Today’s Current Affairs: 25th August 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Mithi River : In News

The Economic Offences Wing (EOW) of the Mumbai Police recently arrested a 49-year-old contractor in connection with the multi-crore Mithi river desilting fraud that has caused losses of over ₹65 crore to the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC).
- Mithi river is one of the four rivers flowing through the Mumbai city, Maharashtra.
- The river originates from the overflow of Vihar Lake and also receives the overflows from the Powai Lake about 2 km downstream.
- It flows for 18 km before discharging into the Arabian Sea at Mahim Creek, flowing through residential and industrial complexes of Powai, Saki Naka, Kurla, Kalina, Vakola, Bandra Kurla Complex, Dharavi and Mahim.
- The river has an average width of 5 metres in the upper reaches, has been widened to 25 m in the middle reaches and up to 70 m in the lower reaches after the 26 July 2005 deluge (944 mm in 24 h on 26 July 2005)
- It is a seasonal river, which feeds on the monsoons.
Blue Carbon:

Seaweed farming has emerged as a potential Blue Carbon strategy, yet empirical estimates of carbon burial from such farms remain lacking in the literature
- Blue Carbon refers to organic carbon captured and stored by the ocean in vegetated coastal ecosystems such as mangrove forests, saltmarshes, or seagrass meadows.
- “Blue” refers to the watery nature of this storage.
- The vast majority of blue carbon is carbon dioxide that has dissolved directly into the ocean.
- Much smaller amounts are stored in underwater sediments, coastal vegetation, and soils; carbon-containing molecules, such as DNA and proteins; and ocean life from whales to phytoplankton.
- These ecosystems store massive amounts of carbon, making them an integral part of global efforts to combat climate change.
- They cover just 2% of the total ocean surface but account for 50% of the ocean’s carbon absorption.
Transforming India’s Electoral Landscape:

The Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR) recently issued a show cause notice to the Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS), asking it to disclose the source of funding for its studies on the Election Commission’s Special Intensive Revision (SIR) exercise and the Maharashtra Assembly polls.
- Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR) is the apex body of the Government of India for research in the social and human sciences.
- It was established in the year 1969 by the Government of India on the recommendation of Prof. V. K. R. V. Rao Committee.
- It is an autonomous organisation working under the aegis of the Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education.
- ICSSR plays a pivotal role in advancing knowledge and understanding of various social issues and challenges, and providing research-based solutions to policymakers and stakeholders in the development of the nation through initiatives and schemes such as
- research projects
- doctoral, postdoctoral, senior fellowships, and national fellowships
- research internships; training and capacity building of early career researchers
- publication grants
- national and international seminars, conferences, and workshops
- publication of cutting-edge research
- national and international collaboration
- promotion of social science and humanities research through research institutes, recognised institutes, and regional centres.
- An all-India network of 24 frontline research institutes and six regional centres is maintained, and five recognized institutes are programmatically supported by the ICSSR.
- The Documentation center of ICSSR – National Social Science Documentation Centre (NASSDOC)-provides library and information support services to researchers in social sciences.
- ICSSR has developed the ICSSR Data Service to serve as a national data service for promoting a powerful research environment through sharing and reuse of data among the social science community in India.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan:

India is grappling with an escalating drug abuse crisis. The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan was launched to address this issue and has now completed five years of implementation.
- Three-pronged strategy—supply control, demand reduction, and medical treatment.
- Key Achievements:
- Mass Sensitisation (18.10+ crore people, 4.85+ lakh institutions)
- Youth Mobilisation (1.67+ crore students, pledge & events)
- Digital & Tech Integration (social media, website, app, geo-tagging)
- Volunteer Network (20,000+ Master Volunteers)
- Community Outreach (campaigns, monitoring, awareness drives)
- Collaborations (MoUs with spiritual/social organisations including The Art of Living, Brahma Kumaris, Sant Nirankari Mission, Ram Chandra Mission (Daaji), ISKCON etc).
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan Launched on 15th August 2020 by the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- It aims to raise awareness on substance use, focusing on educational institutions, universities, and schools.
- It targets the identification of dependent populations and strengthens counseling and treatment facilities.
- Initially focused on 272 vulnerable districts, now extended to all districts in India.
Kerala ‘First’ Digitally Literate State in India:

Kerala has been declared the first fully digitally literate state in India, marking a milestone in bridging the digital divide through the Digi Keralam Project.
- Digi Keralam Project targeted senior citizens, homemakers, and digitally excluded groups, using youth volunteers and the K-SMART (Kerala Solutions for Managing Administrative Reformation and Transformation) platform to provide online access services, boosting inclusion and governance.
- Earlier in 2002, the Akshaya project was launched by then President A.P.J. Abdul Kalam in Kerala, to make one family member digitally literate, promoting IT access and citizen service delivery across the state.
- Digital Literacy is the ability of individuals and communities to understand and use digital technologies for meaningful actions within life situations.
- According to the Central Board for Workers Education Only 38% of India households are digitally literate (61% in urban areas and 25% in rural areas).
WHO–WMO report Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress (2025):

The WHO–WMO report Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress (2025) highlights how rising global temperatures are creating a severe occupational health and productivity crisis. With 2024 the warmest year on record (1.45°C above pre-industrial levels), both outdoor and indoor workers face growing risks.
Key Findings of the WHO–WMO Report:
- Productivity Losses – Each 1°C rise in WBGT above 20°C reduces productivity by 2–3%; sun exposure adds another 2–3°C
- Scale of Exposure – Over 4 billion workers affected; annually 22.85 million injuries, 18,970 deaths, and 2.09 million DALYs linked to heat stress.
- Geographical Hotspots – 30% of the world’s population faces heat stress as an everyday or seasonal problem, with South Asia, Middle East, and Sub-Saharan Africa worst hit.
- Health Impacts – Over one-third of workers in hot conditions report physiological heat strain. WHO guidance (1969) states that core body temperature should not exceed 38°C during an 8-hour shift, but this is increasingly breached.
- Climate Change Dimension – 40–50°C daytime peaks now frequent, spreading risks beyond tropics; worker fatalities recorded in Europe’s 2023 heatwaves.
Rethinking Homestays: Navigating Policy Pathways

NITI Aayog released the report “Rethinking Homestays: Navigating Policy Pathways” on 22 August 2025 in collaboration with IAMAI. The report aims to provide a strategic roadmap for strengthening India’s homestay and BnB sector.
- It is a policy-oriented document highlighting opportunities and challenges in India’s homestay ecosystem.
- Developed through consultations with policymakers, hosts, and aggregators.
- NITI Aayog is National Institution for Transforming India, a policy think-tank of the Government of India.
- Established in: 1 January 2015, replacing the Planning Commission.
- Organisation:
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Vice-Chairperson: Appointed by PM.
- Members: Full-time, part-time (experts), and ex-officio (Union Ministers).
- Governing Council: CM of states and LGs of UTs.
UN declares famine in Gaza:

The United Nations has declared a famine in Gaza, affecting nearly 500,000 people, citing systematic obstruction of humanitarian aid by Israel.
- Famine Declaration is A formal global classification used by the UN and partners to signal catastrophic food insecurity.
- Declared through the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) framework, jointly managed by UN agencies and humanitarian organisations.
Criteria for Declaration:
- A famine is declared when all three thresholds are met:
- At least 20% of households face extreme food shortages.
- Acute malnutrition exceeds 30% in children.
- Mortality rate is over 2 deaths per 10,000 people per day.
Great Nicobar Project:
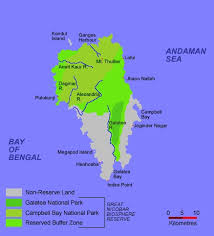
The Tribal Council of Great Nicobar has complained that the forest rights of Nicobarese tribals under FRA, 2006 have not been settled for the ₹72,000-crore Great Nicobar Project.
- Great Nicobar Project is a mega infrastructure project proposed on Great Nicobar Island, Andaman & Nicobar.
- Implemented by NITI Aayog and A&N Administration, with strategic backing from the Government of India.
- Conceptualised in 2015, formally cleared in 2022 with environmental and forest clearances.
- Aims and Objectives
- Enhance India’s maritime security in the Bay of Bengal and Indo-Pacific.
- Boost trade, connectivity, and regional development.
- Create employment opportunities for local population.
- Strengthen India’s presence in global shipping and logistics chains.
Trump Appoints Sergio Gor as US Ambassador to India and Special Envoy for South, Central Asia:
US President Donald Trump has nominated his long-time aide, Sergio Gor, as the next United States Ambassador to India and Special Envoy for South and Central Asian Affairs. This nomination comes amid rising tensions between the US and India over steep tariffs and geopolitical disagreements, making the role particularly sensitive and high-stakes. Gor’s appointment highlights Trump’s intent to ensure loyalists take on critical global roles during his second term.
India’s GDP in Q1 FY26 is projected to grow 6.7%:
India’s economy is projected to grow at a robust 6.7% in the first quarter (Q1) of FY26, according to a median estimate by economists. The growth is underpinned by strong government capital expenditure, reviving rural consumption, and a resilient services sector. This estimate aligns closely with the Reserve Bank of India’s forecast of 6.5%, suggesting stable economic momentum in the post-pandemic recovery phase.
Centre has set up two Rajiv Gauba-led panels to implement next-generation reforms:
Central Government has established two high-level committees under the leadership of Rajiv Gauba, a full-time NITI Aayog member and former Cabinet Secretary. These panels are designed to fast-track next-generation reforms and realize the ambitious Viksit Bharat (Developed India) vision.
The two newly formed panels led by Rajiv Gauba will work in parallel but with distinct objectives:
- Panel on Viksit Bharat Goals: Focused on strategizing long-term policies and actions needed to fulfill India’s aspiration of becoming a developed nation by 2047.
- Panel on Non-Financial Regulatory Reforms: Concentrated on overhauling and simplifying regulatory frameworks across non-financial sectors to boost economic competitiveness and ease of doing business.




