Today’s Current Affairs: 19th June 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Aedes Albopictus Mosquito : Study

Warmer conditions are helping the Aedes albopictus mosquito, which transmits dengue, chikungunya and Zika viruses thrive, said the EU health agency.
- Climate change is expected to significantly impact the spread of dengue in Europe.
- Rising temperatures and increased rainfall create more favorable conditions for the spread of the disease, particularly in areas where the Aedes albopictus mosquito is present.
- In southern Europe, particularly in Spain, Italy, and France, the risk of dengue is expected to increase due to the presence of Aedes albopictus and the rising temperatures and humidity.
- However, in some countries like Spain and Portugal, the expected rise in summer droughts may decrease habitat suitability for Aedes albopictus.
Aedes albopictus mosquito:
- The Aedes albopictus mosquito, commonly known as the Asian tiger mosquito, is a highly invasive species known for its distinctive black and white striped appearance.
- This mosquito is a known vector for several diseases, including: Dengue fever, Chikungunya, Zika virus, Yellow fever.
Joint Communique On a Peace Framework:

Only proposals acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine can lead to peace, said India as New Delhi decided to disassociate itself from the final document issued on June 16 at the conclusion of a Peace Summit in Switzerland.
- The ongoing war in Ukraine, initiated by the Russian Federation, continues to cause significant human suffering and global crises.
- A high-level summit was held in Switzerland on 15-16 June 2024 to discuss pathways to a comprehensive, just, and lasting peace for Ukraine.
- Attendees reaffirmed their commitment to international law and the United Nations Charter, referencing resolutions A/RES/ES-11/1 and A/RES/ES-11/6 from the UN General Assembly.
- Ensuring the safe operation of Ukraine’s nuclear power plants, including Zaporizhzhia, under Ukraine’s sovereign control and in line with IAEA principles. Any threat or use of nuclear weapons in the conflict is unacceptable.
- Emphasizing the importance of uninterrupted food production and supply, safe navigation, and access to sea ports.
- Attacks on merchant ships and port infrastructure are unacceptable, and Ukrainian agricultural products should be freely provided to other countries.
- Calling for the release of all prisoners of war through complete exchange and the return of all unlawfully displaced Ukrainian children and civilians.
Matsya 6000:

India set to be the 6th country to have its own Deep Sea Mission; 1st Stage of harbor trail (40-50m) deep of deep sea mission planned by September 2024; The Mission has the potential to contribute greatly to the overall growth of Indian economy
- The Matsya 6000 is a three-person submersible that will be able to go 6,000 metres under the sea.
- The vessel is being developed by Chennai’s National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT).
- Made of 80mm-thick titanium alloy, it will be able to withstand a pressure 600 times greater than that at sea level. The
- Matsya 6000 will be able to operate from 12 to 16 hours straight and will have an oxygen supply of 96 hours.
National Institute of Ocean Technology:
- It was established in November 1993 as an autonomous society under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- Objectives to develop reliable indigenous technologies to solve the various engineering problems associated with harvesting of non-living and living resources in the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), which is about two-thirds of the land area of India.
Deep Sea Mission:
- The Deep Ocean Mission (DOM) is an ambitious Indian initiative to explore and harness the depths of the ocean.
- It is a five-year mission, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2021, with a budget of nearly ₹4,077 crore.
- The mission aims to develop technologies for deep-sea mining, manned submersibles, and underwater robotics, as well as for ocean climate change advisory services, deep-ocean survey and exploration.
SDG 7: Energy Progress Report 2024

SDG 7: Energy Progress Report 2024, released recently, finds that the world remains off course to achieve Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 7 for energy by 2030.
Highlights of 2024 Report:
- The latest report confirms that the number of people without access to electricity increased for the first time in over a decade, as population grew—mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa—at a higher rate than that of new electricity connections, leaving 685 million people without electricity in 2022, 10 million more than in 2021.
- The world remains off track to achieve universal access to clean cooking by 2030.
- 1 billion people still live without access to clean cooking fuels and technologies, largely in Sub-Saharan Africa and Asia.
- Renewable electricity consumption grew more than 6% year-on-year in 2021, bringing the share of renewables in global electricity consumption to 28.2%.
- Installed renewable energy-generating capacity per capita reached a new record in 2022 at 424 watts per capita globally.
- However, considerable disparities exist. Developed countries (at 1,073 watts per capita) have 3.7 times more capacity installed than developing countries (at 293 watts per capita).
- It warns that current efforts are not enough to achieve SDG 7 on time.
- Between 2010 and 2021, India, along with China and Indonesia, achieved significant advancements in modern renewable energy use.
- Between 2010 and 2021, India recorded one of the highest increases in the use of modern renewable energy, with the share of renewables in total final energy consumption (TFEC) rising by nearly 7 percentage points.
- India’s transition to renewable energy has been bolstered by substantial international financial support.
- In 2022, the country received a notable USD 627 million for 47 renewable energy projects, many of which were valued at less than USD 1 million.
- A significant portion of this funding came from Germany and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
- India’s role in renewable energy extends to the transportation sector, where it, alongside the United States, Brazil, Europe, and China, accounts for 85 percent of renewable energy use.
Exercise Red Flag 2024:

An Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent participated in the Exercise Red Flag 2024 conducted at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska of the United States Air Force, from 04 Jun to 14 Jun 24.
- This was the second edition of Ex Red Flag 2024, which is an advanced aerial combat training exercise, held four times in a year by the US Air Force.
- Participation of the Indian Air Force along with Republic of Singapore Air Force (RSAF), Royal Air Force (RAF) of the United Kingdom, Royal Netherlands Air Force (RNLAF), German Luftwaffe, and the US Air Force (USAF).
- Red Flag is an air combat exercise featuring realistic combat scenarios. Forces are divided into Red Force (simulating Air Defence, primarily with USAF Aggressor Squadron’s F-16 and F-15 aircraft) and Blue Force (simulating Offensive Composite elements).
- This year marked the debut of the Indian Air Force’s Rafale aircraft in the exercise, operating alongside RSAF and USAF F-16s, F-15s, and A-10s.
- The missions included Beyond Visual Range combat exercises in Large Force Engagements, focusing on Offensive Counter Air and Air Defence roles.
Pantanal Wetland:

Fires in Brazil’s Pantanal wetlands have surged nearly tenfold so far this year to the highest levels since 2020.
- Pantanal Wetland is the world’s largest tropical wetland.
- It is located in the upper Paraguay River basin, the Pantanal straddles Brazil’s border with Bolivia and Paraguay.
- About 80 percent of the Pantanal is in Brazil.
- It’s a 185,000-square-kilometer (71,000-square-mile) mosaic of grassland swamps fed by rivers, streams and seasonal floods and dense, low-forested savanna.
- It was developed in a structural basin formed as the Andes Mountains rose.
- The climate is tropical, wet and dry.
- It is one of the most biologically rich environments on the planet, with more than 4,700 plant and animal species.
- Noteworthy animals include the jaguar, giant otter, giant armadillo, marsh deer, pampas deer and hyacinth macaw (the biggest parrot on the planet).
- It has the largest concentration of crocodiles in the world, with approximately 10 million caimans.
- In 2000, the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared a small portion of the Pantanal a World Heritage Site.
- Around 95% of the Pantanal is under private ownership, the majority of which is used for cattle grazing.
Hindu Kush Himalaya:
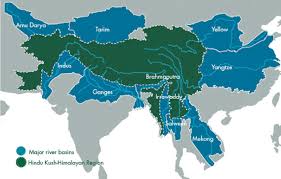
A recent report by the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) analysed data on snow persistence from 2003 to 2024 and found it to be significantly lower than normal in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) this year.
- Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region stretches 3,500 kilometres and spans eight countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal and Pakistan.
- The range has numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir or Terichmir at 7,708 meters (25,289 ft) in Chitral, Pakistan.
- It is considered the Third Pole(after the North and South Poles) and has significant implications for climate.
- It contains the largest volume of ice and snow outside of the Arctic and Antarctica.
- The HKH region is the source of ten large Asian river systems: the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra, Irrawaddy, Salween, Mekong, Yangtse, Yellow River, and Tarim.
- The basins of these rivers provide water to 1.9 billion people, a fourth of the world’s population.
- HKH may be divided into three main sections: the eastern Hindu Kush, the central Hindu Kush, and the western Hindu Kush, also known as the Bābā Mountains.
- The inner valleys of the Hindu Kush see little rain and have desert vegetation.
Dead Zone:
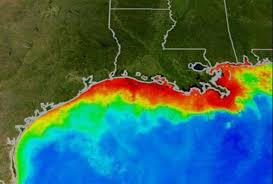
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is forecasting an above-average summer “dead zone” in the Gulf of Mexico covering approximately 5,827 square miles.
- The term “dead zone” or “hypoxia” refers to low-oxygen areas in the world’s lakes and oceans.
- Because most organisms need oxygen to live, few organisms can survive in hypoxic conditions.
- That is why these areas are called dead zones.
- Hypoxic zones can occur naturally, but human activities can also lead to the creation of new dead zones or the enhancement of existing ones.
- Dead Zone occurs as a result of eutrophication, which happens when a body of water is inundated with too many nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen.
- At normal levels, an organism called cyanobacteria – or blue-green algae – feeds on these nutrients.
- With too many nutrients, it can cause an overgrowth of algae in a short period of time, also called algae blooms.
- Dead zones form when the algae die, sink to the bottom, and are decomposed by bacteria—a process that strips dissolved oxygen from the surrounding water.
- Dense algal blooms also block sunlight, which prevents underwater grasses from growing.
- In turn, the animals that depend on these grasses for food and shelter suffer, as well.
- Human activities mainly cause these excess nutrients to be washed into the ocean, which is why dead zones are often located near inhabited coastlines.
New Supernova : SN 2023adsy

Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers recently discovered a new supernova, designated SN 2023adsy, the most distant Type Ia supernova so far detected.
- Supernova is the name given to the cataclysmic explosion of a massive star.
- Supernovas are the largest explosions that take place in space.
- A star can go supernova in one of two ways:
- Type I supernova: A star accumulates matter from a nearby neighbour until a runaway nuclear reaction ignites. They’re typically called Type Ia supernovae.
- Type II supernova: A star runs out of nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity.
- Supernovas can briefly outshine entire galaxiesand radiate more energy than our sun will in its entire lifetime.
- They’re also the primary source of heavy elements in the universe.
- On average, a supernova will occur once every 50 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way.
- The oldest recorded supernova is RCW 86, which Chinese astronomers spotted in A.D. 185.
- After a supernova, a few different things can happen.
- Sometimes the exploded star will partially collapse into a black hole or a neutron star and the rest of the mass will get converted into energy or will be blown away by the force of the explosion.
- This blown-away material is sometimes called a “supernova remnant,” which is a type of nebula.




