Today’s Current Affairs: 10th February 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
HbA1c Test:

A new study has found that glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), a laboratory test commonly used in India for detecting type-2 diabetes, may not accurately reflect blood glucose levels.
- A hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) test is a blood test that shows average level of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past two to three months.
- An A1C test measures the percentage of RBCs that have glucose-coated hemoglobin.
- An A1C test can show average glucose level for the past three months because:
- Glucose sticks to hemoglobin for as long as the RBCs are alive.
- RBCs live about three months.
- High A1C levels are a sign of high blood glucose from diabetes.
- Diabetes can cause serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
- With treatment and lifestyle changes, blood glucose levels can be controlled.
SCALP Missile:

India and France are in discussions to finalise a major deal for the procurement of SCALP cruise missiles, following their successful use by the IAF in precision strikes against terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan during Operation Sindoor last year.
- The SCALP missile, also known as Storm Shadow, is a long-range, air-launched cruise missile.
- It was developed together by France and the United Kingdom.
- It is in service with multiple NATO and allied air forces.
- It is powered by turbojet engines and has a range of 250 km.
- The missile has a tandem warhead configuration, comprising a shaped charge for initial penetration and a secondary high-explosive charge for enhanced lethality.
- Capable of night and all-weather operations, SCALP is particularly effective for penetrating hardened bunkers and ammunition stores.
Himalayan Griffon:

The Himalayan Griffon Vulture- which is usually found in the high-altitude region and migrates to Indian states, was recently spotted in Melghat in the Amravati district of Maharashtra due to the presence of recently released captive-bred vultures.
- It is one of the nine species of vultures found in India.
- It is a type of Old World Vulture.
- Scientific Name: Gyps himalayensis
- It is found along the Himalayas and the adjoining Tibetan region and is also found in the Central Asian mountains.
- Occasionally it migrates to northern India, but migration usually only occurs altitudinally.
- These are monogamous, and pairs return to the same nesting and roosting sites from year to year.
- Nests are built on ledges or in small caves.
- These are diurnal and mostly solitary
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened.
Kimberley Process:

India has assumed the chair of the Kimberley Process (KP) for the year 2026.
- It is a coalition of governments, civil society and the diamond industry to eliminate the trade in so-called conflict diamonds.
- Conflict diamonds are defined by the relevant United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSC resolution 1459) as “rough diamonds used by rebel movements or their allies to finance conflict aimed at undermining legitimate governments”.
- Based on a mandate from the United Nations, the Kimberley Process regulates the international trade in rough diamonds.
- Participants in the scheme are required to:
- Satisfy ‘minimum requirements’ and establish national legislation, institutions and import/export controls;
- Commit to transparent practices and to the exchange of critical statistical data;
- Trade only with other participants in the Scheme;
- Certify shipments as conflict-free.
- Currently it has 60 participants, representing 86 countries (with the EU as a single participant) which account for more than 99% of the global rough diamond production and trade.
- The KP meets twice a year at the Intersessional and Plenary meetings. It is chaired by a participating country on an annual, rotating basis.
- As a consensus-based body, the KP relies on the constructive engagement from all participants of the tripartite structure.
- Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) is the mechanism the KP uses to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds.
- Under this scheme, the Government implements safeguards on shipments of rough diamonds and certifies the diamond as conflict-free.
- According to this Scheme, each rough diamond shipment must be accompanied by the Kimberley Process certificate and transported in a tamper-resistant container.
- The KP certificate states the authenticity of the rough diamond.
- Since 2003, India has been actively participating in the KPCS process.
- The Department of Commerce is the nodal Department.
- Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) is designated as the KPCS Importing and Exporting Authority in India.
- GJEPC is responsible for issuing KP Certificates and is also the custodian of KP Certificates received in the country.
Mons Mouton:

Scientists from ISRO’s Space Applications Centre (SAC) have identified a landing zone in the rugged south polar region of the Moon called Mons Mouton for India’s first lunar sample return mission, Chandrayaan-4.
- Mons Mouton is a mountain located near the South Pole of the Moon.
- Its peak is largely flat, which is favorable for landing.
- It is situated in the South Circumpolar Region (SCR) of the Moon.
- It is believed to be positioned on the rim of the South-Pole-Aitken basin (the largest and most ancient impact basin on the Moon).
- This area is also important because it receives sunlight for a long time.
- The Mons Mouton area is of particular scientific interest because it lies near permanently shadowed craters believed to contain water-ice deposits.
- Studying samples from this region could help scientists better understand the Moon’s geological history and the distribution of lunar resources.
- Radio communication with Earth also remains clear from this region, which prevents any major contact issues during the mission.
Ethylene Glycol:
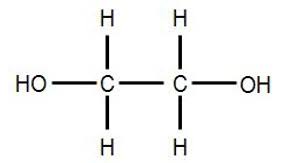
The government of Tamil Nadu issued a public notice against a batch of Almond Kit syrup, after laboratory tests detected adulteration with ethylene glycol.
- It is the simplest member of the glycol family of organic compounds.
Properties: - It is a colourless, odourless, slightly viscous liquid with a faintly sweet taste.
- It mixes easily with water and alcohol, does not evaporate quickly.
- It remains stable over a wide temperature range, and is inexpensive to manufacture.
- Ethylene glycol metabolism produces toxic metabolites that can cause significant morbidity and mortality if left untreated.
- It is used to make antifreeze and de-icing solutions for cars, airplanes, and boats.
- It is also used in hydraulic brake fluids and inks used in stamp pads, ballpoint pens, and print shops.
- It is also used as a reagent in making polyesters, explosives, alkyd resins, and synthetic waxes.
Swavalambini Scheme:

The Minister of State (Independent Charge), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship informed the Lok Sabha about the Swavalambini Scheme.
- It is a woman Entrepreneurship Programme which empowers young women with the skills and confidence needed to establish their own businesses.
- It introduces a structured, multi-stage training approach to help young women transition from ideation to successful enterprise creation.
- It aims to cultivate an entrepreneurial mindset among female students, equipping them with awareness of available support mechanisms, schemes, resources and networks essential for pursuing entrepreneurship as a career.
- It is implemented through National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD), Noida and Indian Institute of Entrepreneurship (IIE), Guwahati.
- Target group: 1200 female students from Higher Educational Institutes (HEIs) and Universities
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP): The female students undergo introductory programme on entrepreneurial awareness through entrepreneurial awareness programme.
- Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): It covers business aspects like skilling, finance, market linkages, compliance, and networking
- This is followed by mentorship and handholding support to help participants translate their ideas into sustainable enterprises.
- Support: MSDE will oversee the execution, supervision, and monitoring of the programme.
- NITI Aayog will provide mentoring support, facilitate seed funding, and recognize successful entrepreneurs through the Award To Reward (ATR) initiative.
Giant Phantom Jellyfish:
Scientists on a month-long deep-sea expedition off Argentina’s coast documented a rare giant phantom jellyfish recently.It is a rare and mysterious deep-sea jellyfish known for its ghostly, translucent appearance.It is among the largest jellyfish.Scientific Name: Stygiomedusa gigantea.It is in the Ulmaridae family.It is believed to be widespread throughout the world’s oceans, except in the Arctic Ocean.Unlike most jellyfish, it lacks tentacles. Instead, they use ribbon-like arms to grab prey, typically plankton or small fish, and pull them into their mouths.
Lyriothemis keralensis : New Species Of Dragonfly
Researchers recently confirmed the discovery of a new species of dragonfly, Lyriothemis keralensis, from the low-lying coastal regions of Kerala.It is a new species of dragonfly.It was discovered in the low-lying coastal regions of Kerala.It is commonly called the Slender Bombardier.Unlike many dragonflies found in forest areas, the Slender Bombardier prefers human-modified landscapes.It thrives in irrigation ecosystems such as pineapple and rubber plantations and is commonly seen in shaded canals and seasonal pools within agricultural areas.It is a seasonal resident, emerging during the monsoon and retreating as rainfall declines.
Kordofan Region:
A drone attack by Sudan’s Rapid Support Forces struck a vehicle carrying displaced families near Rahad in North Kordofan, killing at least 24 people, including eight children and two infants.It is a region constituting the central and southern area of Sudan.The region is divided into three federal states: North Kordofan (capital: El Obeid), South Kordofan (capital: Kadugli), and West Kordofan (capital: Al Fula).Traditionally the area is known for the production of gum Arabic. Most of the people in Kordofan are Arabs. Minorities include the Nubian, Beja, Daju, Zaghawa, and Darfunj peoples.It has been a conflict-prone area, especially since Sudan’s civil wars.It is a strategic region due to:Proximity to South Sudan,Oil fields in West Kordofan.
Paraleocrates indica : New Species Of Marine Worm
Researchers recently discovered a new species of marine worm named Paraleocrates indica hiding in the muddy banks of the Champa Estuary in the Bay of Bengal.It is a new species of marine worm discovered in the muddy banks of the Champa Estuary in the Bay of Bengal.It marks the first time this rare group of creatures has ever been recorded in Indian waters.It is a type of muddy bristle worm in the family Hesionidae, known for its colourful bodies and often symbiotic relationships with other sea life, such as starfish.
Sahyadri Tiger Reserve:
In a significant boost to tiger conservation in western Maharashtra, a third tigress was released into the wild at the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR) recently.It is located in the Sahyadri Ranges of the Western Ghats in Maharashtra.It is spread over two protected areas of Koyana Sanctuary (KWLS) and Chandoli National Park (CNP).The central portion of STR is occupied by the “Shivsagar” reservoir of the Koyana River and the “Vasant Sagar” reservoir of the Warana River.It is home to the endangered species of top carnivores such as Tiger, Wild dog, and Leopard.
Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project:
India recently started work on the Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project on the River Chenab in Jammu and Kashmir—the first such new project to get the green light from the government after the abrogation of the Indus Water Treaty.It is a 1,856-MW run-of-the-river hydropower project on the Chenab River in the Ramban District of Jammu and Kashmir.The project will be built by the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC).The plant will ensure reliable power supply to the region, particularly during the harsh winter months, when electricity demand peaks and shortages are common.It also has the potential to turn J-K into a power-surplus region, creating scope for exporting surplus energy to the national grid.It is a key part of India’s plan to fully utilise its share of water from the western rivers under the 1960 Indus Waters Treaty (IWT).




