Today Current Affairs: 3rd July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Freight Smart Cities:

Commerce Ministry’s Logistics Division unveils plans for ‘Freight Smart Cities’ to improve the efficiency of urban freight and create an opportunity for reduction in the logistics costs.
- Under the Freight Smart Cities initiative, city-level logistics committees would be formed.
- These committees would have related government departments and agencies at the local level, state and from the reacted central ministries and agencies.
- These would also include private sector from the logistics services and also users of logistics services.
- These committees would co-create City Logistics Plans to implement performance improvement measures locally.
- On the Freight smart city initiatives, the Logistics Division is working closely with GIZ (Germany) under Indo-German Development Cooperation, Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) and RMI India.
- This is all the more relevant as the demand for urban freight is expected to grow by 140 per cent over the next 10 years.
- Final-mile freight movement in Indian cities is currently responsible for 50 per cent of total logistics costs in India’s growing e-commerce supply chains.
15th Finance Commission Report:

The Supreme Court directed the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) to frame guidelines for payment of ex-gratia compensation to family members of persons who succumbed to COVID-19, while considering the recommendations in the 15th Finance Commission Report.
Key recommendations in the Report of the 15th Finance Commission for 2021-26:
- The share of states in the central taxes for the 2021-26 period is recommended to be 41%, same as that for 2020-21.
- The criteria for distribution of central taxes among states for 2021-26 period is same as that for 2020-21.
- However, the reference period for computing income distance and tax efforts are different (2015-18 for 2020-21 and 2016-19 for 2021-26), hence, the individual share of states may still change.
- Fiscal deficit and debt levels: The Commission suggested that the centre bring down fiscal deficit to 4% of GDP by 2025-26. For states, it recommended the fiscal deficit limit (as % of GSDP) of: (i) 4% in 2021-22, (ii) 3.5% in 2022-23, and (iii) 3% during 2023-26.
- Health: States should increase spending on health to more than 8% of their budget by 2022.
- A dedicated non-lapsable fund called the Modernisation Fund for Defence and Internal Security (MFDIS) will be constituted to primarily bridge the gap between budgetary requirements and allocation for capital outlay in defence and internal security.
President’s Rule In West Bengal:

The Supreme Court has agreed to hear a plea seeking directions to the Centre to impose President’s Rule in West Bengal over alleged incidents of post-poll violence in the state.
Allegations:
- During the violence, the government and administration remained silent spectators and no protection was provided to the victims by them.
- No appropriate action was taken against the culprits, due to which the life, liberty, dignity of the women and children are in peril and the future of Hindu residents is in jeopardy.
- The National Human Rights Commission on June 21 has already set up an eight-member committee headed by NHRC member Rajiv Jain in compliance with a Calcutta High Court direction to investigate incidents of post-poll violence in West Bengal.
Crop Insurance Week::

Government has launched the Crop Insurance Awareness Campaign for Fasal Bima Yojana during the Crop Insurance Week (being observed from July 1 to 7).
- Till date, the scheme has insured over 29.16 crore farmer applications (5.5 crore farmer applications on year-on-year basis).
- Over the period of 5 years, more than 8.3 crore farmer applications have benefited from the scheme.
- Moreover, Rs.95,000 crores claims have been paid as against Rs. 20,000 crore farmers share.
About Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana:
- It is in line with the One Nation – One Scheme theme- It replaced National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- Launched in 2016.
- Coverage: All food & oilseed crops and annual commercial/horticultural crops for which past yield data is available.
- Premium: The prescribed premium is 2% to be paid by farmers for all Kharif crops and 1.5% for all rabi crops. In the case of annual commercial and horticultural crops, the premium is 5%.
- Objectives:
- To provide insurance coverage and financial support to the farmers in the event of failure of any of the notified crops as a result of natural calamities, pests & diseases.
- To stabilise the income of farmers to ensure their continuance in farming.
- To encourage farmers to adopt innovative and modern agricultural practices.
- To ensure flow of credit to the agriculture sector.
- The Scheme covers all Food & Oilseeds crops and Annual Commercial/Horticultural Crops for which past yield data is available and for which requisite number of Crop Cutting Experiments (CCEs) are being conducted under General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
Forex Reserves:

According to the recent data from the Reserve Bank of India, India’s Foreign Exchange (Forex) Reserves surged by $ 5 billion to $ 609 billion in the week ended 25th June, 2021.
- Increase in the Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) is the major component of overall reserves.
Changes in forex reserves holdings:
- FCA rose by $ 4.7 billion to $ 566 billion.
- Gold reserves rose by $ 365 million to $ 36.296 billion.
- The special drawing rights (SDRs) with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) remained unchanged at $1.498 billion.
- The country’s reserve position with the IMF increased marginally by $ 1 million to $ 4.965 billion in the week.
Foreign Exchange Reserves:
- Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies, which can include bonds, treasury bills and other government securities.
- It needs to be noted that most foreign exchange reserves are held in US dollars.
India’s Forex Reserve include:
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold reserves
- Special Drawing Rights
- Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Objectives of Holding Forex Reserves:
- Supporting and maintaining confidence in the policies for monetary and exchange rate management.
- Provides the capacity to intervene in support of the national or union currency.
- Limits external vulnerability by maintaining foreign currency liquidity to absorb shocks during times of crisis or when access to borrowing is curtailed.
Trafficking In Persons Report 2021:

According to the Trafficking in Persons report 2021, released by the US State Department, the Covid-19 pandemic has resulted in an increase in vulnerability to human trafficking and interrupted existing anti-traffic efforts.
- Human trafficking, also called trafficking in persons, form of modern-day slavery involving the illegal transport of individuals by force or deception for the purpose of labour, sexual exploitation, or activities in which others benefit financially.
Findings of the Report:
- While India did not meet the minimum standards to eliminate trafficking, the government was making significant efforts, although these were inadequate, especially when it came to bonded labour.
- Chinese government engaged in widespread forced labour, including through the continued mass arbitrary detention of more than one million Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, ethnic Kyrgyz, and other Muslims.
Conservation Of Vultures:

150 vultures were seen in the Valmiki Tiger Reserve (VTR), Bihar, which has prompted a vulture conservation plan in the protected region of VTR.
- Vultures is one of the 22 species of large carrion-eating birds that live predominantly in the tropics and subtropics.
- They act an important function as nature’s garbage collectors and help to keep the environment clean of waste.
- Vultures also play a valuable role in keeping wildlife diseases in check.
- India is home to 9 species of Vulture namely the Oriental white-backed, Long-billed, Slender-billed, Himalayan, Red-headed, Egyptian, Bearded, Cinereous and the Eurasian Griffon.
- Most of these 9 species face danger of extinction.
- Bearded, Long-billed, Slender-billed, Oriental white-backed are protected in the Schedule-1 of the Wildlife Protection Act 1972. Rest are protected under ‘Schedule IV’.
- Recently, the Ministry for Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched a Vulture Action Plan 2020-25 for the conservation of vultures in the country.
- It will ensure minimum use of Diclofenac and prevent the poisoning of the principal food of vultures, the cattle carcasses.
- The Vulture Safe Zone programme is being implemented at eight different places in the country where there were extant populations of vultures, including two in Uttar Pradesh.
- To upscaling conservation four rescue centres will be opened like Pinjore in the north, Bhopal in central India, Guwahati in Northeast and Hyderabad in South India.
- The ministry has now also launched conservation plans for the red-headed and Egyptian vultures, with breeding programmes for both.
- To study the cause of deaths of vultures in India, a Vulture Care Centre (VCC) was set up at Pinjore, Haryana in 2001.
- Later in 2004, the VCC was upgraded to being the first Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centre (VCBC) in India.
- At present, there are nine Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centres (VCBC) in India, of which three are directly administered by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS).
Retail And Wholesale Trades:

Minister of MSME announced revised guidelines for MSMEs with inclusion of Retail and Wholesale trades as MSMEs.
- The revised guidelines will benefit 2.5 Crore Retail and Wholesale Traders.
- Retail and wholesale trade which were left out of the ambit of MSME are now under the revised guidelines and thus will also get benefit of priority sector lending under RBI guidelines.
- With the revised guidelines the Retail and wholesale trades will be now be allowed to register on Udyam Registration Portal.
Global Peace Index (GPI):
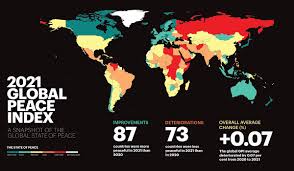
The 15th edition of the Global Peace Index (GPI) was released which ranks 163 independent states and territories according to their level of peacefulness. Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP).
- The GPI covers 99.7 per cent of the world’s population, using 23 qualitative and quantitative indicators and measures the state of peace across three domains:
- the level of Societal Safety and Security,
- the extent of Ongoing Domestic and International Conflict, and
- the degree of Militarisation.
Findings:
- India ranked 135/163 with an improvement of 2 ranks.
- Iceland remains the most peaceful country in the world, a position it has held since 2008.
- Afghanistan is the least peaceful country in the world for the fourth consecutive year, followed by Yemen, Syria, South Sudan, and Iraq.
Istanbul Convention On Violence Against Women:

Turkey’s controversial exit from Istanbul Convention on Violence Against Women on July 1 has received severe criticism from various quarters and has led to protests across the country.
- The Council of Europe established the Istanbul Convention, a human rights treaty, with the aim to prevent and prosecute all forms of violence against women, promote gender equality and ensure protection and rehabilitation of women who are victims of violence.
- The treaty was opened for ratification in May 2011. From the European Union, 34 countries signed this treaty.
- On November 24, 2011, Turkey became the first country to ratify the Istanbul convention and, on March 8, 2012, it incorporated the Istanbul Convention into domestic law.
- some officials of Erdogan’s nationalist party claimed that the convention demeans traditional family structure, promotes divorces and encourages acceptance of LGBTQ in the society.
- Violence against women and honour killings are persistent in Turkey.
- The country ranks 133 out of 156 countries in the Global Gender Gap report 2021. According to UN women data, 38 per cent of women in Turkey face violence from a partner in their lifetime.
Sardar Patel National Unity Award:
The online nominations/recommendations process for the Sardar Patel National Unity Award is on and the last date for nominations/recommendations is 15th August 2021.
- The Government of India has instituted the highest civilian award in the field of contribution to the unity and integrity of India, in the name of SardarVallabhbhai Patel.
- The Award seeks to recognize notable and inspiring contributions to promote the cause of national unity and integrity and to reinforce the value of a strong and united India.
- Any citizen of India without distinction of religion, race, caste, gender, place of birth, age or occupation, and any institution/organization would be eligible for the Award.
- Any Indian national or institution or organization based in India may nominate an individual or institution or organization for consideration for this Award.
- Individuals/institutions/organizationsmay also nominate themselves. State Governments, Union Territory Administrations and Ministries of the Government of India may also send nominations for the award.
Organisation For Economic Co-operation And Development (OECD) And G20:

India has joined the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and G20 Inclusive Framework tax deal of global corporate tax.
- Majority of the members OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting(including India)adopted a high-level statement containing an outline of a consensus solution to address the tax challenges arising from the digitalisation of the economy.
- The proposed solution consists of two components –
- Pillar One which is about reallocation of additional share of profit to the market jurisdictions and
- Pillar Two consisting of minimum tax and subject to tax rules.
- Further, the technical details of the proposal will be worked out in the coming months and a consensus agreement is expected by October.
- Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) refers to tax-avoiding strategies used by big multinational companies that exploit the gaps and mismatches in tax rules across the globe.
Short Span Bridging System (SSBS)-10 m:

The first production lot of 12 Short Span Bridging System (SSBS)-10 m, designed and developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has been inducted into Indian Army.
- The SSBS-10 m plays a crucial role of bridging the gaps up to 9.5 m as a single span providing a 4 m wide, fully decked roadway, ensuring faster movement of the troops.
- Research & Development Establishment (Engrs) Pune, a premier engineering laboratory of DRDO, has designed and developed the system in association with M/s L&T Ltd.
- The 12 bridges are part of 102 SSBS-10 m from M/s L&T Ltd, which is the production agency.
- The Project Short Span Bridging System involved the development of two prototypes of 5 m SSBS on Tatra 6×6 chassis and another two prototypes of 10 m SSBS on Tatra 8×8 re-engineered chassis.
- This bridging system is compatible with Sarvatra Bridging System (75 m), where the last span requires covering gaps less than 9.5 m.




