Today’s Current Affairs: 23rd October 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024:
India ranks 105th out of 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024 with a score of 27.3, highlighting a “serious” hunger crisis driven by ongoing challenges of food insecurity and malnutrition.
- India-Specific Findings: GHI Score (2024) – 27.3 (‘serious’) slightly improved from GHI Score (2023) – 28.7 (‘serious’).
- Undernourished children – 13.7%
- Stunted children – 35.5%
- Wasted children – 18.7% (highest globally)
- Child mortality rate – 2.9%
Malaria Free : Egypt

Egypt was officially declared ‘malaria-free’ by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Malaria is an acute febrile illness caused by Plasmodium parasites, which are spread to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- It is a life-threatening disease primarily found in tropical countries.
- It is not contagious and cannot spread from one person to another; the disease is transmitted through the bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes
- Five species of parasites can cause malaria in humans and 2 of these species – Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax– pose the greatest threat.
- The first symptoms of malaria usually begin within 10–15 days after the bite from an infected mosquito.
- Fever, headache and chills are typically experienced, though these symptoms may be mild and difficult to recognize as malaria.
- In malaria endemic areas, people who have developed partial immunity may become infected but experience no symptoms.
- Vector control is the main approach to prevent malaria and reduce transmission.
- It is preventable and curable.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of malaria reduces disease and prevents deaths, and also contributes to reducing transmission.
Carbon Capture:
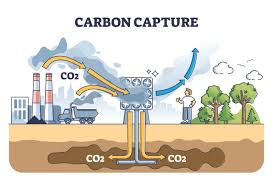
Alt Carbon, a Darjeeling-based company, accelerates the natural process of rock weathering to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) by using crushed basalt, a type of volcanic rock rich in minerals like calcium and magnesium.
- Crushed basalt, a type of volcanic rock, is spread over land to increase surface area, accelerating natural weathering processes.
- Atmospheric CO2 reacts with minerals in the basalt, forming bicarbonates that are washed into oceans where carbon is stored for long periods.
- This speeds up the natural carbon capture process, which normally takes thousands of years, making it efficient in 2-4 years.
- Basalt-rich regions like the Deccan Traps in Maharashtra and Gujarat, as well as Jharkhand and West Bengal (Rajmahal Traps), are ideal for sourcing the basalt rock.
- Apart from capturing carbon, basalt also acts as a soil enhancer, improving fertility and benefiting agricultural productivity.
- For every 3-4 tonnes of basalt dust, 1 tonne of CO2 can be sequestered over a few years.
- Companies can purchase carbon credits generated from this process to offset their emissions voluntarily.
International Workshop on the use of “Modern Technologies in Survey-Resurvey for Urban Land Records:

The Ministry of Rural Development organised the International Workshop on the use of “Modern Technologies in Survey-Resurvey for Urban Land Records”.
- It reaffirmed the commitment of digitising land records under the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP).
- A pilot program named National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations (NAKSHA) was introduced to create urban land records in over 100 cities/towns.
- Use of drones and aerial photography with 3D imagery in land record creation was highlighted.
- DILRMP (erstwhile National Land Record Modernization Programme) is a Central Sector Scheme with effect from 1st April 2016 with 100% funding by the Centre.
- It aims to develop a modern, comprehensive and transparent land record management system.
Sri Singeeswarar Temple : Study

A set of copper-plate inscriptions dating back to the 16th Century CE have been discovered at the Sri Singeeswarar temple at Mappedu village in Tiruvallur district recently.
- Singeeswarar Temple (Mappedu) Situated in Mappedu, Tiruvallur district, Tamil Nadu, approximately 20 km from Poonamallee on the Chennai-Poonamallee-Perambakkam highway.
- Built in 976 A.D. by Aditya Karikal Chola II, the elder brother of Rajaraja Chola.
- In the 16th century, Ariyanatha Mudaliar, an officer under King Tirumala Nayaka, renovated the temple, particularly erecting the main tower (Raja Gopuram).
- Copper-plate inscriptions from 1513 CE, written in Sanskrit and Nandinagari script during the reign of Vijayanagara King Krishnadevaraya, were recently discovered at the temple. These inscriptions hold significant historical value.
- The temple is known for its unique depiction of Anjaneya (Hanuman) playing the Veena in a subtle state, making it a special spiritual site.
Nature Restoration Law:

The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), which was enacted by the European Union (EU), is an inspiring model from which India can draw points to tackle its growing environmental crises.
- It is a European Union (EU) law to tackle the triple crises of climate change, biodiversity loss, and environmental degradation.
- It is the first continent-wide, comprehensive law of its kind.
- It is a key element of the EU Biodiversity Strategy, which sets binding targets to restore degraded ecosystems, in particular those with the most potential to capture and store carbon and to prevent and reduce the impact of natural disasters.
- Under the NRL, Member States will have to restore at least 20% of the EU’s land and sea by 2030, including terrestrial, coastal, and freshwater, forest, agricultural, and urban areas.
- By 2050, the measures should extend to all ecosystems “requiring restoration”.
- The EU NRL also targets an obligation to improve urban green spaces, contribute to free-flowing rivers by removing artificial barriers, increase pollinator populations, and contribute to the target of 3 billion additional trees throughout the EU.
- Member States must adopt “restoration plans” detailing how they intend to achieve these targets and ensure that the restored areas do not significantly deteriorate.
- While drafting these Nature Restoration Plans, Member States also need to consider socio-economic impacts and benefits and estimate the financial needs for its implementation.
India’s Fourth Nuclear-Powered Ballistic Missile Submarine:

India quietly launched its fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) at the Ship Building Center (SBC) in Visakhapatnam, enhancing its nuclear deterrence capabilities.
- India’s fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) boasts nearly 75 percent indigenous content and is equipped with K-4 ballistic missiles, which have a range of 3,500 km and are fired through vertical launching systems.
- While the first of its class, INS Arihant carries 750 km range K-15 nuclear missiles, its successors, INS Arighaat and INS Aridhaman, are all upgrades of the previous ones and carry only K-4 ballistic missiles.
- The launch of S4* follows the commissioning of INS Arighaat in August 2024, and the INS Aridhaman is set for commissioning next year. Both INS Arihant and INS Arighaat are already on deep sea patrols.
- Since national security planners named India’s first leased nuclear attack submarine INS Chakra as S1, INS Arihant was named S2, INS Arighaat S3, INS Aridhaman S4 and hence the newly launched one is the last of its class, S4* with the formal name yet to be given.
SSBN:
- SSBNs are a potent and highly specialised military asset. Operated by only the United States, Russia, China, the United Kingdom, France, and India, these are armed with submarine-launched nuclear ballistic missiles.
- These submarines are designed to provide a reliable second-strike capability and underpin strategic nuclear deterrence via the principle of mutual assured destruction.
Hornets:

According to a recent study, a species of hornet that often munches on foods containing alcohol can hold its liquor, without any side effects, at levels that no other known animal can tolerate.
- Hornets are a breed of social wasps, living in large, highly organized colonies.
- They are a group of 20 species occurring naturally only in Asia, Europe, and Africa, with one species introduced to North America.
- Hornets belong to the insect family Vespidae.
- This family contains each species of hornets as well as wasps such as yellow jackets, paper wasps, potter wasps, and pollen wasps.
- Hornets tend to be black or brown with yellow or yellowish markings.
- Due to their size, hornets have a reputation for being more dangerous than other wasp species, though they are not always more aggressive.
- Hornets release more venom per sting than any other stinging insect.
- One species, the northern giant hornet, or Asian giant hornet (V. mandarinia), which is native to Asia, is the largest known wasp species in the world.
- Typically, hornets like to build their nests in high areas.
- Hornets are known to have a rich diet of sugar and protein, among other things.
- They prey on other insects, including honeybees and social wasps, and chew them into a paste as food for their larvae.
Nilgiri Tit Butterfly:

Nilgiris have recorded for the first time in India, the Nilgiri tit Butterfly (Hypolycaena nilgirica) utilising a large terrestrial orchid plant as a host.
- Nilgiri tit Butterfly belongs to the family Lycaenidae.
- It was first described in 1884 from Coonoor in the Nilgiris, it has since been recorded in Sri Lanka.
- It was also found in Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary of Idukki district, and Silent Valley National Park of Palakkad district in Kerala.
- The male is dark reddish purple-brown on the upper side. It has two black spots capped in orange near the tails. The female is pale brown.
- This is the first known record of the butterfly using this particular species of plant as a host.
- This terrestrial orchid was found on rocky slopes in humid areas.
- This endemic butterfly is classified under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act.
Mission Basundhara 3.0 : Assam
Assam Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma officially launched Mission Basundhara 3.0 at an event held at Srimanta Sankardev Kalakshetra in Guwahati. This ambitious initiative is designed to empower indigenous communities by providing them with formal land rights, ensuring greater security and recognition of their holdings.The world’s total public debt is projected to exceed $100 trillion for the first time in 2024. This figure is expected to reach 93% of global GDP by the end of 2024 and approach 100% by 2030, surpassing the 99% peak seen during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Pakistan Limits Chief Justice’s Term to Three Years:
Pakistan enacted the Constitution (26th Amendment) Act, 2024, limiting the Chief Justice’s tenure to three years and establishing a special commission for appointing the top judge from three senior-most Supreme Court judges. The amendment received President Asif Ali Zardari’s assent after being passed by both Houses of Parliament amid strong opposition from the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party, led by former Prime Minister Imran Khan. This legislation prevents Justice Masoor Ali Shah from succeeding current Chief Justice Qazi Faez Isa, who is set to retire on October 25.
Global Public Debt Set to Exceed $100 Trillion, Warns IMF:
According to a report released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the world’s total public debt is poised to surpass $100 trillion this year for the first time. The IMF warns that this figure may rise even more rapidly than previously anticipated, driven by political sentiment favoring increased spending and the growing borrowing needs associated with slow economic growth.
Vikram Dev Dutt Takes Charge as Coal Secretary:
Vikram Dev Dutt, a 1993-batch IAS officer from the AGMUT cadre, has officially assumed the role of Coal Secretary. Previously serving as the Director General of the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), Dutt takes over from VL Kantha Rao, who held the additional charge after Amrit Lal Meena was appointed as the Chief Secretary of Bihar. With India’s power demand projected to grow by 6-7% annually, Dutt faces the significant challenge of enhancing coal production to meet the rising needs of the Power and Industrial sectors.
ECI Appoints Ajay Kumar Singh as Jharkhand’s New DGP Ahead of Elections:
Ajay Kumar Singh, a senior IPS officer, has been appointed as the new Director General of Police (DGP) for Jharkhand. His selection comes from a panel of three IPS officers recommended by the State Government, following the Election Commission’s order for the immediate removal of acting DGP Anurag Gupta.
Namo Bharat Diwas:
The first anniversary of Namo Bharat train operations was celebrated as Namo Bharat Diwas in New Delhi, marking a significant milestone in India’s transportation history. The National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) organized the event, attended by Union Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs, Shri Manohar Lal Khattar, and Union Minister of State for Housing and Urban Affairs, Shri Tokhan Sahu. During the celebration, excellence awards were presented to outstanding employees who contributed to the success of the Namo Bharat initiative.
Cyclone Dana:
The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has issued a warning regarding a low-pressure area over the Bay of Bengal, predicting it will intensify into a severe cyclonic storm by October 23. The storm is expected to make landfall along the coasts of Odisha and West Bengal on October 24. It is likely that Cyclone Dana will bring heavy rains in both states for at least three days.
Goa Hosts 24th National Para-Swimming Championship:
The 24th National Para-Swimming Championship commenced on 20th October in Goa, showcasing a vibrant celebration of exceptional talent and unwavering determination among athletes from across the nation. The event has attracted para-swimmers from various states, highlighting their skills and resilience in the sport.




