Today’s Current Affairs: 8th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
FWD-200B : India’s First Indigenous Bomber UAV Aircraft

India’s first indigenous bomber UAV aircraft, the FWD-200B, developed by Flying Wedge Defence, an Indian defence and aerospace company, was unveiled recently.
- FWD-200B is an indigenous military grade bomber unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). It is India’s first indigenous unmanned bomber aircraft.
- It is designed and manufactured by Flying Wedge Defence and Aerospace Technologies, an Indian defence and aerospace company.
- It has a payload capacity of 100 kg and is classified as a MALE (medium-altitude, long-endurance) Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle.
- The Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) consists of optical surveillance payloads and is integrated with missile-like weapons for precision air strikes.
- It has a maximum speed of 370 kmph (200 knots), an endurance capacity of 12 to 20 hours, and a ground control station range of 200 km.
Choline : Study

Researchers recently discovered that an essential nutrient called choline is transported into the brain by a protein called FLVCR2.
- It is an essential nutrient that supports various bodily functions, including cellular growth and metabolism.
- It exists as both water-soluble and fat-soluble molecules. The body transports and absorbs choline differently depending on its form.
- The body can also produce small amounts of choline on its own in the liver, but not enough to meet daily needs.
- As a result, humans must obtain some choline from the diet.
- The richest dietary sources of choline are meat, fish, dairy, and eggs. Many fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain choline as well.
- It is a constituent of an important class of lipids (fats) called phospholipids (e.g., lecithin), which form structural elements of cell membranes.
- Therefore, all plant and animal cells need choline to preserve their structural integrity.
- It serves as a source of the methyl groups (―CH3 groups), which are required in various metabolic processes.
- Choline is also required to clear cholesterol from your liver.
- Deficiencies cause fat and cholesterol accumulation in your liver, which puts you at risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Fusobacterium nucleatum : New Study
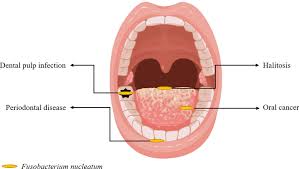
In a new study, a group of researchers has identified a distinct subtype of the Fusobacterium nucleatum that’s found in relatively greater quantities in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumours.
- Fusobacteria are Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli with species-specific reservoirs in the human mouth, gastrointestinal tract and elsewhere.
- It has long been considered as an opportunistic pathogen given its frequent isolation and identification in anaerobic samples from patients with different infections.
- The researchers first analyzed the genomes of F. nucleatumtypes taken from human colorectal tumors and from the mouths of people without cancer. Out of its several known subspecies, only one, called nucleatum animalis (or Fna), was routinely found in the tumor samples.
- Additional genetic analyses revealed that Fna could be divided even further, into two separate groups.
- While both groups were found in about equal proportions in the mouth, only one, dubbed Fna C2, was found in colorectal tumor samples in substantial numbers.
- Fna C2’s higher resistance to acid, which could allow it to potentially reach the intestines directly from the mouth, through the stomach.
- Fna C2 also had the ability to hide inside certain tumor cells, which could protect it from the immune system.
- And it was able to use nutrients found in the gastrointestinal tract, which are very different from those found in the mouth.
Chloropicrin : Chemical Weapon

The U.S. State Department accused Russia of using chemical agent chloropicrin in Ukraine which is a violation of the Chemical Weapons Convention.
- Chloropicrin is a chemical compound which is also known as nitrochloroform. It is used both as a warfare agent and pesticide. It is a colourless to yellow oily liquid.
- It is used broadly as a fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, nematicide and antimicrobial.
- It is an irritant with characteristics of a tear gas. It has an intensely irritating odour and can be absorbed through inhalation, ingestion and the skin.
- It was first made for use as a poison gas in the First World War, by both the Allied and the Central Powers.
- It’s manufactured in a chemical reaction involving sodium hypochlorite (which in dilute form is called bleach) and nitromethane (a common industrial solvent).
- It can also be made by combining chloroform with nitric acid, which yields chloropicrin and water.
- Chloropicrin has documented irritating and tears-inducing effects on humans, and is also known to be highly toxic and carcinogenic and also induce vomiting.
Chemical Weapons Convention: It is a multilateral treatythat bans chemical weapons and requires their destruction within a specified period of time. It entered into force on April 29, 1997.
Cyclone Hidaya:

A severe storm named Cyclone Hidaya is set to hit the coast of Tanzania near Dar es Salaam from the Indian Ocean.
- Cyclone Hidaya (Guidance in Arabic), may bring heavy rain and strong winds to regions in Tanzania like Tanga, Morogoro, the islands of Unguja and Pemba.
- It formed over the South Indian Ocean and was named by France’s overseas tertiary in the Indian Ocean.
- Even though Kenya is usually considered safe from cyclones, now it is preparing for the impact of Cyclone Hidaya.
- Kenya falls within the latitude of 4° North and South and is considered safe from cyclones because they typically don’t form within 5 degrees of the equator due to the weak Coriolis force there, which is necessary for creating cyclones.
- Tropical cyclones usually develop in areas between 5° and 30° North or South of the equator.
- Kenya now faces the possibility of being impacted by Cyclone Hidaya.
Drip Pricing:

The Centre recently warned about “drip pricing”, saying it can surprise consumers with “hidden charges”.
- The Department of Consumer Affairs asked consumers to reach out to NCH 1915 for assistance or via WhatsApp at if they need help with ‘drip pricing’.
- Drip pricing is a pricing technique used by firms where they initially advertise only part of a product’s price referred to as the “headline price”.
- As the customer proceeds through the buying process, additional charges are gradually revealed.
- This technique can lead to “hidden charges” that surprise consumer.
7th India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee:

The recent 7th India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee (JDCC) meeting highlights the ongoing efforts of both nations to bolster their defence collaboration.
- Progress on various bilateral defence cooperation initiatives was reviewed, including those deliberated in meetings of Working Groups on Defence Cooperation and Defence Industries Cooperation.
- Means to enhance existing collaboration, particularly in defence industry ties, maritime security, and multilateral cooperation, were identified.
- JDCC is an annual meeting between the Indian and Indonesian Defence Ministries, discussing a wide range of bilateral cooperation.
- India and Indonesia upgraded their strategic partnership to a “Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2018, and also signed a Defence Cooperation Agreement, aligned with a shared vision of the Indo-Pacific.
- Indonesia is a crucial partner in India’s Act East Policy and holds significance in the Indo-Pacific region.
Rat Hole Mining : Death Of Six Workers

Authorities were given four weeks by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) to respond in a case related to the death of six workers in a rat-hole coal mine fire in Nagaland’s Wokha district.
- Rat-Hole Mining named for its resemblance to rodent burrows, is an illegal and highly hazardous method of extracting coal prevalent in certain pockets of India, particularly the state of Meghalaya.
- Unlike large-scale mechanised mines, this practice involves digging narrow, horizontal tunnels barely large enough for a single person to squeeze through.
- These tunnels, often referred to as “rat holes,” can extend tens of meters underground.
- Miners descend precariously using ropes, bamboo ladders, or makeshift supports and work in cramped, poorly ventilated conditions with basic tools like pickaxes and shovels.
- The extracted coal is then hauled back up through these narrow passages, making the entire process incredibly dangerous and backbreaking.




