Today’s Current Affairs: 9th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Carbon Farming : Technique To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emission

Some techniques within carbon farming can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- By adopting carbon-smart farming methods, we can simultaneously meet food demands and combat climate change.
- Carbon farming also known as carbon sequestration refers to a set of practices aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture and land use.
- It aimed at storing carbon in the soil, crop roots, wood, and leaves.
Techniques in Carbon Farming:
- Rotational Grazing: This involves moving livestock between pastures to allow vegetation to recover, enhancing soil carbon storage.
- Agroforestry: Incorporating trees and shrubs into farming systems to sequester carbon in vegetation.
- Conservation Agriculture: Practices like zero tillage, crop rotation, and cover cropping to minimize soil disturbance and improve organic content.
- Integrated Nutrient Management: Using organic fertilizers and compost to promote soil fertility and reduce emissions.
- Livestock Management: Optimizing feed quality and managing animal waste to lower methane emissions.
Border Roads Organisation : 65th Raising Day

The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) celebrated its 65th Raising Day on 7th May 2024.
- Established in 1960 with only two projects, Project Tusker (now Vartak) in the East and Project Beacon in North India, the BRO has grown to become a vibrant organisation with 18 projects operating in 11 States and three Union Territories.
- It is now recognised as the leading infrastructure construction agency in high-altitude and difficult snow-bound areas.
- In 2023-24, the BRO completed 125 infrastructure projects, including the construction of the Sela Tunnel in Arunachal Pradesh on Balipara-Chardwar-Tawang Road.
- The BRO will soon start construction on the 4.10-km long Shinkun La Tunnel, which will become the world’s highest tunnel at 15,800 ft once completed, bypassing China’s Mila Tunnel at 15,590 ft.
- The BRO is an Indian executive force under the Ministry of Defence, to secure India’s borders and develop infrastructure in remote areas of the north and north-eastern states.
- It operates under the Border Roads Development Board (BRDB) and is responsible for road networks in border areas and neighbouring countries.
- The motto of BRO is “Shramena Sarvam Sadhyam”, which translates to “Everything is achievable through hard work.”
SPACE For Indian Navy:

Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has set up a premier testing & evaluation hub for SONAR Systems named “SPACE” in Kerala which is dedicated to the Indian Navy.
- It stands for Submersible Platform for Acoustic Characterisation and Evaluation (SPACE).
- It will mainly be utilised for evaluation of complete Sonar Systems. It consists of two distinct assemblages.
- Floating Part is a platform which floats on the water surface, and
- Submerged Part is a submersible platform which can be lowered to any depth upto 100 m using winch systems.
- Upon completion of operations, the submersible platform can be winched up and docked with the floating platform.
- It will allow quick deployment and easy recovery of scientific packages such as sensors and transducers.
- It will be suitable for survey, sampling, and data collection of air, surface, mid-water, and reservoir floor parameters using modern scientific instrumentation.
- It will bring a new era of Anti-Submarine Warfare research capabilities.
SONAR (SOund Navigation And Ranging):
- It is a device used for measuring distance using ultrasonic waves.
- The sonar technique is used to determine the depth of the sea and to locate underwater hills, valleys, submarines, icebergs, sunken ships etc.
Gaia BH3: Massive Black Hole

Astronomers have discovered a massive Black Hole in our Galaxy, named “Gaia BH3”.
- It’s the 2nd-closest known Black hole to Earth. It is 33 times heavier than the sun and the most massive black hole of stellar origin in the Milky Way, surpassing Cygnus X-1.
- Stellar black holes are formed as a result of the collapse of a single star.
- Black holes are extraordinarily dense objects with gravity so strong that not even light can escape, making it difficult to spot them.
- They are formed when a massive star collapses in on itself at the end of its life, creating an incredibly dense object with a gravitational pull that is so strong that it warps space-time around it.
- Supermassive Black Hole masses ranging from millions to billions of times that of the sun, found at the centres of most galaxies including our own Milky Way galaxy.
China’s Chang’e-6 Mission : Launched Successfully

China’s Chang’e-6 mission, launched successfully, aims to collect rocks from the Moon’s far side, a complex endeavour requiring precise planning.
- Chang’e-6, China’s mission to the Moon’s far side, aims to retrieve 2 kilograms of samples, a feat never accomplished before. Unlike the Chang’e-5 mission, which brought back samples from the near side in 2020, this mission targets the unexplored territory of the far side.
- The spacecraft, equipped with a communications satellite called Queqiao-2, will land in the South Pole-Aitken basin, the Moon’s largest impact basin.
West Nile Fever : Cases In Three Districts Of Kerala

Kerala’s health department recently reported West Nile fever cases in three districts.
- West Nile Fever is a disease caused by the West Nile Virus (WNV).
- WNV is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
- Birds are the natural hosts of WNV.
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- It can cause a deadly neurological disease in humans.
- It is named after the West Nile district of Uganda, where it was first identified in 1937.
- It is most commonly spread to people by the bite of an infected mosquito. The mosquitoes get the virus when they bite an infected bird.
- There is no evidence that WNV can be spread directly from one person to another.
- But there have been a few cases where it has spread through organ transplants.
- Symptoms:
- Most people infected by the virus are asymptomatic (no symptoms).
- Symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, body aches, nausea, vomiting, occasional skin rash, and swollen lymph glands.
- Treatment: There is no medicine or vaccine available against the WNV.
- Treatment is based on supportive care involving hospitalisation, intravenous fluids, respiratory support, and prevention of secondary infections.
Pyrenees Mountains:
The French President recently hosted Chinese President Xi Jinping at the Tourmalet Pass in the Pyrenees for private meetings
- Pyrenees Mountains are a chain of mountains in southwestern Europe that form a natural border between Spain and France.
- It is a fold mountain chain created by the continental collision of the microcontinent of Iberia with the massive Eurasian plate.
- They are quite old mountains in comparison to the Alps.
- It extends for about 500 km from the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea in the east to the Bay of Biscay (Atlantic Ocean) in the west.
- Politically, it is divided into the Spanish and French Pyrenees.
- The tiny country of Andorra is found sandwiched between them, in the eastern part of the Pyrenees Mountains.
- It separates the rest of continental Europe from the Iberian Peninsula.
- The western end of the Pyrenees Mountains merges with the Cantabrian Mountains, located in the northern part of the Iberian Peninsula.
- Located in Spain, Aneto Peak, is the highest mountain peak in the Pyrenees Mountains (3,404 m).
Spektr-RG:

Astronomers report the discovery of a new pulsar using the Spektr-RG space observatory.
- Spektr-Rentgen-Gamma (Spektr-RG, SRG) is a German-Russian high-energy astrophysics space observatory to study the universe in the X-ray range of electromagnetic radiation.
- It was launched on July 13, 2019, on a Proton-M rocket from the cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan.
- It moves along a so-called halo orbit around the outer Lagrange point (L2) of the Sun-Earth system at a distance of 1.5 million km from the Earth with a period of about 6 months.
- A Lagrange point is a position in space where the gravitational pull of two large masses precisely equals the centripetal force required for a small object to move with them.
- The primary instrument of the mission is eROSITA, built by the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE) in Germany.
- It is designed to conduct a seven-year X-ray survey, the first in the medium X-ray band less than 10 keV energies, and the first to map an estimated 100,000 galaxy clusters.
- This survey may detect new clusters of galaxies and active galactic nuclei.
- The second instrument, ART-XC, is a Russian high-energy X-ray telescope capable of detecting supermassive black holes.
- It is intended to replace the Spektr-R, known as the “Russian Hubble”.
- Spektr-R was launched in 2011 to observe black holes, neutron stars, and magnetic fields, aiding understanding of cosmic expansion.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation:

The CDSCO has become the sole authority for issuing manufacturing licences for new drugs meant for exports, withdrawing the power from state governments amid heightened global scrutiny of Indian made drugs.
- Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India for the medical devices industry under the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- It is responsible for overseeing the import, manufacture, sale, and distribution of medical device in the country.
- The CDSCO ensures that medical devices comply with safety, quality, and efficacy standards.
- It works under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) is the head of the CDSCO.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for,
- Approval of new drugs;
- Conduct of clinical trials;
- Laying down the standards for drugs;
- Control over the quality of imported drugs in the country;
- Coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations;
- CDSCO, along with state regulators, is jointly responsible for the grant of licenses for certain specialized categories of critical Drugs such as blood and blood products, I. V. Fluids, Vaccine, and Sera.
- The CDSCO conducts inspections and audits to ensure that medical device companies are complying with regulations related to safety, quality, and efficacy.
Leber Congenital Amaurosis:
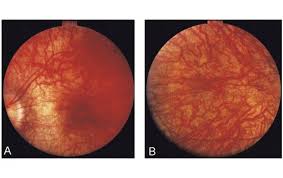
Researchers have used a CRISPR-Cas9 tool to restore vision in a group of adults and children with congenital blindness known as Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA).
- Leber Congenital Amaurosis is a rare genetic eye disorder affected infants are often blind at birth. Children born with LCA have light-gathering cells (rods and cones) of the retina that do not function properly.
- It affects about one in 40,000 people and causes severe vision loss at an early age.
- This blindness is caused by a gene mutation that prevents a protein from functioning properly.
- That protein CEP290 is critical for sight.
- Scientists used a human gene editing tool, CRISPR-Cas9, to restore vision of people who are affected by this disorder and the trial was called “BRILLIANCE”.
- Participants in the study received a single dose of a CRISPR gene therapy called EDIT-101.
- In the case of EDIT-101, the treatment cuts out the mutation in CEP290 and inserts a healthy strand of DNA back into the gene.
- This restores normal function of the protein CEP290, allowing the retina to detect light.
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence.
Interactive Voice Response System:

Voters are receiving Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) calls every day from political parties.
- Interactive Voice Response System is an automated telephone system technology that enables callers to receive or provide information, or make requests using voice or menu inputs, without speaking to a live agent.
- It is powered by a pre-recorded messaging or text-to-speech technology with a dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) interface.
- It prompts callers to use a touch-tone keypad selection to access information. For example, a pre-recorded message might say, “Press one for store hour information,” and the caller would respond with “one.”
- It provides specific verbal prompts to callers depending on their inquiry.
- It uses speech recognition to better understand user requests.
- A well designed IVR software system can help increase customer satisfaction and improve contact center operations and KPIs.
- Particularly during times of high call volume, an effective interactive voice response system can help avoid hold time by helping customers find answers.
- These systems are incredibly cost-effective.
- They not only reduce high call volumes for customer service representatives
- It has been utilized across a wide variety of industries like: Banking, Customer service, education, Health care, travel etc.
Glyptothorax punyabratai:

The ICAR-NBFGR discovered a new catfish species in the pristine waters of Arunachal Pradesh, India and named it as Glyptothorax punyabratai.
- The ICAR-NBFGR discovered a new catfish species in the pristine waters of Arunachal Pradesh, India and named it as Glyptothorax punyabratai.
- The species was collected from Tung Stream, a tributary of the Tissa River, in the Brahmaputra River basin. It is a new catfish species.
- Catfish represent one of the largest groups of freshwater fishes, with more than 2000 species.
- Most catfish are found in freshwater but a few are marine. Most species of catfish are nocturnal.
- Catfish are primarily benthic or bottom-dwellers.




