Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 19th August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- PM CARES Fund as a “public charitable trust”
- Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) has released data related to jobs gained or lost during the Covid-19 lockdown period (April-July 2020).:
- Dhanwantri Rath: Ayurveda Health Services:
- ARIIA-2020 (Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements).:
- Sutlej Yamuna Link (SYL) Canal::
- Digital Quality of Life Index 2020::
- Other important current affairs:
1.PM CARES Fund as a “public charitable trust” :

The Supreme Court endorsed the PM CARES Fund as a “public charitable trust” to which donors contribute voluntarily.
- There is “no occasion” for the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) to audit a public charitable trust independent of budgetary support or government money.
- The court said that it is “not open” for a PIL petitioner to question the “wisdom” that created the fund in an hour of need.
- NGO Centre for Public Interest Litigation, represented by advocate Prashant Bhushan, had argued that the PM-CARES Fund was not subject to CAG audit. It was not under “public scrutiny”. Contributions to it were “100% tax-free”.
- The court dismissed the idea that the PM CARES was constituted to “circumvent” the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) — the statutory fund already in existence under the Disaster Management Act of 2005 to receive contributions to finance the fight against a calamity.
- The court refused to direct the transfer of funds from the PM CARES Fund to the NDRF. It said they were two separate entities.
2. Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) has released data related to jobs gained or lost during the Covid-19 lockdown period (April-July 2020).:
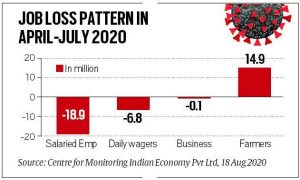
CMIE is a leading business information company. It was established in 1976, primarily as an independent think tank.
- CMIE produces economic and business databases and develops specialized analytical tools to deliver these to its customers for decision making and for research. It analyses the data to decipher trends in the economy.
Points to be noted:
Salaried Jobs:
- They suffered a total loss estimated to be 18.9 million during April-July 2020.
- 17.7 million salaried jobs were lost in April. After gaining 3.9 million jobs in June, 5 million jobs were again lost in July.
- They offer better terms of employment and better wages, and have a higher share in urban parts of the country than rural parts.
- They are more resilient to economic shocks and not lost easily, however, once lost they are far more difficult to retrieve.
- Only 21% of all employment in India is in the form of a salaried employee.
- Loss of urban salaried jobs is likely to have a particular debilitating impact on the economy, besides causing immediate hardship to middle-class households.
- Since the lockdown was announced, several companies across sectors have taken to job cuts, along with salary reductions and leave without pay.
Informal and Non-Salaried Jobs:
- This category of the job has shown improvement during the April-July 2020 increasing to 325.6 million in July 2020 from 317.6 million in 2019, an increase of 2.5%.
- This is because of the opening of the country in a phased manner.
- This category of employment accounted for about 32% of the total employment but it suffered 75% of the hit in April 2020.
- Out of a total of 121.5 million jobs lost in April 2020, 91.2 million of the jobs were lost from this category.
- Small traders, hawkers, and daily wage laborers were the worst hit by the lockdown.
Farm Jobs:
- The jobs lost in the non-farm sectors have resulted in people moving towards farm employment. The farm sector gained 14.9 million jobs in the April-July 2020 period.
- In 2019, 42.39% of the workforce in India was employed in agriculture.
3.Dhanwantri Rath: Ayurveda Health Services:

A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) has been signed between the All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA) and Delhi Police for extending the Ayurveda Preventive and Promotive health services in the residential colonies of Delhi Police.
- These services are to be provided through a mobile unit named ‘Dhanwantari Rath’ and Police Wellness Centres and are to be catered by AIIA, supported by the Ministry of AYUSH.
- Dhanwantari Rath and Police Wellness Centres would be outreach OPD (OutPatient Department) services of AIIA and aim to benefit the Families of Delhi Police through Ayurveda preventive health care services.
- Dhanwantari Rath – a mobile unit of Ayurveda health care services would consist of a team of Doctors who would be visiting Delhi Police colonies regularly.
- These Ayurveda health care services are expected to reduce the incidence/prevalence of various diseases and also reduce the number of referrals to hospitals thereby reducing the cost to the healthcare system as well as patients.
- Earlier, AYURAKSHA, a joint venture of AIIA and Delhi Police aimed for maintaining the health of frontline COVID warriors like Delhi police personnel through Ayurveda immunity-boosting measures were launched.
- With the latest MoU, Ayurveda Preventive and Promotive health care will be extended to the families of Delhi Police personnel.
4.ARIIA-2020 (Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements).:

The results of the rankings have been evaluated based on seven parameters. These include budget and funding support, infrastructure and facilities, awareness, promotions, and support for idea generation and innovation.
- This year, the ARIIA announcement included classification of the institutes into two broad categories and six subcategories.
- Among these, IIT Madras bagged the top position under the category of Institutes of National Importance, Central Universities, and Centrally Funded Technical Institutes.
- Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai got the top position under Government and Government Aided Universities.
- College of Engineering, Pune got the top position under Government and Government Aided Colleges.
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Bhubaneswar got the top position under Private or Self-Financed Universities.
- SR Engineering College, Warangal got the top position under Private or Self-Financed Colleges.
- This year, a special category for higher educational institutions for women has been introduced to bring gender parity in the areas of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science and Higher Education for Women secured top place under this category.
5.Sutlej Yamuna Link (SYL) Canal::
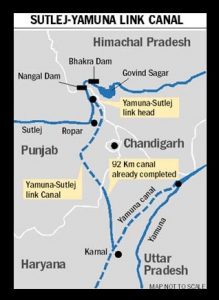
At a recent meeting, the Punjab Chief Minister asked the Central government to be cautious about the contentious Sutlej-Yamuna Link (SYL) canal issue, saying it has the potential to disturb the nation’s security.
- The meeting was convened following the Supreme Court’s direction to the Centre on July 28 to mediate between the two States to resolve the issue.
- Pakistan has been making continuous attempts to foment trouble and to try and revive the separatist movement through the banned Sikhs for Justice organization.
- The water issue could further destabilize the State.
Punjab’s demands:
- Suitable amendments should be made to the proposed Inter-State River Water Disputes Act to set up a new tribunal, to ensure that Punjab gets adequate water “in a just and equitable manner in keeping with its total demand and securing livelihood of the future generations.”
Sutlej Yamuna Link (SYL) Canal, and the controversy:
- The creation of Haryana from the old (undivided) Punjab in 1966 threw up the problem of giving Haryana its share of river waters.
- Punjab was opposed to sharing waters of the Ravi and Beas with Haryana, citing riparian principles, and arguing that it had no water to spare.
- However, Centre, in 1976, issued a notification allocating to Haryana 3.5 million acre feet (MAF) out of undivided Punjab’s 7.2 MAF.
- The Eradi Tribunal headed by Supreme Court Judge V Balakrishna Eradi was set up to reassess availability and sharing of water.
- The Tribunal, in 1987, recommended an increase in the shares of Punjab and Haryana to 5 MAF and 3.83 MAF, respectively.
- The canal:
- To enable Haryana to use its share of the waters of the Sutlej and its tributary Beas, a canal linking the Sutlej with the Yamuna, cutting across the state, was planned.
- A tripartite agreement was also negotiated between Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan in this regard.
- The Satluj Yamuna Link Canal is a proposed 214-kilometer long canal to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. However, the proposal met obstacles and was referred to the Supreme Court.
6.Digital Quality of Life Index 2020::

The report was released recently.
- The index is prepared by Surfshark, a virtual private network (VPN) provider based in the British Virgin Islands.
- It seeks to rank countries on internet affordability and quality, and electronic infrastructure, security and government. All parameters have equal weightage.
- Top 3: Scandinavian countries Denmark and Sweden topped the index, with Canada rounding up the top three.
- Israel offered the cheapest internet — calculated by considering how much time one must work to be able to afford the cheapest mobile internet and broadband.
- Of the total countries, 75% of them have to work more than the global average to afford the internet.
- Singapore, the UK and the US performed the best on the e-government indicator — arrived at by checking the state of government’s online presence and readiness to employ artificial intelligence technology and help “minimize bureaucracy, reduce corruption and increase the transparency of the public sector”.
- The UK, France and Lithuania offer the most security — cybersecurity and status of personal data protection.
- Best Internet Quality- Singapore, Sweden and the Netherlands.
- The UAE, Sweden and Denmark have the most developed e-infrastructure.
India’s performance:
- Of 85 countries, India ranked 9th on the internet affordability indicator and 15th on e-government.
Overall, India is ranked 57th. - Internet cost- India scored the best on this parameter, leading countries like the UK, US, and China.
- e-government indicator- India secured 15th position on this, ahead of the Netherlands, China and Belgium.
- Security- India performed poorly here, standing at 57th position.
- Internet quality- With a rank of 78, it fell behind countries such as Bangladesh, Nepal, Nigeria, and the Philippines.
- On electronic infrastructure — focusing on active internet users and information and communications technology adoption rate — India ranked 79th, behind neighbors Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal.
Other important current affairs:
1. On August 19, the World Humanitarian Day (WHD) is being celebrated to commemorate humanitarian workers killed and injured in the course of their work.
- This day was designated in memory of the 19 August 2003 bomb attack on the Canal Hotel in Baghdad, Iraq, killing 22 people, including the chief humanitarian in Iraq, Sergio Vieira de Mello.
- In 2009, the United Nations General Assembly formalized the day as World Humanitarian Day.
- This year World Humanitarian Day is being celebrated with the theme “#RealLifeHeroes” paying special tribute to the real-life heroes who have committed their lives to help others in the most extreme circumstances throughout the world.
2. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has announced the ‘Swadeshi Microprocessor Challenge- Innovate Solutions for #Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ to provide further impetus to the Start-up ecosystem, innovation, and research in the country.
- MeitY has taken various initiatives and measures to improve the innovation-led ecosystem with a Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE) scheme, Centre of Excellences in IoT/FinTech space, etc.
- ‘Swadeshi Microprocessor Challenge- Innovate Solutions for #Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ seeks to invite innovators, startups and students to use microprocessors, developed by IIT Madras and C-DAC, to generate various technology products.
- IIT Madras and Center for Development of Advance Computing (C-DAC) have developed two microprocessors named SHAKTI (32 bit) and VEGA (64 bit) respectively using Open Source Architecture under the aegis of Microprocessor Development Programme of MeitY.
- The Challenge demands contestants to not only tinker with the Swadeshi Processor IPs and facilitate them with innovating the economical solutions for societal needs but also make available the entire home-grown ecosystem around Swadeshi Processors to develop the complex designs for catering to both global and domestic requirements in near future.
- The Challenge spread over 10 months, kick-started with the registration process through MyGov Portal on 18th August 2020 and will culminate in June 2021
3. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has approved the establishment of 19 Integrated Regional Offices (IROs).
- This has been done to achieve outcomes related to the mandates of Ministry in an improved manner and to further enhance its outreach to stakeholders.
- These IROs of the MoEF&CC will start functioning from October 1st, 2020.
- Each IRO shall have representation from the existing Regional Office/Regional Centre of MoEF&CC, Forest Survey of India (FSI), National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Central Zoo Authority (CZA), and Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) as available to them from time to time.
- The head of each of the IRO will be called “Regional Officer” of MoEF&CC.
4. Union Minister of Health & Family Welfare inaugurated a Thalassemia Screening and Counselling Centre at Indian Red Cross Society’s National Headquarters (IRCS NHQ) Blood Bank.
- Haemoglobinopathies, such as Thalassemia and sickle cell disease are inherited disorders of red blood cells and are preventable.
- In India, Thalassemia Major (TM) and the severe form of Thalassemia Intermedia (TI) constitute the major burden of disease.
- These Thalassemia syndromes are caused by inheritance of abnormal (beta) Thalassemia genes from both parents or abnormal beta-Thalassemia gene from one parent and abnormal variant hemoglobin gene (HbE, HbD) from the other parent.
- India has the largest number of children with Thalassemia major in the world, about 1 to 1.5 lakhs, and about 10,000 -15,000 children having Thalassemia major are born every year.
- The only cure available for such children is bone marrow transplantation (BMT). However, BMT is difficult and not affordable by the parents of all these children.
- Therefore, the mainstay of treatment is repeated blood transfusions, followed by regular iron chelation therapy to remove the excess iron overload, consequent to the multiple blood transfusions.
5. Solapur based social activist Ganesh Vilas Lengare has been awarded the Star 2020 Certificate by the World Book of Records, London.
- The organisation, founded in 2017, honours personalities for their outstanding contribution towards humanity and universal peace.
- Recognizing his efforts to help the needy during the coronavirus induced lockdown, Ganesh Lengare has been awarded the Star 2020 e-citation certificate.
- Out of the 21 schemes that were launched by him to assist the people, the most important was the COVID patient contact tracing, that was implemented with the help of Solapur district authorities.
6.As per the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE):
- Since 2015, of the 49 blocks cleared for coal mining, 9 were in ‘No-Go’ areas, or regions that were once classified by the Ministry of Environment and Forests and Climate Change as containing very dense forests and hence closed to coal mining.
- In 2020, of the 41 blocks put up for auction, 21 features in the original No-Go list.
Currently, India is not utilizing its existing capacity fully: 67% of the mines auctioned since 2015 are were not operational yet. - The environment ministry‘s ban on mining in areas of thick forest cover has locked away millions of tonnes of coal reserves.
- According to the power ministry, coal shortage is likely to hold up new power projects of over 17,000 MW aggregate capacity. This has triggered debate among the ministries of coal, power, and steel on the ‘Go, No-Go’ concept’s merits.
- In 2009, the environment and coal ministries had jointly placed the country’s forested areas under two categories – Go and No-Go – and imposed a ban on mining in the ‘No-Go’ zones on environmental grounds.
- No Go’ areas are those having either more than 10 percent weighted forest cover (WFC) or more than 30 percent gross forest cover (GFC).




