Today’s Current Affairs: 7th Feb 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Grammy Awards 2024:

The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, congratulated musicians Ustad Zakir Hussain, Rakesh Chaurasia, Shankar Mahadevan, Selvaganesh V and Ganesh Rajagopalan for winning the Grammy award.
- Grammy Awards are presented by the Recording Academy of the US.
- The awards are presented to recognize the works of the music industry.
- The first Grammy Awards ceremony was held on May 4, 1959, to honour the musical accomplishments of performers for the year 1958.
First National Conference On The Promotion Of Seaweed Cultivation:

The first National Conference on the Promotion of Seaweed Cultivation took place at Koteshwar, Kutch in Gujarat.
- It was chaired by Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Shri Parshottam Rupala .
- Implementing seaweed cultivation on a pan-India basis, emphasizing the promotion of seaweed cultivation to diversify marine production and enhance fish farmer income.
- Seaweed is the name given to the many species of marine algae and plants.
- These species grow in water bodies such as rivers, seas and oceans.
- They generally grow in the shallow waters in the tidal zone.
- Some seaweeds are microscopic, such as the phytoplankton that live suspended in the water column.
- Seaweed is full of vitamins, minerals, & fibre.
- Many seaweeds contain anti-inflammatory & anti-microbial agents.
- They are known to process significant medicinal effects.
- Certain seaweeds possess powerful cancer-fighting agents.
- They are used in organic cosmetics & skin-care products.
- Seaweed Farming is the practice of cultivating and harvesting seaweed.
- Seaweeds are abundant along the Tamil Nadu and Gujarat coasts and around Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Seaweed Mission aims to commercialize seaweed farming and processing for value addition.
- It also aims to increase cultivation along India’s 7,500-kilometer coastline.
India Energy Week 2024:

The Prime Minister of India inaugurated the India Energy Week (IEW) 2024 in Goa and the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC) Sea Survival Centre, and also participated in the Viksit Bharat, Viksit Goa 2047 programme.
- India Energy Week 2024 is being held from 6th to 9th February in Goa. It is India’s largest and only all-encompassing energy exhibition and conference, bringing together the entire energy value chain, and will catalyse India’s energy transition goals.
- Encouraging, fostering and integrating startups into the energy value chain will be an important focus for IEW 2024.
- The event reflects India’s commitment to global cooperation in the energy sector, with a focus on collaboration and knowledge sharing in sustainable energy development.
- ONGC Sea Survival Centre is an Integrated Sea Survival Training Centre to advance the Indian sea survival training ecosystem to global standards.
- It is anticipated to train 10,000-15,000 personnel annually, emphasising simulated exercises in harsh conditions.
What Is Humboldt’s Enigma?

Humboldt’s enigma has garnered increased attention in the field of ecology as researchers seek to understand the unexpected biodiversity found in mountain ecosystems, challenging traditional beliefs.
- Sparked by Alexander von Humboldt’s observations, it questions the conventional notion that tropical regions, fueled by ample sunlight, are the primary centres of biodiversity on Earth.
- It contends that despite receiving less sunlight and enduring colder temperatures, mountain ecosystems defy this notion by showcasing exceptional biodiversity, thereby challenging traditional ecological theories and prompting investigation into this anomaly.
- Humboldt suggested there was a relationship between temperature, altitude, and humidity on one hand and the occurrence patterns of species or their biodiversity on the other.
- His example of choice was the Chimborazo mountain in Ecuador, which has today become an important illustration of mountain diversity.
Renewables 2023 Report : IEA

The International Energy Agency (IEA)’s recent Renewables 2023 report paints a complex picture of the renewable energy sector, highlighting both progress and challenges.
Major Highlights of the Renewables 2023 Report:
- Global annual renewable capacity additions surged by nearly 50% to almost 510 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, marking the fastest growth rate in two decades.
- China played a pivotal role, commissioning as much solar photovoltaics (PV) in 2023 as the entire world did in 2022, while wind additions grew by 66% year-on-year.
- Renewables are projected to surpass coal as the largest source of electricity generation by 2025, with wind and solar PV becoming dominant sources by 2028.
- US, EU, India, Brazil: Supportive policies and improving economic attractiveness are driving accelerated growth in solar PV and onshore wind installations in these regions.
- Middle East and North Africa: Policy incentives are spurring renewable capacity growth.
- While sub-Saharan Africa is lagging despite its resource potential.
- India is forecast to add 205 GW over 2023-2028, doubling 2022’s cumulative installed capacity, making it the world’s third-largest market for renewables.
- Solar PV module prices dropped by nearly 50% in 2023 due to increased manufacturing capacity.
- Solar PV and onshore wind are cheaper than both new and existing fossil fuel plants, driving their rapid adoption globally.
- Emerging economies, led by Brazil, are driving biofuel expansion.
- Biofuels and renewable electricity in EVs are forecasted to offset significant oil demand by 2028, emphasizing their complementary role.
Guidelines On State Guarantees On Borrowings : RBI

A Working Group constituted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has made certain recommendations to address issues relating to Guarantees extended by State governments.
- The Working Group constituted during the 32nd Conference of the State Finance Secretaries held in July 2022.
- The term Guarantee should be used in a broader sense and include all instruments if they create an obligation on the guarantor (State) to make a payment on behalf of the borrower at a future date.
- Further, it must make any distinction between conditional or unconditional, or financial or performance guarantees in order to assess the fiscal risk.
- These are conditional liabilities that may present a potential risk in the future.
- The government guarantees should not be used to obtain finance through State-owned entities, which substitute budgetary resources of the State Government.
- Additionally, they should not be allowed to create direct liability/de-facto liability on the State.
- There should be adherence to Government of India guidelines that stipulate that guarantees be given only for the principal amount and normal interest component of the underlying loan.
- Guarantees must not be extended for External Commercial Borrowings, must not be extended for more than 80% of the project loan (depending on the conditions imposed by the lender) and must not be provided to private sector companies and institutions.
- Appropriate preconditions such as the period of guarantee, levy of (guarantee) fee to cover risk, government representation on the management board of the borrowing entity, and right to audit, etc, must be specified.
- The Group recommends that States assess the risk associated with guarantees by categorising them as high, medium, or low risk, taking into account the entity’s past default history.
- The methodology used for assigning these risk weights should be transparent and disclosed.
- Based on the risk assessment minimum guarantee fee must be set at a minimum of 2.5% per annum.
- The report emphasises that invoking a guarantee could impose considerable fiscal strain on the state government.
- To mitigate potential stress, the Group proposes imposing a ceiling on guarantees, limiting them to 5% of Revenue Receipts or 0.5% of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP), whichever is lower.
- The Group recommends that the RBI should suggest banks/NBFCs to disclose the credit given to State-owned entities with State-government guarantees.
- The report emphasises the need for a comprehensive database to track extended guarantees, proposing the creation of a unit at the State level for this purpose.
- The report highlights that delays in honoring guarantees could harm the State government’s reputation and pose legal risks.
- It advises States to be cautious when providing finance to entities with a history of not meeting commitments.
- The report emphasizes the importance of promptly honoring guarantees to maintain credibility with lenders and investors
Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar Programme:

The Union Minister for Culture, Tourism And Development of North Eastern Region informed the Lok Sabha about the Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar programme.
- Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar programme is a pan-India initiative of the Ministry of Culture under the National Mission on Cultural Mapping and was launched on 27th July 2023.
- It seeks to compile comprehensive information detailing the life, history, and ethos of Indian villages and to make the same available to virtual and real-time visitors.
- Under the MGMD, information is collected under seven broad categories as given below-
- Arts and Crafts Village
- Ecologically Oriented Village
- Scholastic Village Linked with Textual and Scriptural Traditions of India
- Epic Village linked with Ramayana, Mahabharata and/or Puranic legends and oral epics
- Historical Village linked with Local and National History
- Architectural Heritage Village
- Any other characteristic that may need highlighting such as fishing village, horticulture village, shepherding village etc.
- The main objective of the project is to culturally map India’s 6.5 lakh villages, spanning 29 States and 7 Union Territories, on a comprehensive virtual platform.
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite : NASA

Using data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), astronomers have recently discovered and characterised a habitable zone planet named TOI-715b.
- Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a NASA mission that’s searching for planets orbiting the brightest stars in Earth’s sky.
- The satellite is a follow-up to NASA’s highly successful Kepler space telescope, which found thousands of exoplanets during a decade of work after its launch in 2009.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket out of Cape Canaveral.
- TESS circles Earth in a unique high Earth orbit of 12 to 15 days, which is inclined in such a way that the telescope’s sky view is largely free from obstructions by our bright planet and the Moon.
- Over the course of its two-year primary mission, TESS’ four sensitive cameras systematically scanned over 200,000 of the nearest and brightest stars, imaging 75% of the sky. It found 2,100 planetary candidates and 66 confirmed exoplanets.
- The prime mission ended on July 4, 2020, and TESS is now on an extended mission.
- TESS is finding planets ranging from small, rocky worlds to giant planets, showcasing the diversity of planets in the galaxy.
ABHYAS : Flight Trials

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted four flight trials of the high-speed expendable aerial target ‘ABHYAS’ recently.
- ABHYAS is a high-speed expendable aerial target (HEAT).
- It is designed by the DRDO’s Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE).
- ABHYAS offers a realistic threat scenario for the practice of weapon systems.
- It is the ideal platform for the validation of Armed Forces equipment slated for induction,only those that require aerial engagement.
- It is designed for autonomous flying with the help of an autopilot indigenously made by the ADE.
- It has a radar cross-section and a visual and infrared augmentation system required for weapon practice.
- The target drone has a laptop-based Ground Control System with which the aircraft can be integrated and pre-flight checks, data recording during the flight, replays after the flight and post-flight analysis can be carried out.
Messinian Event:
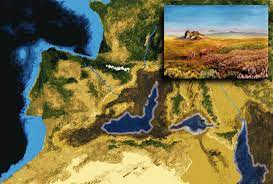
The Geological Institute of Israel recently uncovered a never-before-known underwater canyon near Cyprus that dates back to the Messinian Event.
- Messinian Event also known as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC), the Messinian event was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (drying up).
- It was one of the most severe ecological crises in the Earth’s history.
- The MSC began approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and lasted until around 5.3 MYA.
Nagoya Protocol:
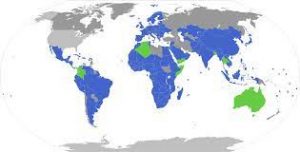
Cameroon recently adopted the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilisation (the Protocol) is a legally binding global agreement that implements the access and benefit-sharing obligations of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- It was adopted by the CBD in Nagoya, Japan, in October 2010 and entered into force on October 12, 2014, 90 days after the deposit of the fiftieth instrument of ratification.
- It provides a transparent legal framework for the effective implementation of one of the three objectives of the CBD: the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilisation of genetic resources.
- It establishes a framework that helps researchers access genetic resources for biotechnology research, development, and other activities, in return for a fair share of any benefits from their use.
- This provides the research and development sector with the certainty they need to invest in biodiversity-based research.
- Indigenous and local communities may receive benefits through a legal framework that respects the value of traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources.




