Chikungunya : Outbreak
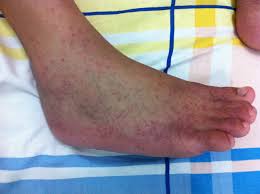
The chikungunya outbreak in Pune and nearby regions has been traced to the Indian Ocean lineage of the virus, according to scientists at the National Institute of Virology (NIV).
- Chikungunya is a viral diseasetransmitted to humans through the bites of mosquitoes infected with the chikungunya virus.
- The word comes from the African Makonde language and means “bent over in pain.”
- It is most commonly transmitted by mosquitoes, Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti and Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus, which can also transmit dengue and Zika viruses.
- It is not spread from person to person.
- It was first described during an outbreak in southern Tanzania in 1952 and has now been identified in nearly 40 countries in Asia, Africa, Europe and the Americas.
- Symptoms usually begin 4 to 8 days after a mosquito bite but can appear anywhere from 2 to 12 days.
- The most common symptom is an abrupt onset of fever, often accompanied by joint pain.
- Other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash.
- Serious complications are uncommon, but atypical severe cases can cause long-term symptoms and even death, especially in older people.
- There is currently no approved vaccine or specific treatmentfor chikungunya virus infections.




