Today’s Current Affairs: 14th July 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
ADEETIE Scheme:

The Union ministry of power, through the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), is launching a first-of-its-kind scheme called ADEETIE (Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments).
- ADEETIE (Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments) Scheme is a flagship initiative of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- It aims to catalyze the adoption of energy-efficient technologies among Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), enhancing their competitiveness and contributing to India’s climate goals.
- This Scheme offers comprehensive financial and technical support to Udyam-registered MSMEs, enabling them to implement energy-efficient technologies with a proven potential to save at least 10% of energy.
- The scheme is structured to provide targeted assistance in the form of interest subvention on loans, Investment Grade Energy Audits (IGEA), Detailed Project Reports (DPRs), and post-implementation Monitoring and Verification (M&V).
- The scheme is envisaged to provide interest subvention of 5% for Micro and Small Enterprises and 3% for Medium Enterprises on loans, ensuring accessibility and affordability for MSMEs seeking financial aid for energy efficiency projects.
- The scheme also includes provisions for capacity building, with BEE providing assistance through its ADEETIE online platform, designed to facilitate financing for energy-efficient projects in the MSME sector.
3I/ATLAS:

Scientists using the ATLAS telescope in Chile reported discovering an object named 3I/ATLAS, tracked since June 14.
- It is an interstellar comet, likely to be the oldest comet ever observed by scientists, potentially predating the formation of the solar system by over 3 billion years.
- Its identification as an interstellar object was based on its highly elliptical orbit, and fast velocity through space, travelling at 57–68 km/s relative to the Sun.
- The comet’s trajectory traces back to the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, suggesting its origin lies far outside our solar system, possibly from the Milky Way’s thick disk.
- Its orbit is hyperbolic, which means it will pass once through the solar system and never return.
- It will exit the solar system permanently after a brief interaction with the Sun.
- Closest approach to Earth: About 270 million km.
- Closest approach to the Sun: Around 210 million km, expected on October 29–30, 2025, slightly within Mars’s orbit.
- 3I/ATLAS is confirmed to be an active comet, with a visible coma, a cloud of ice particles and dust surrounding the nucleus.
- As it nears the Sun, it is expected to develop a tail, a characteristic cometary feature formed by solar heating.
Carbon Credit Trading Scheme:
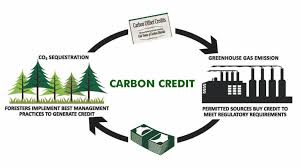
The Indian government announced greenhouse gas emissions intensity targets for entities in eight of the nine heavy industrial sectors participating in the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme’s compliance mechanism.
- The Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) is a market-based framework developed under the Indian Carbon Market (ICM) to regulate and trade carbon credits.
- It aims to accelerate India’s transition to a low-carbon economy by assigning a monetary value to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- The primary aim of CCTS is to decarbonise industrial sectors by shifting focus from energy efficiency (PAT Scheme) to GHG emissions intensity
- The CCTS is overseen by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) and the National Steering Committee for Indian Carbon Market (NSCICM), ensuring transparent and accountable governance.
Key Mechanisms under CCTS:
- Compliance mechanism: Entities in obligated sectors must meet sector-specific emission intensity targets. Those who exceed targets earn tradable CCCs, while others must buy credits.
- Offset mechanism: Entities outside the compliance mandate can voluntarily participate by reducing emissions and earning carbon credits, promoting broader climate participation.
- Under its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), India targets a 45% reduction in emission intensity of its GDP by 2030
- The CCTS is a key policy instrument toward achieving this goal.
- The eight sectors include aluminium, cement, paper and pulp, chlor-alkali, iron and steel, textiles, petrochemicals, and petro refineries.
Flue Gas Desulphurisation: In News

The Environment Ministry has exempted most coal-fired plants in India from installing Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) systems aimed at reducing sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions.
- Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) is a pollution-control process that removes Sulphur Dioxide (SO₂) from the flue gases produced by the combustion of fossil fuels, especially coal.
- The key aim of FGD is to reduce SO₂ emissions, which are major contributors to acid rain and particulate matter pollution, harming crops, soil, water bodies, infrastructure, and human health.
- FGD systems typically use limestone (CaCO₃), lime (CaO), or ammonia (NH₃) to react with and neutralize SO₂ in flue gases.
- In 2015, India’s Environment Ministry mandated that all coal-fired thermal power plants must install FGD systems by 2017 to curb SO₂ pollution. There are about 180 such plants, comprising 600 individual units.
- This exemption decision was based on scientific studies suggesting:
- Indian coal has low sulphur content.
- SO₂ levels near plants with and without FGDs were similar.
- Sulphates may have a cooling effect, counteracting global warming.
- As of now, only ~8% of these units have installed FGDs, with most installations by NTPC (public sector). The rest failed due to vendor shortages, high costs, COVID-related delays, and an anticipated rise in power tariffs.
Sierra Leone’s First UNESCO Site Gola-Tiwai Complex:

Sierra Leone’s Gola-Tiwai complex, comprising the Gola Rainforest National Park (GRNP) and the Tiwai Island Wildlife Sanctuary, has been inscribed as its first United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Site, due to decades-long conservation efforts by a non-governmental organization Environmental Foundation for Africa (EFA).
- Tiwai Island, located on the Moa River, spans just 12 sq. km and hosts 11 species of primates, including endangered western chimpanzees and king colobus monkeys.
- Tiwai now serves as a biodiversity research hub and model for community-based conservation in West Africa.
- GRNP is Sierra Leone’s largest tropical rainforest, rich in biodiversity, including pygmy hippopotamuses and African forest elephants.
- EFA was established in 1992 and began conservation efforts in Tiwai in the early 2000s, especially after damage from Sierra Leone’s 1991–2002 civil war.
- During the war, deforestation, poaching, and illegal logging nearly destroyed Tiwai, but EFA led reconstruction, community engagement, and biodiversity protection.
- Despite the Ebola outbreak (2014), Covid-19, and extreme weather, EFA protected Tiwai and surrounding forests from ecological collapse.
- The UNESCO recognition is a landmark for Sierra Leone, validating grassroots conservation models rooted in local empowerment and ecological resilience.
Grey Seal:

As climate change, pollution, and overfishing threaten the Grey seal (Halichoerus grypus) in the Baltic Sea, Lithuania has launched a rehabilitation effort to support their survival and restore population balance.
- Gray seals live in coastal waters of the North Atlantic, from the US and Canada to the Baltic Sea and parts of Europe. They haul out on rocky coasts, islands, sandbars, and ice.
- Males can grow up to 10 feet long, females are smaller. Males have large, horse-like heads. Pups are born with white lanugo fur that helps retain warmth.
- They gather in large groups for mating and molting, but often live alone or in small groups otherwise. Their diet includes fish, squid, and sometimes seabirds.
- The seals, being apex predators, absorb high levels of pollutants, making them indicators of marine ecosystem health.
- Gray seals live 25–35 years. Females give birth to a single pup after an 11-month pregnancy.
- The Baltic Sea subpopulation of grey seal is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
- Threats: Grey seals in the Baltic Sea face major threats from receding ice cover, pollution, shrinking fish stocks, and disease.
Informal Credit in India:

Despite nearly universal bank account penetration in India, fresh data (CMIE, Piramal Enterprises) show a sharp shift by poor households towards informal borrowing, due to limited access to formal credit channels.
- Informal Credit is Credit from non-regulated entities like moneylenders, pawnshops, friends/family, chit funds.
- Typically lacks transparency, documentation, or consumer protection.
- Recent Trends and Shifts:
- 96% of Indian households have at least one bank account (NFHS-5, 2021).
- Despite this, credit access remains skewed:
- 4.2% fall in formal credit among poor households (CMIE 2023).
- 5.8% rise in informal borrowing by those earning ₹1–2 lakh annually.
- 75% of rural adults still rely on informal credit in some form (NABARD Financial Inclusion Survey, 2019).
- ₹1.4 lakh crore was the estimated outstanding informal credit as of 2022 (CRISIL report).
Silent Salt Consumption Epidemic:
The ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology (NIE) has flagged a silent health crisis in India due to excessive salt intake, launching a community-driven intervention in Punjab and Telangana to promote low-sodium alternatives. Silent Salt Consumption Epidemic is a a public health crisis marked by widespread excessive intake of salt, contributing silently to chronic diseases. Average salt consumption in urban India is 9.2g/day, and 5.6g/day in rural areas — both exceeding the WHO’s safe limit of 5g/day. A three-year project aims to study salt-reduction counselling to lower blood pressure and sodium intake. Pilot States: Punjab and Telangana have been selected for targeted interventions among hypertensive individuals.
Air India Flight AI171 crash investigation:
The Air India Flight AI171 crash investigation revealed that both engines of a Boeing 787-8 shut down moments after take-off due to an abrupt movement of fuel control switches to the “CUTOFF” position, triggering loss of thrust and a fatal crash. Fuel control switches are cockpit levers that regulate the flow of fuel to each engine, enabling engine start-up, shutdown, and emergency actions. On Boeing 787-8 aircraft, these are placed just below the thrust levers, one for each engine. They are spring-loaded and feature a pull-to-unlock mechanism, ensuring deliberate and intentional use.
Hindi as a compulsory third language : Maharashtra
The Maharashtra government scrapped its government resolutions (GRs) mandating Hindi as a compulsory third language from Grades 1 to 5 in Marathi and English medium schools.Though the move was in line with National Education Policy (NEP), 2020, which promotes multilingualism through the three-language formula, it was withdrawn due to concerns over linguistic identity, cultural hegemony, and the feasibility of implementation.
The government has appointed a committee under renowned economist Dr. Narendra Jadhav to study the three-language policy.
Phase 3 Trials of Its First Indigenous Dengue Vaccine:
India has enrolled over 8,000 participants in Phase 3 trials of its first indigenous dengue vaccine, developed by Panacea Biotec and supported by ICMR.DengiAll – a tetravalent dengue vaccine designed to protect against all four dengue virus serotypes (DENV-1 to DENV-4).
Origin: Derived from the TV003/TV005 strain originally developed by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) and licensed to Indian firms.
Organisations Involved: ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research): Primary funder and scientific lead. Panacea Biotec: Vaccine developer holding process patents and leading formulation trials.
Chin Refugee:
Over 4,000 refugees from Myanmar’s Chin State entered Mizoram’s Champhai district in July 2025 after violent clashes between Chin rebel groups.The Chins are an ethnic minority primarily from Myanmar’s Chin State, culturally and linguistically aligned with the Mizo people of India. They belong to the broader Zo ethnic group, which includes Mizos (India), Bawms (Bangladesh), and Kuki-Zos (Manipur). They share Mongoloid features, speak Tibeto-Burman languages, and follow a mix of Christianity and indigenous customs. Many Chins are involved in anti-junta resistance movements like CNDF and CDF-H in Myanmar. Places in news regarding Chin migration: Zokhawthar (Champhai district), Saikhumphai, Vaphai, Farkawn (Champhai South), and Tiau River crossing points.




