Today’s Current Affairs: 3rd July 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Facciolella smithi:

Indian scientists recently discovered a new deep-sea eel species, Facciolella smithi (Smith’s witch eel), in the Arabian Sea.
- Facciolella smithi (Smith’s witch eel) is a new species of deep-sea eel.
- It was discovered by the scientists at the ICAR–National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources, Lucknow.
- The specimen was collected at a depth ranging from 260 to 460 meters off the Kerala coast in the Arabian Sea.
- It belongs to the family Nettastomatidae.
- The eel likely inhabits the seafloor or burrows into soft sediments, navigating the pitch-black waters with the help of its sensory adaptations rather than sight.
- The species has been named in honour of eminent ichthyologist Dr. David G. Smith for his significant contributions to eel taxonomy.
- The eel has an elongate, ribbon-like body that reaches just over two feet in length. This slender shape allows it to glide smoothly through deep-sea waters.
Coloration: One of the most striking visual features is its two-tone body. The upper half is a rich brown, while the underside is described as “milky white.” This contrast may aid in camouflage in the dim oceanic depths. - Tail Regeneration: Remarkably, most of the specimens showed evidence of regrown or regenerated tails, indicating either predator encounters or natural loss due to environmental factors.
- This regenerative trait is crucial for survival in the harsh and competitive deep-sea ecosystem.
Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve:

The elusive and endangered white-eared night heron has been camera-trapped in Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh recently.
- Namdapha, a national park and tiger reserve, lies on the international border between India and Myanmar within Changlang District in the state of Arunachal Pradesh.
- It covers an area of 1985.23 sq.km.
- It is located at the junction of the Indian subcontinent and Indo-China biogeographic Regions.
- It is nestled between the Dapha Bum ridge of the Mishmi Hills of the northeastern Himalayas and the Patkai Ranges.
- It has a common boundary with Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary (Arunachal Pradesh).
- The Namdapha River (a tributary of Noa-Dihing River) flows right across in a north-south direction of this reserve, and hence the name Namdapha has been given.
- White-Eared Night Heron is a medium brown heron with a brown-streaked breast and a white patch on the side of the head. Scientific Name: Oroanassa magnifica. It is primarily found in southern China and northern Vietnam and has an estimated global population of fewer than 1,000 individuals. Known for being extremely secretive and nocturnal, the white-eared night heron is rarely observed in the wild .It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Volume Weighted Average Price:
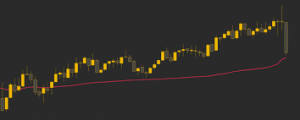
To make trading easier for institutional investors and market participants, SEBI recently made it mandatory to issue a Common Contract Note with a single volume weighted average price.
- The Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is, as the name suggests, is the average price of a stock weighted by the total trading volume.
- The VWAP is used to calculate the average price of a stock over a period of time.
- It helps compare the current price of the stock to a benchmark, making it easier for investors to decide when to enter and exit the market.
- Also, the VWAP can assist investors in determining their approach towards a stock (active or passive) and make the right trade at the right time.
- The VWAP is calculated for each day.
- It starts when the markets open and ends when the markets close for the day. Since it is done every day, the calculation uses intraday data.
- The formula for calculating VWAP is as follows:
- VWAP = Typical Price*Volume / Cumulative Volume
- Here, the numerator indicates the total value of all the trades for any specific period, and the denominator indicates the total trading volume for the same duration.
- The typical price is the average of the high price, the low price, and the closing price of the stock for that day.
- The VWAP ratio is then presented on a chart as a line.
- It has been likened to a moving average, in that when the price is above the VWAP line, the market is seen as in an uptrend, and when the price is below the VWAP, the market is in a downtrend.
Scheme for Promotion of Registration of Employers and Employees (SPREE) 2025:

The Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) has launched SPREE 2025 to expand social security coverage.
- The scheme offers a one-time opportunity for employers and workers to register under ESI without facing penalties or retrospective inspections.
- A special scheme to bring unregistered employers and employees—especially contractual and temporary workers—under the ESI social security net.
- Launched by: Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
- Ministry: Ministry of Labour and Employment
- Objective is To formalize employment by facilitating voluntary compliance and expanding ESI coverage to informal workers.
- Key Features of SPREE 2025:
- Digital Registration: Registration via ESIC portal, Shram Suvidha portal, and MCA portal.
- No Retrospective Penalty: No contribution, inspection, or legal demand for the pre-registration period.
- Declared Validity: Registration valid from the date declared by the employer.
- No Legal Hurdles: Removes fear of litigation for past non-compliance.
- Boost to Informal Sector: Brings temporary, contractual, and unorganised workers under formal coverage.
- One-Time Amnesty: Encourages large-scale participation without penal action.
RECLAIM Framework:

The Coal Ministry is set to launch RECLAIM framework on 4th July, 2025.
- RECLAIM Framework is a community engagement and development framework designed specifically for mine closures.
- The Coal Controller Organisation, under the Ministry of Coal, in partnership with the Heartfulness Institute, has developed this comprehensive Community Development Framework.
- Recognizing that mine closures significantly impact both landscapes and local livelihoods, this framework is a key step toward ensuring a just and sustainable transition for communities that have developed alongside mining operations over decades.
- Features of the RECLAIM Framework
- The framework—referred to as the RECLAIM—serves as a structured guide for inclusive community engagement and development throughout the mine closure and post-closure phases.
- It offers a practical, step-by-step approach to institutionalizing community participation in the transition process.
- It is supported by a suite of actionable tools, templates, and field-tested methodologies tailored to the Indian context. Special emphasis is placed on gender inclusivity, the representation of vulnerable groups, and alignment with Panchayati Raj Institutions, ensuring that the transition is equitable and locally relevant.
- Ultimately, the RECLAIM Framework aspires to facilitate a seamless and resilient transition for mining communities—grounded in trust, ecological restoration, and long-term socio- economic well-being.
Genome:
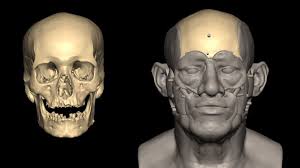
Researchers recently sequenced the first whole ancient Egyptian genome from an individual who lived 4,500 to 4,800 years ago — the oldest DNA sample from Egypt to date.
- A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic information.
- A genome includes all of the hereditary instructions for creating and maintaining life, as well as instructions for reproduction.
- The human genome, like all other cellular life forms, consists of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and includes both the nuclear and mitochondrial DNA.
- This is in contrast to ribonucleic acid (RNA) viruses, whose genome is composed of RNA.
- The instructions in our genome are made up of DNA.
- Within DNA is a unique chemical code that guides an organism’s growth, development and health.
- This code is determined by the order of the four nucleotide bases that make up DNA: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.
- DNA has a twisted structure in the shape of a double helix.
- Single strands of DNA are coiled up into structures called chromosome.
- Within chromosomes, sections of DNA are organised into genes.
- Genes control different characteristics such as eye colour and height.
- All living things have a unique genome.
- There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human genome.
- Between 1990 and 2003, all twenty-three pairs were fully sequenced through an international research undertaking known as the Human Genome Project.
Kariyachalli Island:

The Tamil Nadu government has started an initiative to save the sinking Kariyachalli island.
- Kariyachalli Island is located in the Gulf Of Mannar region which is one of India’s most ecologically sensitive marine zones.
- Kariyachalli is one of the 21 islands in the Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park region, located on the southeastern coast of India between Rameshwaram and Thhothukudi.
- The gulf is home to one of the four major coral reefs in India.
- Kariyachalli island possess beaches, sand dunes, spit and sandy plains.
- The uninhabited island has sunk significantly over the past few decades due to rapid erosion, rising sea levels and degradation of the surrounding coral reef and seagrass meadows.
- According to a report by the Indian Institute of Technology Madras’s (IIT Madras), the Department of Ocean Engineering island’s landmass shrank by over 70 per cent in 2024 compared to 1969.
- About a third of the coral around the island has bleached on average and further degradation and disappearance of coral reefs would make the island more vulnerable to erosion, the report stated.
- At the current rate of erosion, the island is expected to be submerged by 2036. With just a decade left, government authorities are now racing to save it from disappearing.
- The Tamil Nadu Sustainably Harnessing Ocean Resources (TNSHORE) project, expected to start in August 2025, will try to restore the reefs with artificial modules, planting seagrass beds and reviving marine life.
Terbium:

Scientists from Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a simple, glowing paper sensor that could help detect liver cancer early — using the green glow of a rare earth metal called terbium.
- Terbium is a rare-earth metal of the lanthanide series of the periodic table.
- It occurs in many rare-earth minerals but is almost exclusively obtained from bastnasite and from laterite ion-exchange clays. It is also found in the products of nuclear fission.
- It is a moderately hard, silvery white metal that is stable in air when in pure form.
- The metal is relatively stable in air even at high temperatures, because of formation of a tight, dark oxide layer that can be represented as a mixed oxide composed of Tb2O3 and TbO2.
- It readily reacts with dilute acids, but it is insoluble in Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) because the presence of the fluoride ion protects the metal from further reaction by forming a protective layer of TbF3.
- It exhibits strong paramagnet above 230 K and antiferromagnetic between 220 K and 230 K, and it becomes ferromagnetic below 220 K.
- Terbium compounds are used as green phosphors in fluorescent lamps, computer monitors, and TV screens that use cathode-ray tubes. Another major use is with dysprosium and iron in the magnetostrictive alloy.
Financial Fraud Risk Indicator:

The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) directed all Scheduled Commercial Banks, Small Finance Banks, Payments Banks, and Co-operative Banks to integrate the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) developed by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) into their systems.
- Financial Fraud Risk Indicator was launched by the Department of Telecommunications Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU).
- It is a risk-based metric that classifies a mobile number to have been associated with Medium, High, or Very High risk of financial fraud.
- This classification is an outcome of inputs obtained from various stakeholders including reporting on Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C’s) National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), DoT’s Chakshu platform, and Intelligence shared by banks and financial institutions.
- It empowers stakeholders-especially banks, NBFCs, and UPI service providers- to prioritize enforcement and take additional customer protection measures in case a mobile number has high risk.
- The Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU) of DoT regularly shares the Mobile Number Revocation List (MNRL) with stakeholders, detailing numbers disconnected due to cybercrime links, failed re-verification, or misuse—many of which are tied to financial frauds.
- Banks and financial institutions can use FRI in real time to take preventive measures such as declining suspicious transactions, issuing alerts or warnings to customers, and delaying transactions flagged as high risk.
- The system’s utility has already been demonstrated with leading institutions such as PhonePe, Punjab National Bank, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Paytm, and India Post Payments Bank actively using the platform.
- The FRI allows for swift, targeted, and collaborative action against suspected frauds in both telecom and financial domains.
C-FLOOD Platform:

The Union Minister of Jal Shakti inaugurated the C-FLOOD platform.
- C-FLOOD Platform is a Unified Inundation Forecasting System.
- It is collaboratively developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune and Central Water Commission (CWC), Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This initiative, executed under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) jointly steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Department of Science and Technology (DST), marks a transformative step towards strengthening India’s flood management and disaster response framework.
- It is a web-based platform that provides two-days advance inundation forecasts up to village level in the form of flood inundation maps and water level predictions.
- The platform will act as a unified system integrating flood modelling outputs from national and regional agencies, offering a comprehensive decision-support tool for disaster management authorities.
- At present, the system covers the Mahanadi, Godavari, and Tapi river basins, with more river basins to be incorporated in the future.
- The C-FLOOD platform uses advanced 2-D hydrodynamic modelling to simulate flood scenarios.
- The simulations for Mahanadi Basin are run on High Performance Computing (HPC) infrastructure under NSM at C-DAC Pune, with integration of outputs for Godavari and Tapi Basins, which have been developed by National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) under the National Hydrology Project (NHP).
National Sports Policy (NSP) 2025:

The Union Cabinet has approved the National Sports Policy (NSP) 2025 (Khelo Bharat Niti 2025), replacing the National Sports Policy, 2001. It outlines a roadmap to make India a global sporting powerhouse with a focus on the 2036 Olympics.
Key Pillars of the National Sports Policy 2025:
- Excellence on the Global Stage: Focuses on strengthening sports from grassroots to elite levels through early talent identification, development of competitive leagues and infrastructure, and creation of world-class training and coaching systems. It also aims to enhance National Sports Federations’ governance, promote sports science and technology, and train coaches, officials, and support staff.
- Sports for Economic Development: It promotes sports tourism, startups, and private investment to strengthen India’s role in the global sports economy.
- Sports for Social Development: The policy emphasizes the role of sports in promoting social inclusion by encouraging participation from marginalized groups, reviving traditional and indigenous games, and fostering diaspora engagement and volunteering.
- Sports as a People’s Movement: To make sports a national movement, the policy aims to promote mass participation and a fitness culture through campaigns, introduce fitness indices for institutions, and improve access to sports facilities across the country.
- Integration with Education (NEP 2020): Aligned with National Education Policy 2020, it seeks to integrate sports into school curricula and train educators to foster early sports engagement.
Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development:
The National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development (NIPCCD) has been renamed as the Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development. A new Regional Centre in Ranchi will also be inaugurated to strengthen grassroots implementation of women and child welfare schemes in Eastern India.A premier autonomous body under the Ministry of Women and Child Development, serving as the national apex institute for training, research, and capacity-building in women and child welfare. Objectives is to strengthen capacity building for the implementation of women and child development schemes,to support region-specific interventions aligned with national missions like Mission Shakti, Vatsalya, Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0.
Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), under Operation MED MAX:
The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), under Operation MED MAX and in coordination with international agencies, has dismantled a transnational drug cartel operating across more than 10 countries in Asia, North America, Europe, and Oceania. NCB: Headquartered in New Delhi, NCB is the apex drug law enforcement and intelligence agency in India, constituted in 1986 under the provisions of the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985. The National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances is based on Article 47 of the Indian Constitution, a Directive Principle of State Policy, which mandates the prohibition of the consumption of intoxicating drugs except for medicinal purposes.NCB Operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs and coordinates with various central and state agencies for enforcement and policy implementation. Plays a key role in national security and public health, especially in light of increasing international drug syndicates. Leads India’s response to digital and transnational narcotic crimes. NCB supports multilateral enforcement actions involving agencies like the US DEA and Interpol.
DengiAll:
India’s efforts to develop a safe and effective dengue vaccine have taken a significant leap forward, with its first indigenous tetravalent dengue vaccine, DengiAll, reaching 50% enrolment in Phase 3 clinical trials. It is developed by Panacea Biotec under a licensing agreement with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), targeting all four dengue virus subtypes. The vaccine has shown a balanced and robust immune response in Phase I and II trials, with no major safety concerns reported. The vaccine is significant as dengue currently has no specific treatment for everyone, and severe cases can lead to life-threatening complications like internal bleeding and shock. It is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the dengue virus (genus Flavivirus), primarily transmitted by the female Aedes aegypti mosquito. This mosquito also spreads chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika. There are four distinct but related dengue serotypes: DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4. Symptoms: High fever, severe headache, eye pain, muscle and joint pain, rash, and fatigue. Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosis is done via blood test. There is no specific antiviral treatment; care is supportive.
Fourth International Financing for Development Conference (FfD4):
The Fourth International Financing for Development Conference (FfD4) is underway in Seville, Spain, focusing on overhauling the global financial architecture.A United Nations-led global forum to address sustainable development financing gaps and reform global economic governance. Held in Seville, Spain in 2025 under the aegis of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA).Objective is to align development finance with climate goals, restore trust between developed and developing nations, and create equitable financial systems.
Gaden Phodrang Trust:
The 14th Dalai Lama declared that the Gaden Phodrang Trust would be the sole authority to recognize his reincarnation, reaffirming his earlier 2011 statement. This announcement precedes his 90th birthday and reiterates Tibetan Buddhist autonomy in succession matters.The term ‘Gaden Phodrang’ originally referred to the Dalai Lama’s residence at Drepung Monastery in Lhasa, Tibet. It evolved into the institutional base of the Dalai Lama lineage.
The Gaden Phodrang Trust is a registered non-profit body based in Dharamshala, India, formed in 2011. It functions out of the Dalai Lama’s office.The Trust is chaired by His Holiness the Dalai Lama and is managed by close aides, including Prof. Samdhong Rinpoche, a senior monk and former Prime Minister (Kalon Tripa) of the Central Tibetan Administration.




