “judiciary is not allowed to challenge the constitutionality of laws relating to the boundaries of electoral districts or the allocation of seats.
- Article 329(b) as amended by the Constitution (19th Amendment) Act, 1966, provides that notwithstanding anything in the Constitution, no election to either House of Parliament or the Legislature of a State shall be called into question except by an election petition presented to such authority and in such manner as may be provided for by or under any law made by the appropriate Legislature.
- It stipulates that election-related inquiries are exclusively addressed through election petitions presented to the authority designated by that law.
- The Representation of the People Act, 1951, furthers this clause as it empowers the high courts to hear and decide election petitions.
- A decision in such petitions can be challenged in the Supreme Court (SC).
Campi Flegrei : Recent Phenomenon

The strongest earthquake to hit Italy’s Campi Flegrei supervolcano region in decades struck recently.
- Campi Flegrei is an active volcanic area located in the vicinity of Naples, Italy.
- Unlike the nearby Mount Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei is not characterised by a single volcano.
- It is more of a volcanic system, with several centres situated within a caldera (the depression created when emptying magma chambers causes the roof of a volcano to collapse).
- The Campi Flegrei caldera has a diameter of about 12-15 km (7.5-9.3 miles).
- It was formed 39,000 years ago after an eruption emptied it of magma. According to a new hypothesis, this eruption could have been the beginning of the end of the Neanderthal.
- One-third of it lies under the Tyrrhenian Sea, between the Italian mainland and the country’s island of Sardinia.
- It is the largest active caldera in Europe.
- It is much larger than the cone-shaped Vesuvius, which destroyed the ancient Roman city of Pompeii in AD79 and is much more active.
- Campi Flegrei has been in a restless state since 1950.
- It is a result of a phenomenon known as bradyseism, which scientists understand to be the gradual movement of part of Earth’s surface caused by the filling or emptying of an underground magma chamber or hydrothermal activity.
Strain Rate:

Researchers have reported in a study that when pure copper is heated and also subjected to an extreme strain rate, it behaves like a much harder material would
- Strain is how much a material deforms when stress is applied. It is a measure of the change in shape or size of an object relative to its original shape or size.
- It has units of meters divided by meters, so it ends up without physical units.
- Strain rate is the rate of deformation caused by strain in a material within a corresponding time.
- It is a measure of how quickly a material is deformed over time.
- It involves both the rate wherein a certain material expands and shears.
- Strain Rate = Change in Strain / Change in Time
- The unit of strain rate is per second.
- It is an important factor in materials science and engineering because it influences the mechanical properties and behavior of materials.
- It can be highly beneficial in the field of metallurgy and corrosion engineering.
- Since materials may undergo deformation in various rates and directions, learning how to gauge strain rate with respect to certain elements like time, velocity and others is vital in determining the material strength and the point at which corrosion, specifically stress corrosion cracking, could take place.
- The use of low strain rates is now a widely used technique in evaluating the response of materials against stress.
ZiG : Reserve Bank Of Zimbabwe

To address its long-standing economic instability, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe (RBZ) has launched a new gold-backed currency called the ZiG.
- The Zimbabwe Gold (ZiG) is a new gold-backed currency launched by Zimbabwe.
- The ZiG, now the sixth currency used by Zimbabwe, has been in circulation since April 5, 2024.
- The ZiG stands out as a new currency backed by gold reserves, ensuring its value is supported by the physical gold held by the government.
- ZiG notes and coins will be available and issued in denominations: 1ZiG, 2ZiG, 5ZiG, 10ZiG, 20Zig, 50ZiG, 100ZiG and 200ZiG, with the gold backing aims to provide stability and prevent currency devaluation.
- Zimbabwe has grappled with high inflation, with rates surpassing 500% in recent years.
- Consequently, the Zimbabwean dollar, introduced in 1980, lost its value due to Following this, the country relied on various currencies, primarily the US dollar, leading to limited control over its economy.
- The collapse of the Zimbabwean dollar in 2009, with hyperinflation peaking at 5 billion per cent, marked one of the most severe currency crashes in history.
Oedocladium sahyadricum:
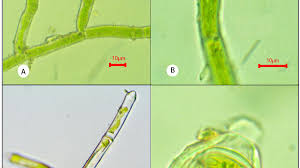
A group of phycologists from the Department of Botany at Catholicate College in Pathanamthitta has discovered a new algal species in the Western Ghats.
- Oedocladium sahyadricum is a new algal species and it is named as Oedocladium sahyadricum.
- The name ‘sahyadricum’ refers to the Western Ghats, also known as Sahyadri, which is rich in plant diversity and provides ideal conditions for the growth of terrestrial microalgae.
- It is dioecious and terrestrial, having a superior operculum, and possessing ellipsoid oogonium and oospore.
- The alga was found as a thin mat of elongated strands on damp soil.
- The species, which looks like moss protonema, is velvety green but turns yellowish-green as it matures. Rainy weather is likely needed for its abundant growth.
- This is the first time a species in the Oedocladium category has been recorded in Kerala.
- Species of Oedocladium have potential practical applications
- In medicine, agriculture and in the production of a natural pigment, astaxanthin which is well-documented for its unique biological activities and health benefits.
- Algae plays a significant role in ecosystems and has enormous economic importance in the world market, from high-value products to wastewater treatment.
Business Responsibility And Sustainability Reporting Initiative:

Delhi-based think tank Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) welcomed the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) initiative by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting Initiative is a mandatory disclosure mechanism for top 1000 listed companies or businesses to report their performance on environmental, social and governance (ESG) aspects and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
- It was introduced in May 2021 by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- This initiative was intended to provide policymakers and investors with robust data to make informed decisions.
- The disclosure requirements are grouped into nine core categories, based on the principles of the National Guidelines for
Responsible Business Conduct introduced by SEBI:
- Key performance indicators cover electricity consumption, water usage and air emissions.
- Focus on human rights violations and minimum and fair wages.
- Performance indicators include anti-corruption, anti-bribery and conflicts of interest policies.
- Metrics focused on parental benefits, employee accessibility and the percentage of unionized workers.
- Policies favouring vulnerable and marginalized groups.
- Information on investments in social and environmental impacts.
- KPIs encompass handling consumer complaints and feedback, product recall procedures and cybersecurity and data privacy policies.
- Describing engagement with vulnerable and marginalized groups.
- Listing trade and industry affiliations and detailing issues relating to anticompetitive conduct.
INS Kiltan:

Indian Naval Ship Kiltan arrived at Muara, Brunei and was accorded a warm welcome by the Royal Brunei Navy
- INS Kiltan is an indigenously-built anti-submarine warfare stealth corvette.
- This is the third of the four Kamorta-class corvettes being built under Project 28.
- The ship derives its name from one of the islands in Aminidivi group of the strategically located Lakshadweep and Minicoy group of islands.
- Designed by the Indian Navy’s in-house organisation Directorate of Naval Design and built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- It is India’s first major warship to have a superstructure of carbon fibre composite material resulting in improved stealth features, lower top weight and maintenance costs.
- The ship hosts a predominantly indigenous cutting-edge weapons and sensors suite which includes heavyweight torpedoes, ASW rockets, 76 mm caliber Medium Range gun and two multi-barrel 30 mm guns as close-in-weapon system (CIWS) with dedicated fire control systems, missile decoy rockets (Chaff), advanced ESM (Electronic Support Measure) system, most advanced bow mounted sonar and air surveillance radar.
Virupaksha Temple : Restoration Work

The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is set to begin restoration work on the collapsed saalu mantapa or pavilion (a type of Mandapa) at the iconic Virupaksha temple aPrauda Deva Raya part of the Group of Monuments at Hampi, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Virupaksha Temple is the 7th-century Shiva temple in Hampi, Central Karnataka.
- Lord Virupaksha, also referred to as Pampapathi is the main deity in Virupaksha Temple.
- The Virupaksha Temple was built in the Vijayanagara style of architecture and was built by Lakkan Dandesha, a nayaka under the ruler Deva Raya II, also known as of the Vijayanagara Empire.
- Hampi, located in central Karnataka on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Spread over an area of nearly 4,200 hectares, the site contains over 1,600 surviving monuments, including forts, temples, palaces, and other structures.
- It was once the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire, known for its historical and archaeological significance.
- The location of Hampi, amid craggy hills and the Tungabhadra River, provided a natural defensive setting for the capital city.
- Hampi’s monuments showcase the pinnacle of Vijayanagara architecture, a synthesis of the Dravidian style with Indo-Islamic influences.
Manama Declaration:

The Arab League called for UN peacekeeping forces in the Palestinian territories during a summit in Manama, Bahrain.
- The “Manama Declaration” (Manama is the capital and largest city of Bahrain) urged international protection and UN peacekeeping forces in the occupied Palestinian territories until a two-state solution is achieved.
- It also demanded an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and an end to forced displacement in the region.
- Arab League is a regional organization of Arab states in the Middle East and parts of Africa.
- Formed in Cairo on March 22, 1945, it aims to promote Arab interests and coordinate political, cultural, economic, and social programs among its members.
- The League also seeks to settle disputes among member states and provide mutual military support.
- Its headquarters is in Cairo, Egypt, and its official language is Arabic.
- The League has 22 members, with founding members including Egypt, Syria, and Iraq. Four nations have observer status: Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Venezuela.
WIPO Treaty:

WIPO member states approved a historic new Treaty on intellectual property (IP), genetic resources (GR), and traditional knowledge (TK), following decades of negotiations.
- It Ensures traditional knowledge is not exploited without permission or compensation.
- Utilization: Genetic resources and traditional knowledge are often used in patented inventions and scientific research.
- The Treaty marks the first WIPO Treaty to include provisions for Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Patent applicants must disclose the country of origin or source of GR and the Indigenous Peoples or local community that provided the associated TK.
- Any WIPO member state can join.
- The treaty does not apply to patents filed before its entry into force.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) was established in 1967 through the WIPO Convention, transforming the earlier United International Bureau for the Protection of Intellectual Property (BIPRI) into WIPO.
National Fossil Park In Ghugwa : Madhya Pradesh

Archaeologists from Ashoka University recently unearthed prehistoric artefacts made from fossil wood at the National Fossil Park in Ghugwa, Madhya Pradesh.
- Ghughwa National Fossil Park located in the Dindori district, Madhya Pradesh, was established as a National Park in 1983.
- Situated in a tropical dry deciduous landscape, it boasts fossilized plants dating back between 40 million and 150 million years ago.
- The park is renowned for its preserved fossils of various woody plants like eucalyptus, date palm, and neem, as well as climbers, leaves, flowers, fruits, and even dinosaur egg fossils.
Eucalyptus : Government Order

The Kerala government issued an order allowing the Kerala Forest Development Corporation (KFDC) to plant eucalyptus trees for its financial sustenance in 2024-2025.
- Environmentalists soon protested the decision saying the move would adversely affect forests and heighten human-animal conflicts in future.
- In 2021, the State government had published an eco-restoration policy. Among other things, it sought to address what it called the “proliferation of invasive species that are not suitable for our environment” and the resulting “depletion of natural forests”.
- Environmental activists alleged following the State’s order — permitting the KDFC to plant eucalyptus trees — contravened the policy’s aspirations.
About Eucalyptus :
- It is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of Eucalyptus are native to Australia.
- About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Many eucalypt species have adapted to wildfire, are able to resprout after fire, or have seeds that survive fire.
- Eucalyptus trees are a source of timber, pulpwood, and firewood. They grow rapidly and can be harvested in short rotation cycles.
- Eucalyptus trees have a long history in India.
- Initially, eucalyptus was planted as an ornamental tree to enhance the beauty of gardens. However, its plantation on a larger scale began only in 1952.
- In the 1950s, eucalyptus and acacia trees were planted extensively throughout the Nilgiris to supply pulp wood.Later, eucalyptus was planted extensively with financial assistance from the World Bank.




