Today’s Current Affairs: 30th April 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Critical Minerals Summit:

The Ministry of Mines will hold a two day “Critical Minerals Summit: Enhancing Beneficiation and Processing Capabilities” in New Delhi.
- Critical Minerals Summit is organised by the Ministry of Mines, Government of India, in collaboration with the Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation (Shakti), the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) and the Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD).
- It is designed to foster collaboration, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical mineral beneficiation and processing.
- It will bring together a diverse array of Indian and international stakeholders, including industry leaders, startups, government officials, scientists, academics and policy experts.
- It will address the increasing demand for Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) required for renewable energy systems and electric vehicles as part of India’s strategic development goals.
- The Ministry of Mines has identified eight key minerals for focus at the summit, including Glauconite (Potash), Lithium – Rare Earth Elements (Laterite), Chromium, Platinum Group, Graphite, Tungsten associated with Graphite, Rare Earths (RE) and Vanadium associated with Graphite.
Raja Ravi Varma:

The first true copy of the painting Indulekha by Raja Ravi Varma will be unveiled at the Kilimanoor Palace, Kerala.
- Raja Ravi Varma was an Indian painter and artist. He is considered one of the greatest painters in the history of Indian art.
- He was born as Ravi Varma Koil Thampuran of Kilimanoor palace, in the erstwhile princely state of Travancore (Thiruvithankur) in Kerala.
- He is known for his amazing paintings, which revolve mainly around the Puranas (ancient mythological stories) and the great Indian epics, the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
- In addition to incidents in Hindu mythology, Varma painted many portraits of both Indians and British in India.
- His most famous works include Damayanti Talking to a Swan, Shakuntala Looking for Dushyanta, Nair Lady Adorning Her Hair and Shantanu and Matsyagandha.
- Before Raja Ravi Varma’s paintings, the paintings of Indian artists were greatly influenced by the Persian and Mughal schools.
- Varma was the first Indian to use Western techniques of perspective and composition and to adapt them to Indian subjects, styles and themes.
- His works are one of the best examples of the fusion of European academic art with a purely Indian sensibility and iconography.
- He was one of the first Indian artists to use oil paints and to master the art of lithographic reproduction of his work.
- He was notable for making affordable lithographs of his paintings available to the public, which greatly enhanced his reach and influence as a painter and public figure.
- His paintings often depicted mythological characters and Indian royalty in a realistic style, challenging traditional artistic norms.
Army Tactical Missile Systems:

The United States recently confirmed providing long-range Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine to aid its war effort against Russia.
- Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) is a conventional surface-to-surface artillery weapon system capable of striking targets well beyond the range of existing Army cannons, rockets and other missiles.
- It is manufactured by the US defense company Lockheed Martin.
- It is also designated M39 by the US Army, and its Department of Defence (DoD) designation isMGM-140.
- It first saw use during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- It’s known operators other than the US are Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
- It is 24/7, all-weather, surface-to-surface, inertially guided ballistic missile.
- It is single-stage, solid propellant with a range of about 190 miles (305 km).
- They are fired from the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) The MLRS can fire 12 surface-to-surface missiles in less than a minute.
- It has the ability to carry cluster munitions, which destroy a targeted area by releasing hundreds of bomblets instead of a single warhead.
Opioids:
The US Secretary of State Anthony Blinken’s three-day visit to China spoke about the production and export of “synthetic opioid precursors”, specifically the drug fentanyl.
- Opioids are a class of drugs that derive from or mimic, natural substances found in the opium poppy plant.
- They activate an area of nerve cells in the brain and body called opioid receptors that block pain signals between the brain and the body.
- They produce a variety of effects, including pain relief and euphoria and are highly addictive. Some common opioids include oxycodone, morphine, codeine, heroin and fentanyl.
- It can lead to death due to the effects of opioids on the part of the brain which regulates breathing.
- An opioid overdose can be identified by a combination of three signs and symptoms: pinpoint pupils, unconsciousness and difficulties with breathing.
- Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use as an analgesic (for pain relief) and anesthetic.
- It is approximately 100 times more potent than morphine and 50 times more potent than heroin as an analgesic.
Global Alliance Of National Human Rights Institutions:

The meeting of the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA) of the UN-recognised Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) worldwide will be held on May 1.
- Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions was established in 1993 as the International Coordinating Committee of National Institutions for the promotion and protection of human rights (ICC).
- It has been known as the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) since 2016 and is a member-based network organization that gathers NHRIs from all around the world.
- It has 120 members: 88 “A” status accredited NHRIs and 32 “B” status accredited NHRIs
- In a unique peer-review-based accreditation process, GANHRI ensures individual NHRIs’ compliance with internationally recognised standards – the Paris Principles– to ensure their independence, pluralism and accountability.
- The Paris Principles set out internationally agreed minimum standards that NHRIs must meet to be considered credible.
- The six principles require a country‘s human rights agency to be independent from the government in its structure, composition, decision-making and method of operation.
- The principles were adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1993.
- GANHRI, through the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA), is responsible for reviewing and accrediting NHRIs in compliance with the Paris Principles.
Nephrotic Syndrome:
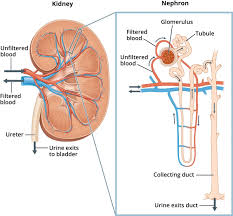
The use of fairness creams has been linked to nephrotic syndrome, with high levels of mercury found in the blood and urine of affected individuals.
- The study, published in Kidney International, reports 15 cases of nephropathy traced to the use of fairness creams.
- Nephrotic Syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by excessive protein in the urine due to malfunctioning kidney filters called glomeruli.
- Cosmetic use, specifically the use of fairness creams containing high levels of mercury, has been linked to Nephrotic Syndrome.
- The mercury in these creams can be absorbed through the skin and lead to systemic toxicity, ultimately causing damage to the kidneys and resulting in Nephrotic Syndrome.
Bru Community:

Bru voters in Tripura participated in the Lok Sabha elections for the first time, having previously voted only in assembly elections. These voters, resettled from relief camps, cast their ballots at various polling stations across the state.
- Bru community (also known as Reangs) historically inhabited Mizoram, Tripura, and parts of southern Assam.
- In Tripura, they are recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG). Following ethnic conflicts in 1997, over 30,000 Brus fled Mizoram and sought refuge in Tripura.
- In 2020, a quadripartite agreement was signed to facilitate their permanent settlement in Tripura, involving the Centre, Tripura and Mizoram governments, and Bru representatives.
Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) Status:

The Ministry of Finance has granted Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) status to the gem and jewellery sector, as part of efforts to promote ease of doing business.
- Asian Star, a leading diamond and diamond jewellery manufacturer, became the first in the industry to receive AEO status.
- Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) program operates under the World Customs Organization (WCO) SAFE Framework.
- Its goal is to boost international supply chain security and smooth the movement of lawful goods.
- Aligned with World Trade Organization trade facilitation agreements, it allows Indian Customs to strengthen cargo security through collaboration with key stakeholders in the international supply chain.
- An entity with an AEO status is considered a ‘secure’ trader and a reliable trading partner. Benefits of AEO status include expedited clearance times, fewer examinations, and improved security and communication between supply chain partners.
- In India, the AEO Programme (a voluntary initiative) was introduced by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) in India in 2011.
- It aims to simplify customs procedures and expedite clearances for businesses demonstrating high-security standards in the supply chain.
Chithirai Festival:

Lord Kallazhagar’s annual ritual in Alagar Temple, Madurai during the Chithirai festival saw thousands of devotees gathering to witness his ceremonial entry into the Vaigai river.
- The festival, merging narratives of Lord Kallazhagar and Goddess Meenakshi’s marriage, holds historical significance and promotes harmony.
- Alagar Temple is situated at the base of Alagar hills in Madurai, Tamil Nadu, and is one of Lord Vishnu’s 108 abodes, revered as Kallazhagar.
- Enclosed by fortress walls, it boasts six corridors and is mentioned in the Tamil epic Silappadikaram and Alvars’ hymns.
- The temple’s mandapam pillars showcase Nayaka’s art style, adding to its historical and architectural significance.
- Vaigai River originates in the Western Ghats (Varushanad Hills) and flows through the Pandya Nadu region of Tamil Nadu.
- Stretching 258 kilometres, it ultimately joins the Palk Strait near the Pamban Bridge in Ramanathapuram district.
- Vaigai holds historical significance as it flowed through Madurai, the capital of the ancient Pandya kingdom, and is mentioned in Sangam literature.
DURGA II Laser Weapon:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has sought USD 100 million from the Ministry of Defence to develop a high-power laser weapon, named Directionally Unrestricted Ray-Gun Array (DURGA) II, a lightweight directed energy weapon (DEW).
- It is a 100-kilowatt lightweight DEW and can be used by armed forces.
- It aims to provide the Indian armed forces with cutting-edge technology capable of neutralising various threats, including drones, missiles, and artillery shells.
- Directed-Energy Weapons (DEWs) is a type of weapon system that emits highly focused energy, typically in the form of lasers, microwaves, or particle beams, to incapacitate or destroy targets.
- Unlike traditional firearms or explosives which rely on kinetic energy (physical impact), DEWs use directed energy to achieve their effects.
- Types:
- Laser Weapons: It uses a concentrated beam of coherent light to heat and damage the target.
They can be used for various purposes, including target destruction, missile defence, and disabling electronics. - Microwave Weapons: They emit electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range to disrupt or damage electronic systems, such as computers, sensors, or communication devices.
- Particle Beam Weapons: They accelerate charged or neutral particles to high velocities and direct them towards the target to cause damage through kinetic energy transfer or ionisation effects.
- Laser Weapons: It uses a concentrated beam of coherent light to heat and damage the target.
- It has advantages including precision targeting, rapid engagement, reduced collateral damage, and potentially lower costs per shot.
- DEWs are believed to be the sole answer to virtually ‘unstoppable’ hypersonic missiles.
- They have applications in military defence, homeland security, space exploration, and law enforcement.
- It transmits lethal force at the speed of light.
- These weapons are not affected by the constraining effects of gravity or atmospheric drag, making them extremely precise.
India’s Forex Reserves Drop:

India’s forex reserves fell by USD 2.282 billion to USD 640.334 billion in the week ending 19th April 2024, as per the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Foreign currency assets decreased by USD 3.793 billion to USD 560.86 billion.
- Gold reserves increased by USD 1.01 billion to USD 56.808 billion.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) decreased by USD 43 million to USD 18.034 billion.
- Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) declined by USD 2 million to USD 4.631 billion.
- This decrease was primarily attributed to strategic interventions by the central bank, which deployed the reserves to defend the rupee amidst economic uncertainties and currency depreciation.
- The RBI intervenes in the market to manage liquidity, including selling dollars to prevent sharp rupee depreciation and prevent excessive volatility in the exchange rate.
- It can be noted that in April 2024, India’s forex kitty had reached an all-time high of USD 645.6 billion.




