Today Current Affairs: 18th January 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Thiruvalluvar Day:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tributes to the Tamil poet and philosopher Thiruvalluvar on Thiruvalluvar Day (15 January).
- Thiruvalluvar, also called Valluvar, was a Tamil poet-saint.
- The period when he lived is debated, as is his religious identity.
- He is believed to have lived between the 3rd-4th century or 8th-9th century.
- He is thought to be linked to Jainism. However, Hindus have also claimed that Thiruvalluvar belonged to hinduism.
- Dravidian groups also count him as a saint, as he dismissed the caste system.
- He had contributed the Tirukkural or ‘Kural’ to the Sangam literature.
- Tirukkural is comprised of 133 sections of 10 couplets each is divided into three books:
- Aram (virtue),
- Porul (government and society), and
- Kamam (love).
- The Tirukkural has been compared to the great books of the world’s major religions.
PASSEX Exercise:

India’s INS Kochi and Russian ships engaged in the international Passage Exercise (PASSEX).
- A passage exercise is normally undertaken whenever an opportunity arises, in contrast to pre-planned maritime drills.
- Earlier, Indian Naval ships conducted PASSEX with the US Navy also
- Other Exercises of India and Russia:
- Exercise TSENTR 2019 (Multilateral Military Exercise).
- Indra Exercises – Joint Tri-Services (Army, Navy, Air Force) Exercises.
- ZAPAD 2021 (Multilateral Military Exercise).
National Startup Awards 2021:

The Union Minister of Commerce & Industry presented the second edition of National Startup Awards 2021.
- It was also announced that 16th January (Startup India Initiative was launched on this day in 2016) will be celebrated as National Start-up Day, to take the Startup culture to the far flung areas of the country.
- The ‘Blockchain-enabled verification for Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) tax incentive certificates’, ‘Digilocker enabled DPIIT Startup recognition certificate’ were also launched.
- Designed by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- Aim is to recognize and reward outstanding Startups and ecosystem enablers that are building innovative products or solutions and scalable enterprises, with high potential of employment generation or wealth creation, demonstrating measurable social impact.
2021 Awards:
- The second edition of the awards invited applications across 15 sectors and 49 sub-sectors.
- The 2021 edition of the awards also recognized exceptional Startups innovating solutions to promote Indic languages and to compliment national efforts to combat Covid-19 pandemic.
- All applicants were evaluated against six broad parameters namely Innovation, Scalability, Economic Impact, Social Impact, Environmental Impact, and Inclusiveness and Diversity.
- The winning startup founders will get a cash prize of Rs. 5 lakh and an opportunity to present their solutions to relevant public authorities and corporates. Incubators and accelerators will get Rs. 15 lakh as the winning amount.
- 46 startups along with 1 incubator and 1 accelerator were honoured with the award.
24th National Conference On e-Governance 2021:

The 24th National Conference on e-Governance (NCeG) was organised by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG, Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions) and Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), in association with the State Government of Telangana.
- DARPG is the nodal agency of the Government of India for administrative reforms as well as redressal of public grievances relating to the states in general and those pertaining to Central Government agencies in particular.
- The Conference provides a platform for constructive exchange of ideas on some of the latest technologies for promoting e-Governance.
- At the conference, the ‘Hyderabad Declaration’ on e-Governance was adopted.
- The declaration aims to bring citizens and governments closer through digital platforms and transform citizen services through the use of technology.
- The Conference resolved that Government of India and State Governments shall collaborate to:
- Transform citizen services through use of technology by leveraging the artifacts of India Stack that include Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, UMANG, e Sign and consent framework.
- Fast track the implementation of the national level public digital platforms in key social sectors viz. Health, Education, Agriculture, etc by adopting open interoperable architecture for joined up connected services.
- Operationalize the data governance framework to facilitate data sharing within Government entities as also make available all data on data.gov.in except for a negative list.
- Foster responsible use of emerging technology such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, 5G, Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, etc for Social Empowerment.
- Make India the global hub for emerging technology through creation of a large pool of skilled resources on futuristic technologies.
- Ensure resilient Government Infrastructure with robust technological solutions to withstand pandemic like disruptions.
- Integration of all State/District portals with Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) for seamless Redressal of Public Grievances.
- National E-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) 2021 to be adopted in collaboration with MeITY for improving e-Governance landscape.
- Theme: “India’s Techade: Digital Governance in a Post Pandemic World”
National e-Governance Awards 2021:
- To recognise the implementation of e-Governance initiatives, the National e-Governance Awards 2021 were presented during the Inaugural Session.
- 26 awards were presented under the 6 categories of the Award Scheme to Central Ministries/Departments, State/UT Governments, Districts, Local Bodies, Public Sector Undertakings and Academic & Research Institutions.
Rare Earth Metals:
The US has proposed a law aiming to end China’s alleged “chokehold” on rare-earth metal supplies.
- The Bill aims to “protect the US from the threat of rare-earth element supply disruptions, encourage domestic production of those elements, and reduce its reliance on China.
- The law would require the creation of a “strategic reserve” of rare earth minerals by 2025.
- That reserve would be tasked with responding to the needs of the army, the tech sector and other essential infrastructure “for one year in the event of a supply disruption”
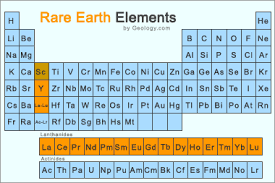
- They are a set of seventeen metallic elements. These include the fifteen lanthanides on the periodic table in addition to scandium and yttrium that show similar physical and chemical properties to the lanthanides.
- The 17 Rare Earths are cerium (Ce), dysprosium (Dy), erbium (Er), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), holmium (Ho), lanthanum (La), lutetium (Lu), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), scandium (Sc), terbium (Tb), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and yttrium (Y).
- These minerals have unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties and thus are used in many modern technologies, including consumer electronics, computers and networks, communications, health care, national defense, etc.
- Even futuristic technologies need these REEs (For example high-temperature superconductivity, safe storage and transport of hydrogen for a post-hydrocarbon economy, environmental global warming and energy efficiency issues).
- They are called ‘rare earth’ because earlier it was difficult to extract them from their oxides forms technologically.
- They occur in many minerals but typically in low concentrations to be refined in an economical manner.
- Exploration in India has been conducted by the Bureau of Mines and the Department of Atomic Energy.
- Mining and processing has been performed by some minor private players in the past, but is today concentrated in the hands of IREL (India) Limited (formerly Indian Rare Earths Limited), a Public Sector Undertaking under the Department of Atomic Energy.
- India has granted government corporations such as IREL a monopoly over the primary mineral that contains REEs: monazite beach sand, found in many coastal states.
- IREL produces rare earth oxides (low-cost, low-reward “upstream processes”), selling these to foreign firms that extract the metals and manufacture end products (high-cost, high-reward “downstream processes”) elsewhere.
- IREL’s focus is to provide thorium — extracted from monazite — to the Department of Atomic Energy.
- India has the world’s fifth-largest reserves of rare earth elements, nearly twice as much as Australia, but it imports most of its rare earth needs in finished form from China.
- In 2019, the US imported 80% of its rare earth minerals from China while the European Union gets 98% of its supply from China.
Special Marriage Act 1954:

The law that governs inter-faith marriages in the country, the Special Marriage Act (SMA), 1954, is being challenged in the Supreme Court.
- In 2021, petitions were filed to strike down several of its provisions.
The Special Marriage Act (SMA), 1954
- It is the legislation made to validate and register interreligious and inter-caste marriages in India.
- It allows two individuals to solemnise their marriage through a civil contract.
- No religious formalities are needed to be carried out under the Act.
- This Act includes Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists marriages.
- This Act applies not only to Indian citizens who belong to different castes and religions but also to Indian nationals who live abroad.
Current Petition:
- Section 5 of the SMA requires a person marrying under this law to give a notice of intended marriage.
- Section 6(2) says it should be affixed at a conspicuous place at the office of the marriage officer.
- Section 7(1) allows any person to object to the marriage within 30 days of the publication of the notice, failing which a marriage can be solemnised under Section 7(2).
- Due to these provisions breaching personal liberties, several inter-faith couples approached the Court, challenging Sections 6 and 7 of the Act.
The Aroma Mission:

While observing the first National Start-up Day, Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh said that “Purple Revolution” is Jammu & Kashmir’s contribution to “Start-ups India”, an initiative that was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2016.
- The Aroma Mission launched by the Union Ministry of Science & Technology through the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), has led to the well-known “Purple Revolution” in India.
- The CSIR had, to begin with introduced high-value essential oil bearing lavender crop through its Jammu based laboratory, Indian Institute of Integrative Medicines (IIIM) for cultivation in districts Doda, Kishtwar, Rajouri and later also in the other districts including Ramban, Pulwama, etc.
- In addition to IIIM, CSIR-IHBT, CSIR-CIMAP, CSIR-NBRI and CSIR-NEIST are also now participating in the Aroma Mission.
China And Iran Agreement:

China would begin implementing a strategic agreement with Iran, strengthening economic and political cooperation between the two countries as Beijing blasted Washington’s sanctions on Tehran.
- China and Iran signed the agreement last year after years of talks, with the wide-ranging partnership set to span areas including energy, security, infrastructure and communications.
- Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi and Iranian counterpart Hossein Amir-Abdollahian announced the start of the partnership’s implementation at a meeting in east China’s Wuxi.
- China is Iran’s leading trade partner and was one of the biggest buyers of the country’s oil before then-U.S. president Donald Trump reimposed sweeping unilateral sanctions in 2018.
- China has officially stopped importing oil from Iran, but analysts say Iranian crude is continuing to enter the country disguised as imports from other countries.
- Beijing has long sought to boost ties with Tehran, with Chinese president Xi Jinping describing Iran as “China’s major partner in the Middle East” on a rare visit to the country in 2016.
- Wang and Mr. Amir-Abdollahian’s meeting comes as talks continue in Vienna over a potential deal to halt Tehran’s development of nuclear weapons.
- A 2015 deal agreed by Iran, the U.S., China, Russia, Britain, France and Germany — offered Tehran sanctions relief in exchange for curbs on its nuclear programme.
- But the U.S. withdrew from the agreement in 2018, reimposing biting sanctions and prompting Tehran to begin rolling back on its commitments.
TRP:

The Information and Broadcasting Ministry has asked the Broadcast Audience Research Council to resume the release of television rating point, also known as target rating points, data.
- It had been suspended in late 2020 after the police unearthed a ratings scandal, acting on a complaint made by the BARC.
- To begin with, BARC has been asked to release data of the last three months in a monthly format for a “fair and equitable representation of true trends.”
- Meanwhile, the I&B Ministry constituted a committee under the Prasar Bharati Corporation CEO, Shashi Shekhar Vempati, to review the existing guidelines for TV ratings and come out with recommendations.
- Acting on a complaint by the BARC, the viewership measurement body for television, and one of its contractors, Hansa Services Pvt Ltd., the Mumbai police on October 8, 2020, said it had busted a TRP racket run by three news channels who were manipulating viewership ratings by bribing panel homes where measurement meters had been placed.
- It is not the first time it has been reported that ratings are being rigged. In 2002-2003, former director general of Doordarshan S.Y. Quraishi wondered how the national broadcaster with a news share of 92% did not figure at the top of the TRP list brought out by the Television Audience Measurement (TAM).
- Eventually, TAM bowed out and BARC was founded in 2010 by the Indian Broadcasting Foundation (IBF), the Advertising Agencies Association of India (AAAI), and the Indian Society of Advertisers —representative of the media industry with all its stakeholders.
Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme:

With an overall vision to create a vibrant ecosystem for Semiconductor Chip Design in the country, the Ministry of Electronics and Information (MeitY) is seeking applications from 100 domestic companies, start-ups and MSMEs under its Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
- The DLI Scheme was announced by Ministry of Electronics and Information (MeitY) as a part of ₹76,000 crore ($10 billion) package that the government announced in December 2021.
- Under it, financial incentives and design infrastructure support will be extended to domestic companies, startups and MSMEs across various stages of development and deployment of semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design for over a period of 5 years.
- The scheme aims to nurture at least 20 domestic companies involved in semiconductor design and facilitating them to achieve turnover of more than ₹1500 Crore in the next 5 years.
- C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), a scientific society operating under MeitY, will serve as the nodal agency for implementation of the DLI scheme.
- The scheme has three components –
- Chip Design infrastructure support,
- Product Design Linked Incentive and
- Deployment Linked Incentive.
Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC):

The United Kingdom-based Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) has listed five sites with unusual features. These sites are associated with World War I and World War II.
- Among them is Nagaland’s Kohima War Cemetery.
- The Kohima War Cemetery is a memorial dedicated to the soldiers of the 2nd British Division of the Allied Forces who died in World War II at Kohima in April 1944.
- The soldiers died on the battleground of Garrison Hill in the tennis court area of the Deputy Commissioner’s residence.
- Among the other unusual sites listed by CWGC are the World War I “crater cemeteries” – Zivy Crater and Litchfield Crater – in the Pas de Calais region in France. The craters were caused by mine explosions.
- Another site listed is the Nicosia (Waynes Keep) Cemetery or the “cemetery in no man’s land” in Cyprus, requiring the presence of armed guards.
- This is because the cemetery is on the border of a patch of land disputed between the southern and northern parts of the island since the 1970s.
- CWGC is an intergovernmental organisation of six member-states who ensure the men and women who died in the wars will never be forgotten.
- The commission was founded by Sir Fabian Ware and constituted through Royal Charter in 1917 as the Imperial War Graves Commission.
- Membership: Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, South Africa and the United Kingdom.
Net-Zero Energy Buildings:

A net-zero energy building is one that relies on renewable sources to produce as much energy as it uses, usually as measured over the course of a year.
- Homes and other structures that create almost as much energy as they use are sometimes called near-zero energy buildings.
- It is also possible for a building to produce an energy surplus, sending excess back to the electrical grid.
- Net-zero energy buildings start with energy-conscious design. Many features work without an energy source.
- In cold climates, south-facing buildings with large expanses of windows on that side can produce heat through passive solar gain.
- On the cold north side of the building, smaller windows can angle to wider openings, permitting more light while limiting heat loss.
- In warmer seasons, passive ventilation systems can pull cool air up from the lower levels and vent it through the building’s highest point.
- Rooftop systems can collect rainwater to reduce usage of treated water.
Sixth Mass Extinction:

The ongoing sixth mass extinction may be one of the most serious environmental threats to the persistence of civilisation, according to new research.
- Earth was once home to two million known species. According to the study, however, since 1500, as many as 7.5%-13% of these species may have been lost. That numbers anywhere from 150,000 to 260,000 different species.
- Mass extinction refers to a substantial increase in the degree of extinction or when the Earth loses more than three-quarters of its species in a geologically short period of time.
- So far, during the entire history of the Earth, there have been five mass extinctions.
- The five mass extinctions that took place in the last 450 million years have led to the destruction of 70-95 per cent of the species of plants, animals and microorganisms that existed earlier.
- These extinctions were caused by “catastrophic alterations” to the environment, such as massive volcanic eruptions, depletion of oceanic oxygen or collision with an asteroid.
- After each of these extinctions, it took millions of years to regain species comparable to those that existed before the event.
- The sixth, which is ongoing, is referred to as the Anthropocene extinction.
- Researchers have described it as the “most serious environmental problem” since the loss of species will be permanent.
- One of the reasons that humanity is an “unprecedented threat” to many living organisms is because of their growing numbers.
- The loss of species has been occurring since human ancestors developed agriculture over 11,000 years ago. Since then, the human population has increased from about 1 million to 7.7 billion.
- More than 400 vertebrate species went extinct in the last century, extinctions that would have taken over 10,000 years in the normal course of evolution.
- In a sample of 177 species of large mammals, most lost more than 80 per cent of their geographic range in the last 100 years, and 32 per cent of over 27,000 vertebrate species have declining populations.
- Many of the species currently endangered or on the brink of extinction are being decimated by legal and illegal wildlife trade.
- Several species of mammals that were relatively safe one or two decades ago are now endangered, including cheetahs, lions and giraffes.
- There are as few as 20,000 lions left in the wild, less than 7,000 cheetahs, 500 to 1,000 giant pandas, and about 250 Sumatran rhinoceros.
Desh Ke Mentor Programme: Delhi Govt

A controversy has broken out over the Delhi government’s flagship ‘Desh ke Mentor’ programme.
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has recommended that the Delhi government suspend its flagship programme till “the time when all the loopholes pertaining to the safety of the children are overhauled”.
- Desh ke Mentor programme Launched in October 2021 and is aimed at connecting students in classes IX to XII with voluntary mentors.
- People between the ages of 18 and 35 can sign up to be mentors through an app created by a team at the Delhi Technological University and will be connected with students based on mutual interests.
- The mentorship entails regular phone calls for a minimum of two months, which can optionally be carried on for another four months.
- The idea is for the young mentors to guide students through higher education and career options, preparation for higher education entrance exams, and dealing with the pressure of it all.
- 44,000 people have signed up as mentors so far and have been working with 1.76 lakh children.
- There are five primary points on which the NCPCR has raised concerns with regard to the programme:
- Safety from abuse: It has stated that assigning children to a mentor of the same gender as them does not necessarily assure their safety from abuse.
- Lack of police verification: It has also expressed concern over the lack of police verification of the mentors.
- Various concerns over the psychometric test.
- It has also stated that limiting interactions to phone calls also does not ensure the safety of children since “child related crime can be initiated through phone calls as well.”
- It has stated that while taking the consent of parents is an essential pre-requisite, the “responsibility and accountability of preventing children from such situation lies with the Department. The consent of parents cannot be used as a cushion in case of any untoward incident.”
What Is postal voting?

The Election Commission of India has allowed journalists to cast their votes through postal ballot facility.
- Any absentee voter wishing to vote by postal ballot has to make an application to the returning officer in Form-12D, giving all requisite particulars and get the application verified by the nodal officer appointed by the organisation concerned.
- Any voter opting for postal ballot facility would not be able to cast a vote at the polling station.
- Currently, the following voters are also allowed to cast their votes through postal ballot:
- Service voters (armed forces, the armed police force of a state and government servants posted abroad),
- Voters on election duty,
- Voters above 80 years of age or Persons with Disabilities (PwD),
- Voters under preventive detention.
- A restricted set of voters can exercise postal voting. Through this facility, a voter can cast her vote remotely by recording her preference on the ballot paper and sending it back to the election officer before counting.
- Representation of the People Act, 1951 provides for the actual conduct of elections in India.




