Today Current Affairs: 14th January 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Indu Malhotra Committee:

The Supreme Court has appointed former SC Judge, Indu Malhotra, as the Chairperson to head the inquiry committee, along with other members.
- The inquiry committee will look into the alleged security breach of Prime Minister’s Punjab visit on 5th January this year.
- The committee headed by Justice (Retired) Indu Malhotra will also comprise DG- NIA, DG Security of Punjab and Registrar General of Punjab and Haryana High Court.
- The Apex court has passed the order after hearing a petition filed by NGO, Lawyers Voice, seeking appropriate directions and or orders in the alleged security breach of the Prime Minister, who was on his way to Punjab to address a rally.
The Investor Education And Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA):

The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) has signed a MoU with Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) for promoting Investor Education and Financial literacy among youth by utilizing the tele-lecturing facility of Gyan Darshan Channel.
- This association with IGNOU/Gyan Darshan channel will help in propagating the message of Investor Education and Awareness among a large group of present and prospective stakeholders.
- The panel of resource persons for the lecture series would include experts from professional institutions such as ICAI, ICSI & Senior officials from IEPFA, Ministry of Corporate Affairs and other regulators.
- The proposed lecture series of 75 episodes will be live tele-lecturing series on 24×7 Gyan Darshan TV channel.
- Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) has been established under Section 125 of the Companies Act 2013 for administration of the IEPF fund as per section 125 (3) of Companies Act 2013.
- The main objective of the authority includes to promote Investor Education, Awareness & Protection, refund unclaimed shares, dividends and other amounts transferred to it under sections 124 and 125 of the Companies Act 2013 to the rightful claimants.
- IEPFA works under the administrative control of Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
BrahMos Supersonic Cruise Missile:

An extended range sea-to-sea variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was test fired from stealth guided missile destroyer INS Visakhapatnam.
- BrahMos is a joint collaboration between India and Russia.
- The BrahMos missile was initially developed with a range capped at 290 km.
- The range of the missile was originally capped at 290 km as per obligations of the Missile Technology Control Regime(MTCR).
- However, following India’s entry into the MTCR club in June 2016, the range is planned to be extended to 450 km and to 600km at a later stage.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India (DRDO) and the NPOM of Russia.
- BrahMos is named on the rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva.
- It is a two-stage (solid propellant engine in the first stage and liquid ramjet in second) missile.
- It is a multiplatform missile i.e it can be launched from land, air, and sea and multi capability missile with pinpoint accuracy that works in both day and night irrespective of the weather conditions.
- It operates on the “Fire and Forgets” principle i.e it does not require further guidance after launch.
- Brahmos is one of the fastest cruise missile currently operationally deployed with speed of Mach 2.8, which is nearly 3 times more than the speed of sound.
About INS Viskhapatnam:
- It is the first ship of the four state-of-the-art stealth guided missile destroyers, developed under Project-15B. Other Three Ships of Project 15B:
- The second ship of P15B, Mormugao was launched in 2016, and is being readied for harbour trials.
- The third ship (Imphal) was launched in 2019, and is at an advanced stage of outfitting.
- The fourth ship (Surat) is under block erection and will be launched within this current financial year (2022) .
- The Guided missile Destroyers of Project 15B (P 15B) are under construction at Mazagaon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Mumbai.
S. Somanath: Chairman Of ISRO

Eminent rocket scientist S. Somanath has been appointed Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Space Secretary.
- Somanath is taking over the reins of ISRO at a critical juncture when sweeping reforms and critical missions and projects — the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission included — are waiting in the wings.
- Somanath, at present, has been serving as the Director of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) and the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST).
- Somanath has played a major role in the development of the PSLV and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III (GSLV Mk-III). He joined the GSLV Mk-III project in 2003, and served as Project Director from 2010 to 2014.
- Later on, he had a two-and-a-half-year stint as Director, Liquid Systems Propulsion Centre (LPSC), Valiamala, where he contributed to the development of the indigenous cryogenic stages for the GSLV. Dr. Somanath took over as the Director, VSSC, in January 2018.
India-US Homeland Security Dialogue:

The Senior Officers Meeting of the India-US Homeland Security Dialogue was held in virtual mode.
- The meeting was co-chaired by Home Secretary Ajay Bhalla and Under Secretary for Strategy, Policy and Plans, Department of Homeland Security, Government of USA, Robert Silvers.
- During the meeting, both sides identified further steps that can be taken to explore opportunities and synergies in advancing cooperation in counter-terrorism, cyber security, securing critical infrastructure, maritime security and aviation security among other issues.
- During the meeting, both sides agreed that the existing sub-groups under the Homeland Security Dialogue on law enforcement engagement, securing global supply chains, investigative cooperation, and capacity building would meet separately in the coming months.
- The two sides look forward to holding the Ministerial-level Homeland Security Dialogue later this year.
Swachh Vidyalaya Puraskar (SVP) 2021 – 2022:

Shri Subhas Sarkar, Minister of State for Education virtually launched Swachh Vidyalaya Puraskar (SVP) 2021 – 2022. The schools have been given sufficient time till March 2022 to apply for the awards so that they can do so at an appropriate and safe time.
- The Swachh Vidyalaya Puraskar recognise, inspire and award the schools who have undertaken exemplary work in the field of water, sanitation and hygiene and also provides a benchmark and roadmap for schools to make further improvements in future.
- In order to create self-motivation and awareness about sanitation the Swachh Vidyalaya Puraskar (SVP) was first instituted by the Department of School Education and Literacy, in 2016-17.
- The SVP 2021-22 is open to all categories of schools. i.e. Government, Government aided and Private schools in both rural and urban areas.
- The schools will be assessed through an online portal & mobile app in 6 sub-categories.
- These are: Water, Sanitation, Hand Washing with soap, Operation and Maintenance, Behaviour Change and Capacity Building and the newly added category on COVID-19 Preparedness and Response and the system will generate the overall score and rating automatically.
- Schools shall be awarded at the District, State and National level based on an internationally recognized five star rating system.
- Also, every school will get a certificate of participation showing the category-wise scores and overall rating of the school.
- At the National level, 40 schools will be selected for awards this year under the overall category.
- The award money for the schools has been enhanced this year from Rs. 50,000/- to Rs. 60,000/- per school, under Samagra Shiksha scheme. Also, 6 sub-category wise awards have been introduced for the first time, with award money of Rs. 20,000/- per school.
Africa’s First Transmission PPP Project.:

Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (POWERGRID) has signed a Joint Development Agreement with Africa50, the pan-African infrastructure investment platform to continue to develop the Kenya Transmission Project on a public-private partnership (PPP) basis, Africa’s first transmission PPP project.
- The project entails the development, financing, construction, and operation of the 400kV Lessos – Loosuk and 220kV Kisumu – Musaga transmission lines under a public-private partnership (PPP) framework.
- Once completed, the project will be the first Independent Power Transmission (IPT) in Kenya and will set a reference point in Africa as the first financing of transmission lines on a PPP basis.
- This Project will also improve both the supply and reliability of power transmission in Western Kenya and further create a demonstration effect to help increase private sector investments into the expansion of Africa’s power transmission networks.
- Africa50 is an infrastructure investment platform that contributes to Africa’s economic growth by developing and investing in bankable infrastructure projects, catalyzing public sector capital, and mobilizing private sector funding, with differentiated financial returns and impact.
- Africa50 currently has 31 shareholders, comprised of 28 African countries, the African Development Bank, the Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO), and Bank Al-Maghrib.
ATL Space Challenge 2021:

The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog declared the results of the ‘ATL Space Challenge 2021’.
- The Challenge was launched in collaboration with Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
- The ATL Space Challenge witnessed over 2500 submissions from both ATL and Non-ATL students across the country from which 75 top innovators were selected. It was the first time that an ATL challenge open to both ATL and non-ATL students.
- The ATL Space Challenge 2021 was launched on 6th September 2021 with an objective to enable innovation among young school students to create something in space sector that will not only help them learn about the space but create something that space programme can use itself.
- The Challenge also aligned with the World Space Week 2021, which is observed from 4 to 10 October each year at the global level in order to celebrate the contributions of space science and technology.
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP):

South Korea has said that it regrets India’s absence from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and hopes to see New Delhi rejoin the agreement.
- The RCEP came into effect on January 1, 2022, marking the formation of the world’s largest free trade zone in terms of trade volume.
- India withdrew from the RCEP in 2019 largely because of concerns it would open it up to Chinese goods amid an already wide trade imbalance with China, and the failure of the agreement to adequately open up to services.
- India had “a crucial role” to play in helping the region build an inclusive architecture at a time of increasing global instability.
- Such trade pacts will also give Indian companies a platform to showcase their strengths across even larger markets.
- Besides, Rising U.S.-China tensions were “deeply worrying” for the region with the pandemic resulting in “heightened tension”.
- RCEP is a trade deal between the 10-member Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
- RCEP will cover about 30% of global gross domestic product (GDP), worth $26.2 trillion (€23.17 trillion), and nearly a third of the world’s population, some 2.2 billion people.
- Under RCEP, around 90% of trade tariffs within the bloc will eventually be eliminated.
- RCEP will also set common rules around trade, intellectual property, e-commerce and competition
Gaganyaan Mission:

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently successfully conducted the qualification test of Cryogenic Engine for Gaganyaan programme for a duration of 720 seconds at ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) in Tamil Nadu’s Mahendragiri.
- The performance of the engine met the test objectives and the engine parameters were closely matching with the predictions during the entire duration of the test.
- This successful long-duration test is a major milestone for the Human Space Programme – Gaganyaan. It ensures the reliability and robustness of the cryogenic engine for induction into the human-rated launch vehicle for Gaganyaan.
- Formal announcement of the Gaganyaan programme was made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his Independence Day address on August 15, 2018.
- The initial target was to launch the human spaceflight before the 75th anniversary of India’s independence on August 15, 2022.
- With this launch, India will become the fourth nation in the world to launch a Human Spaceflight Mission after the USA, Russia and China.
- The objective of the Gaganyaan programme is to demonstrate the capability to send humans to low earth orbit on board an Indian launch vehicle and bring them back to earth safely.
- Four Indian astronaut-candidates have already undergone generic space flight training in Russia as part of the Gaganyaan programme.
- ISRO’s heavy-lift launcher GSLV Mk III has been identified for the mission.
North Korean Missile Launches:

The US has imposed its first sanctions over North Korea’s weapons programs following a series of North Korean missile launches.
- These sanctions were aimed both to prevent the advancement of North Korea’s programs and to impede its attempts to proliferate weapons technologies.
- North Korea is continuing its missile program despite several UN Security Council resolutions and the international community’s calls for diplomacy and denuclearization.
- The present-day conflict between the US and North Korea can be traced from the Cold War between the USSR and US.
- After the defeat of Japan in World War II, the Allied forces at the Yalta Conference (1945), agreed to establish a “four-power trusteeship over Korea”.
- The fear of the spread of communism (state ownership over economic resources of a country) and the mutual distrust between the USSR and the US led to the failure of the trusteeship plan.
- Before a concrete plan could be formulated, the USSR invaded Korea.
- This led to a condition where the north of Korea was under the USSR and the south under the rest of the allies, mainly the US.
- The Korean peninsula was divided into two regions by the 38th parallel.
- In 1948 the United Nations proposed free elections across all of Korea.
- The USSR rejected this plan and the northern part was declared as Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea).
- The election took place in the American protectorate resulting in the establishment of the Republic of Korea (South Korea).
- Both North Korea and South Korea tried to enhance their reach, territorially and ideologically, which gave birth to the Korean Conflict.
Rooftop Solar Scheme:

According to the data available on the website of the Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), India could install just 6GW of Rooftop Solar (RTS) power by the end of October 2021 under the rooftop solar scheme.
- Although utility-scale solar has seen tremendous progress with leading players lining up for projects, tariffs spiralling down and government agencies pushing mega projects, RTS has continued to remain neglected.
Rooftop Solar - Rooftop solar is a photovoltaic system that has its electricity-generating solar panels mounted on the rooftop of a residential or commercial building or structure.
- Rooftop mounted systems are small compared to ground-mounted photovoltaic power stations with capacities in the megawatt range.
- Rooftop PV systems on residential buildings typically feature a capacity of about 5 to 20 kilowatts (kW), while those mounted on commercial buildings often reach 100 kilowatts or more.
Rooftop Solar Scheme:
- The major objective of the scheme is to generate solar power through the installation of solar panels on the roof of the houses.
- Also, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has announced the implementation of Phase 2 of the grid-connected Rooftop Solar Scheme.
- The aim of the scheme is to achieve the final capacity of 40 GW from Rooftop Solar Projects by 2022.
- The 40GW goal is part of India’s ambitious target to achieve 175GW renewable energy (RE) capacity that includes 100GW of solar power by 2022.
- According to a report released in September, 2021, the lockdowns slowed renewable energy installations in the country and the pace of such installations is lagging India’s 2022 target.
Global Risks Report 2022:

The Global Risks Report 2022, an annual report, was released by the World Economic Forum. It tracks global risk perceptions among risk experts and world leaders in business, government, and civil society.
- It examines risks across five categories: economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological.
- Impact of Covid-19: The societal and environmental risks have worsened the most since the start of the pandemic.
- “Social cohesion erosion”, “livelihood crises” and “mental health deterioration” are three of the five risks seen as the most concerning threats to the world in the next two years.
- Apart from this, it has significantly contributed to “debt crises”, “cybersecurity failures”, “digital inequality” and “backlash against science”.
- Global Economic Outlook: It majorly perceived the short-term economic outlook to be volatile, fractured, or increasingly catastrophic.
- The most serious challenge persisting from the pandemic is economic stagnation.
- Environmental Risks: “Extreme weather” and “climate action failure”—appear as top risks in the short-, medium-and long-term outlooks.
- Governments, businesses, and societies are facing increasing pressure to transition to net-zero economies.
- Geopolitical and Technological Risks: In the longer-term horizon, geopolitical and technological risks are of concern too—including “geoeconomic confrontations”, “geopolitical resource contestation” and “cybersecurity failure”.
- International Risks: Artificial intelligence, space exploitation, cross-border cyberattacks and misinformation and migration and refugees were rated as the top areas of international concerns.
- Growing insecurity in the forms of economic hardship, worsening impacts of climate change and political persecution will force millions to leave their homes in search of a better future.
- The prospect of 70,000 satellite launches in coming decades, in addition to space tourism, raises risks of collisions and increasing debris in space, amid a lack of regulation.
National Youth Day:

January 12 marks the birthday of Swami Vivekananda.
- National Youth Day is celebrated on this day. Celebrated since 1984.
- The main objective is to promote rational thinking among the youth, believed to be the future of the country.
- Swami Vivekananda was a true luminary, credited with enlightening the western world about Hinduism.
- He was an ardent disciple of Sri Ramakrishna Paramahansa and a major force in the revival of Hinduism in India.
- He pushed for national integration in colonial India, and his famous speech remains as the one that he gave in Chicago in 1893.
- Born in Kolkata on January 12, 1863 in Kolkata, Swami Vivekananda was known as Narendra Nath Datta in his pre-monastic life.
- He is known to have introduced the Hindu philosophies of Yoga and Vedanta to the West.
- Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose had called Vivekananda the “maker of modern India.”
- In 1893, he took the name ‘Vivekananda’ after Maharaja Ajit Singh of the Khetri State requested him to do so, changing from ‘Sachidananda’ that he used before.
- He formed the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897 “to set in motion a machinery which will bring noblest ideas to the doorstep of even the poorest and the meanest.”
- In 1899, he established the Belur Math, which became his permanent abode.
- He preached ‘neo-Vedanta’, an interpretation of Hinduism through a Western lens, and believed in combining spirituality with material progress.
- Books written by him: ‘Raja Yoga’, ‘Jnana Yoga’, ‘Karma Yoga’ are some of the books he wrote.
Henley Passport Index:

India now ranks at 83rd position in the Henley Passport Index, climbing seven places from 90th rank last year.
- India shares the rank with Sao Tome and Principe in Central Africa, behind Rwanda and Uganda.
- It now has visa-free access to 60 destinations worldwide with Oman and Armenia being the latest additions. It has added 35 more destinations since 2006.
- Japan and Singapore has topped the list.
- The passport of the Maldives is the most powerful in South Asia (58th) enabling visa-free entry to 88 countries.
In South Asia, Bangladesh (103rd) is ahead of Pakistan (108th) and Nepal (105th).
About the Henley Passport Index:
- The Henley & Partners publishes the ranking and the Index of the world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without a prior visa.
- It was launched in 2005.
- The ranking is based on data from the IATA (International Air Transport Association), a trade association of some 290 airlines, including all major carriers.
- The index includes 199 different passports and 227 different travel destinations.
- The data are updated in real time as and when visa policy changes come into effect.
Xenotransplantation:
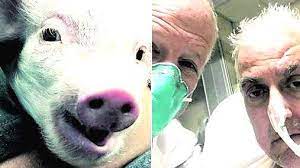
In a medical first, doctors transplanted a pig heart into a patient in a last-ditch effort to save his life in the US.
- Xenotransplantation involves the transplantation of nonhuman tissues or organs into human recipients.
- This is the first successful transplant of a pig’s heart into a human being. However, it’s too soon to know if the operation really will work.
- This time, a heart from a pig that had undergone gene-editing has been used to remove a sugar in its cells that’s responsible for that hyper-fast organ rejection.
- Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism’s Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA).
- Prior attempts at such transplants — or xenotransplantation have failed. One of the biggest obstacles to transplantation is organ rejection.
- This has re-sparked a debate over the use of pigs for human transplants, which many animal rights groups oppose.
- This development could bring us one step closer to solving the global organ shortage.
- In India, patients need 25,000-30,000 liver transplants annually. But only about 1,500 end up receiving them.
- Pigs are increasingly becoming popular candidates for organ transplantation.
- Pigs offer advantages over primates for organ procurements, because they are easier to raise and achieve adult human size in six months.
- Pig heart valves are routinely transplanted into humans, and some patients with diabetes have received porcine pancreas cells.




