Today Current Affairs: 18th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Namami Gange Programme:

An agreement was signed for the Development of 35 MLD (Mega Liters per day) Sewage Treatment Plant in Maheshtala (City situated on the east bank of River Ganga), West Bengal under the Namami Gange Programme.
- The project was signed under Hybrid Annuity PPP model.
Namami Gange Programme:
- Namami Gange Programme is an Integrated Conservation Mission, approved as a ‘Flagship Programme’ by the Union Government in June 2014 to accomplish the twin objectives of effective abatement of pollution and conservation and rejuvenation of National River Ganga.
- It is being operated under the Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The program is being implemented by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), and its state counterpart organizations i.e State Program Management Groups (SPMGs).
- NMCG is the implementation wing of the National Ganga Council (set in 2016; which replaced the National Ganga River Basin Authority – NGRBA).
- It has Rs. 20,000-crore, centrally-funded, non-lapsable corpus and consists of nearly 288 projects.
Hallmarking Of Gold:
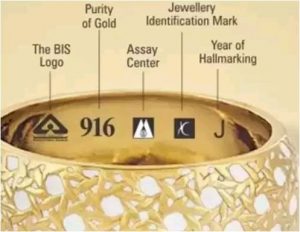
The government has announced the phased implementation of mandatory hallmarking of gold jewellery with effect from June 16.
- In the first phase, gold hallmarking will be available only in 256 districts and jewellers having annual turnover above Rs 40 lakh will come under its purview.
- Hallmarking is the “accurate determination and official recording of the proportionate content of precious metal in precious metal articles.”
- So, it is like a “guarantee of purity or fineness” of precious metal articles.
- The Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS) operates a gold and silver hallmarking scheme in India.
- Metals covered under the purview of hallmarking:
- Gold jewellery and gold artefacts.
- Silver jewellery and silver artefacts.
Twitter Has Lost Its Intermediary Status In India:

According to some media reports, Twitter has lost its intermediary status in India over non-compliance of the new IT rules that came into effect on May 26.
- As per Section 2 (1) of the Information Technology Act, an intermediary is a person/entity that receives, stores and transmits information or provides service for the transmission of information
- This includes telecom service providers, network service providers, internet service providers, search engines, online payment sites, online auction sites, online marketplaces and even cyber cafes.
- Please note, intermediary status is not a registration granted by the government.
- Intermediaries like Twitter are protected under Section 79 of the Information Technology Act that states that they cannot be held liable for the third-party content published on their platform as long as they comply with the legal order to take down content from courts or other authorities.
Safe Harbour Protection:
- Consider, a user’s tweets go viral and that results in death or violence. Now, under safe harbour protection, Twitter cannot be held liable just because of it.
- However, they will have to take down the content if they get a legal order from the court or authorities. This is what termed safe harbour protection.
In the short run, since the protection accorded to Twitter under Section 79 of the IT Act is now gone, it opens up the platform to the possibility of any and all penal action that is likely to be taken against it as a publisher of content.
- This means that if someone puts out any content on Twitter that leads to some form of violence, or violates any Indian law with respect to content, not only the person that has put out the tweet will be held responsible, even Twitter will be legally liable for the content as it no longer has the protection.
Customized Crash Course Programme For Covid 19 Frontline Workers:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will launch the ‘Customized Crash Course program for Covid 19 Frontline workers’ on 18th June 2021.
- The launch will commence the programme in 111 training centres spread over 26 states.
- The programme will create skilled non-medical healthcare workers to fill the present and future needs of manpower in the health sector.
- The programme aims to skill and upskill over one lakh Covid warriors across the country.
- The training will be imparted to Covid warriors in six customised job roles namely
- Home Care Support,
- Basic Care Support,
- Advanced Care Support,
- Emergency Care Support,
- Sample Collection Support, and
- Medical Equipment Support.
- The programme has been designed as a special programme under the Central Component of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 3.0, with a total financial outlay of Rs. 276 crore.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) : Gujrat:

The Ministry of Culture (MoC) and Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) signed an MoU for Cooperation in Development of National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) at Lothal, Gujarat’.
- The foundation stone for the project was laid by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in March 2019.
- National Maritime Heritage Complex, a world-class facility is to be developed in the vicinity of the ASI site of Lothal, located about 80 km away from Ahmedabad, Gujarat.
- It will showcase and preserve India’s rich and diverse maritime heritage. It will display objects relating to ships and travel on large bodies of water. It also intends to highlight the ancient shipbuilding and navigational technologies developed by India.
- The project is being implemented by the Ministry of Shipping through its Sagarmala program, with the involvement of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), the State government and other stakeholders.
- India and Portugal will cooperate in the setting up of a national maritime heritage museum at Lothal in Gujarat. The Portuguese Navy has agreed to assist with their experience of administering the maritime museum in Lisbon.
BRICS Network Universities:

A three-day virtual Conference of BRICS Network Universities on the theme of electric mobility was inaugurated at IIT Bombay.
- This conference is part of the engagements that India is hosting under the education stream during its Chairship of the 13th BRICS Summit this year.
- BRICS Network University is a union of higher education institutions of the five BRICS member countries, formed with the objective of enhancing educational cooperation in general, and especially in the realm of research and innovation.
- IIT Bombay is the lead institution of India for the BRICS Network University.
Cross-Disability Early Intervention Centres:

Minister for Social Justice & Empowerment inaugurated 14 Cross-Disability Early Intervention Centres located at 7 National Institutes and 7 Composite Regional Centres.
- These have been established under the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- These have been set up at 7 National Institutes at Delhi, Mumbai, Dehradun, Secunderabad, Kolkatta, Cuttack and Chennai and 7 Composite Regional Centres at Sundernagar, Lucknow, Bhopal, Rajnandgaon, Patna, Nellore and Kozhikode in the first phase.
- These 14 Centres will provide contiguous facilities for therapeutic, rehabilitative care services and pre-school training for children with disabilities (0-6 years) covering all types of disabilities covered under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- These services will be provided under a single roof with accessible and aesthetically designed environments.
ADI PRASHIKSHAN Portal:

Minister of Tribal Affairs launched the ADI PRASHIKSHAN portal.
- ADI PRASHIKSHAN portal is developed by the Ministry of tribal affairs.
- It would act as a Central Repository of all training programs conducted by Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs), different divisions of Ministry, National Society for Education of Tribal Students (NESTS), Centre of Excellence funded by Ministry of Tribal Affairs and National Tribal Research Institute.
- It will catalyze and improve the processes of conducting training by making it online and accessible to all.
- A unified open platform will give users access to authentic knowledge products.
World Competitiveness Index 2021:

According to the World Competitiveness Yearbook (WCY), India maintained 43rd rank on the annual World Competitiveness Index.
- The World Competitiveness Index is a comprehensive annual report and worldwide reference point on the competitiveness of countries.
- Published by: WCY was first published in 1989 and is compiled by the Institute for Management Development (IMD).
- In 2021, the IMD examined the impact of Covid-19 on economies around the world.
- It provides extensive coverage of 64 economies.
- Factors: It measures the prosperity and competitiveness of countries by examining four factors (334 competitiveness criteria):
- Economic performance
- Government efficiency
- Business efficiency
- Infrastructure
- Top Global Performers:
- The European countries display regional strength in world competitiveness ranking with Switzerland (1st), Sweden (2nd), Denmark (3rd), the Netherlands (4th).
- The top-performing Asian economies are, in order, Singapore (5th), Hong Kong (7th), Taiwan (8th), and China (16th).
- Singapore was 1st in the 2020 World Competitiveness Index.
- The UAE and the USA remain in the same spots as last year (9th and 10th, respectively).
- In Comparison to BRICS Nations: Among BRICS nations, India ranked second (43rd) after China (16th), followed by Russia (45th), Brazil (57th), and South Africa (62nd).
- Performance on Four Factors: Among the four indices used, India’s ranking in government efficiency increased to 46 from 50 a year ago, while it’s ranking in other parameters such as economic performance (37th), business efficiency (32nd), and infrastructure (49) remained the same.
- Improvements in Government Efficiency: Mostly due to relatively stable public finances. Despite difficulties brought by the pandemic, in 2020, the government deficit stayed at 7%. The Government also provided support and subsidies to private companies.
Changes In Cable Television Network Rules:

The central government issued a notification amending the Cable Television Network Rules, 1994 thereby providing a statutory mechanism for redressal of grievances/complaints of citizens.
- These grievances/complaints are related to content broadcast by television channels in accordance with the provisions of the Cable Television Network Act, 1995.
About the Notification: The notification issues Cable Television Networks (Amendment) Rules, 2021.
- It provides for a three-level grievance redressal mechanism — self-regulation by broadcasters, self-regulation by the self-regulating bodies of the broadcasters, and oversight by an Inter-Departmental Committee at the level of the Union government.
Significance Cable Television Networks (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Various Self-regulatory bodies like News Broadcasters Standards Authority (NBSA) and Broadcasting Content Complaints Council (BCCC) will get legal recognition.
- At present, there is an institutional mechanism by way of an Inter-Ministerial Committee to address grievances of citizens relating to violation of the Programme/Advertising Codes under the Rules.
- Various broadcasters have also developed their internal self-regulatory mechanism for addressing grievances.
- There are over 900 television channels that have been granted permission by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB).
- The recent notification is significant as it paves the way for a strong institutional system for redressing grievances while placing accountability and responsibility on the broadcasters and their self-regulating bodies.
- This will bring the television’s self-regulatory mechanism at par with that being set up for OTT players and digital news publishers, as envisaged in the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
Shenzhou-12: Chinese Spaceship:

A Chinese spaceship “Shenzhou-12” carrying a three-person crew docked with China’s new space station module Tianhe-1.
- This has come after the launch of the Tianzhou-2 cargo spacecraft, which carried vital supplies for the space station.
- The Shenzhou-12 craft connected with the Tianhe space station module about six hours after takeoff from the Jiuquan launch center in Gobi Desert.
- The three-man crew will spend three months on the Tianhe module, which is orbiting at some 340km to 380km above the earth.
- China is the third country after the former Soviet Union and the United States to carry out a manned mission on its own.
- This is the first of two manned space missions planned for this year, part of an intense schedule of launches aimed at completing the Chinese space station in 2022.
- At least five more missions are planned for the year, with the Shenzhou-13 manned mission, also carrying three astronauts, set for later this year.
- The three astronauts are the first to take up residency in the main living module and will carry out experiments, test equipment, conduct maintenance and prepare the station for receiving two laboratory modules next year.
- It was China’s seventh crewed mission to space but marked a number of firsts for the country – the first manned one during the construction of China’s space station, the first in nearly five years after the country’s last manned mission in 2016, and China’s longest crewed space mission to date.
- It will help test technologies related to long-term astronaut-stays and health care, the recycling and life support system, the supply of space materials, extravehicular activities and operations, and in-orbit maintenance.
5th Edition Of VivaTech:

Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi delivered the keynote address at the 5th edition of VivaTech on 16th June 2021. The 5th edition of VivaTech is scheduled between 16-19 June 2021.
- He invited the world to invest in India based on the five pillars of Talent, Market, Capital, Eco-system and, Culture of openness.
- The Prime Minister also stressed the strengths like Indian talent pool, mobile phone penetration and Seven Seventy-Five million internet users, the highest and cheap data consumption in the world, and the highest use of social media to invite investors to India.
- VivaTech is one of the largest digital and startup events in Europe, held in Paris every year since 2016.
- It is jointly organized by Publicis Groupe – a prominent advertising and marketing conglomerate and Les Echos – a leading French media group.
- It brings together stakeholders in technology innovation and the startup ecosystem and includes exhibitions, awards, panel discussions, and startup contests.




