Today’s Current Affairs: 9th August 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Clouded Leopard:

The Mizoram governor drew attention to the critical challenges in wildlife conservation during a function to observe International Clouded Leopard Day recently.
- Clouded Leopard is a wild cat inhabiting dense forests of the Himalayas through mainland Southeast Asia into South China.
- There are two species of clouded leopards: the clouded leopard(Neofelis nebulosa) and the Sunda clouded leopard (Neofelis diardi).
- It is found across Southeast Asia and the Himalayas in the following countries: southern China, Bhutan, Nepal, northeast India, Burma, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Cambodia, Laos, and Bangladesh.
- Throughout its range, the clouded leopard spends most of its time in the tropical evergreen rainforests but can also be found in dry tropical forests and mangrove swamps.
- It has been found at relatively high altitudes in the Himalayas.
- In India, it is found in Sikkim, northern West Bengal, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is the State animal of Meghalaya.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar:

The central government recently announced the full list of the first-ever Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP) 2024 awardees.
- The ISRO-Chandrayan 3 Team will be awarded the Vigyan Team award for their contribution in the field of Space Science and Technology.
- Celebrated biochemist Govindarajan Padmanabhan has been selected as the first recipient of the Vigyan Ratna Puraskar.
- Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP) is a new set of awards introduced by the Government of India in the field of Science, Technology, and Innovation.
- Objective is to recognize the notable and inspiring contributions made by scientists, technologists, and innovators individually or in teams in various fields of science, technology, and technology-led innovation.
- It is one of the highest recognitions in the field of science, technology, and innovation in India.
- Scientists will be selected across 13 domains, namely Physics, Chemistry, Biological Sciences, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering Sciences, Agricultural Science, Environmental Science, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science and Technology, and Others.
- The representation from each domain/field, including gender parity will be ensured.
Waqf:

A contentious bill to amend 44 sections of the Waqf Act of 1995 – including changing it ensure representation of non-Muslim individuals and Muslim women in central and state Waqf bodies – is likely to be tabled in the Lok Sabha.
- Under the Waqf Act of 1954, a Waqf refers to a property dedicated in the name of God for religious and charitable purposes.
- Legally, it is the permanent dedication by a Muslim of any movable or immovable property for purposes recognised by Muslim law as pious, religious or charitable.
- A Waqf can be established through a deed or instrument, or a property can be considered a Waqf if it has been used for religious or charitable purposes over a long period.
- The proceeds from Waqf typically fund educational institutions, graveyards, mosques, and shelter homes.
- Once a property is designated as a Waqf, it becomes non-transferable and is detained perpetually as a charitable act toward God, essentially transferring ownership to God.
- Waqfs can be either public, serving charitable ends, or private, benefiting the property owner’s direct descendants.
- To create a Waqf, one must be of sound mind and hold valid ownership of the property.
- The creator of a Waqf, known as the Waqif, does not have to be a Muslim, as long as they profess belief in Islamic principles.
- Waqfs in India are regulated by the Waqf Act, 1995.
- A survey commissioner lists all properties declared as Waqf by conducting local investigations, summoning witnesses and requisitioning public documents.
- The Waqf is managed by a mutawali, who acts as a supervisor.
- Unlike trusts established under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, which can serve broader purposes and be dissolved by the board, Waqfs are specifically for religious and charitable uses and are intended to be perpetual.
Eta Carinae:

Astronomers are closely monitoring Eta Carinae, as it may be on the verge of a spectacular explosion.
- Eta Carinae is a hypergiant star with a mass approximately 100 times that of our Sun.
- It is located about 7,500 light-years away in the Carina Nebula, Eta Carinae is one of the most massive and luminous stars known to science, making it an excellent candidate for a supernova.
- Historical records reveal that about 170 years ago, the star underwent a significant outburst, known as the Great Eruption, which temporarily made it one of the brightest stars in the southern sky.
- This event created the Homunculus Nebula, a distinctive hourglass-shaped cloud of gas and dust that surrounds the star.
- It is the only known star to emit natural laser light, adding to its enigmatic nature.
- Recently the Hubble Space Telescope highlighted the intricate details of the surrounding nebula, including diffraction spikes and radial streaks, which remain unexplained.
- Eta Carinae’s eventual supernova will be a monumental event, potentially outshining any supernova observed in recent history, including SN 2006gy.
- When it does explode, it will provide an extraordinary light show visible from Earth and offer invaluable insights into the life cycles of massive stars.
Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve:

The Chhattisgarh government on Wednesday announced that it would establish a new tiger reserve and named it as Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve.
- Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve is located in the northern part of the state of Chhattisgarh, bordering Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- This will be the fourth Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh, after the Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar and Indravati Reserves.
- It is spread across the combined areas of the Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuaryin Chhattisgarh.
- This area is home to various mammal species, including tigers, leopards, hyenas, jackals, wolves, sloth bears, barking deer, chinkara, and chital.
- It serves as the origin of significant rivers such as Hasdeo Gopad and Baranga and a catchment area for rivers like Neur, Bijadhur, Banas, Rehand, and numerous smaller rivers and rivulets.
Guru Ghasidas National Park
- It connects Jharkhand and Madhya Pradesh and provides a corridor for tigers to move between the Bandhavgarh and Palamau Tiger Reserves.
- It was originally part of the Sanjay Dubri National Park, Guru Ghasidas Park was created as a separate entity in Chhattisgarh’s Sarguja region after the formation of the state in 2001.
Pyrocumulonimbus Cloud:

The wildfires currently raging in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have created ‘pyrocumulonimbus’ clouds, which have the potential to spit out thunder and spark more fires.
- Pyrocumulonimbus clouds occur only when there is an extremely hot wildfire — volcanic eruptions can also lead to the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
- The intense heat from the fire warms the surrounding air which moves upward into the atmosphere.
- As this hot and very buoyant air — carrying water vapour, smoke, and ash — rises, it expands and cools down. Once it is cool enough, water vapour condenses on ash, forming a grey or brown cloud.
- At this stage, the cloud is known as a pyrocumulus cloud, also known as a ‘fire cloud’.
- If there is sufficient water vapour available and the upward movement of hot air intensifies, pyrocumulus clouds can evolve into a pyrocumulonimbus cloud.
- These clouds can reach heights of 50,000 feet and generate their own systems of thunderstorms.
- Although pyrocumulonimbus clouds can produce lighting, they do not generate much rain.
- As a result, they can spark new wildfires many kilometres away from the main blaze.
- These clouds can also trigger strong winds that can make the spread of the wildfire faster and unpredictable.
- Scientists believe that climate change could have a role to play in the increase of their frequency.
- Studies have shown that with temperatures soaring across the world, wildfires are becoming more common and intense.
National Coastal Mission Scheme:

The Minister of State for Environment, Forest and Climate Change informed the Lok Sabha about the National Coastal Scheme.
- National Coastal Mission Scheme was launched in 2014.
- It has been envisaged under the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
- It aims to address the impact of climate change on coastal and marine ecosystems, infrastructure and communities in coastal areas through a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
- It is under the National Coastal Management Program and is implemented with the following components:
- Management Action Plan on Conservation of Mangroves and Coral Reefs
- Research & Development in Marine and Coastal ecosystem
- Sustainable Development of Beaches under Beach Environment & Aesthetic Management Service
- Capacity Building / Outreach Programme of Coastal States/UTs on conservation of marine and coastal ecosystems including beach cleaning drive.
- The implementing agencies of NCM are the State Governments of Coastal States and Union Territory (UT) Administrations.
Neutron Stars:

Astronomers recently discovered ten strange dead stars, or “neutron stars,” lurking near the heart of the Milky Way.
- Neutron Stars are extremely dense and compact celestial objects formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses.
- The very central region of the star, ‘the core’, collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron.
- If the core of the collapsing star is between about 1 and 3 solar masses, these newly created neutrons can stop the collapse, leaving behind a neutron star. (Stars with higher masses will continue to collapse into stellar-mass black holes).
- Since neutron stars began their existence as stars, they are scattered throughout the galaxy in the same places where we find stars.
- And like stars, they can be found by themselves or in binary systems with a companion.
- Neutron stars are typically about 20 km (12 miles) in diameter.
- Their masses range between 1.18 and 1.97 times that of the Sun, but most are 1.35 times that of the Sun.
- Many neutron stars are likely undetectable because they simply do not emit enough radiation.
- Most neutron stars are observed as pulsars.
- Pulsars are rotating neutron stars observed to have pulses of radiation at very regular intervals that typically range from milliseconds to seconds.
- Pulsars have very strong magnetic fields, which funnel jets of particles out along the two magnetic poles.
- These accelerated particles produce very powerful beams of light.
- Neutron stars are also seen as objects called rotating radio transients (RRATs) and as magnetars.
Candida Auris:
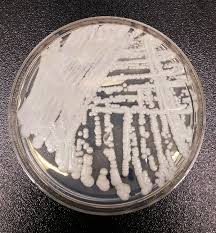
Researchers recently discovered a new clade (or type) of Candida auris, bringing the number of clades known globally to a total of six.
- Candida Auris (C. auris) is a fungal pathogen that is often multi-drug-resistant.
- It is capable of causing invasive infectionsin the human body.
- It can cause a range of infections, from superficial (skin) infections to more severe, life-threatening infections, such as bloodstream infections.
- It can cause infection in different parts of the body, like the blood, wounds and ears.
- It was first identified in Japan in 2009.
- Most casesof the fungus have been reported in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
- It is generally thought to be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or by person-to-person transmission.
- People who are already suffering from other medical conditions, recent hospital stays, and invasive devices are most at risk of contracting the fungus.




