Today’s Current Affairs: 5th August 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL):

The traffic from Sikkim and Kalimpong to Siliguri and vice versa on NH10 remained suspended because of repairs by the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited on a 30 km-long stretch following a landslide and cave-ins.
- It is a Central Public Sector Undertaking (CPSU) under the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Government of India.
- The company was incorporated on the 18th of July, 2014, under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is a wholly owned Government entity.
- It is dedicated exclusively to the task of constructing/upgrading/widening National Highways in parts of the country which shares international boundaries with neighbouring countries in order to promote regional connectivity on a substantial basis.
- NHIDCL’s domain extends across the Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands; the state of Uttarakhand; and the entire Northeastern Region (NER).
- Its ambit includes tunnels, logistics hubs, interstate and international road linkages, and advanced mobility facilities – all serving as the arteries of India’s economic and geopolitical aspirations.
- As the executing arm of the Government of India’s vision to realize the “Act East Policy,” NHIDCL plays a pivotal role as the nodal agency in the Northeastern region.
Sahel Region:
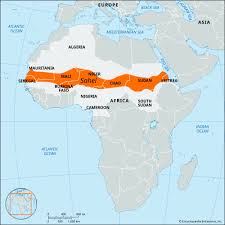
Russia has tightened its grip over the Sahel region in West Africa, signing a key nuclear agreement with Niger recently.
- It is a semi-arid region of western and north-central Africa.
- A 5,000 kilometre belt of land, the Sahel stretches from Africa’s Atlantic Coast to the Red Sea.
- It forms a transitional zone between the arid Sahara (desert) to the north and the belt of humid savannas to the south.
- It runs through portions of the countries of Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, and Eritrea.
- The Sahel is a semiarid steppe, a type of dry grassland.
- The vegetation is chiefly of the savanna type, with little continuous cover.
- It has low-growing grass, thorny shrubs, and scattered acacia and baobab trees.
- Since gaining independence in the 1960s, many countries in the Sahel have experienced violent extremism due to the confluence of weak and illegitimate governance, economic decline, and the worsening effects of climate change.
- The Sahel remains a principal transit point for migrants traveling from sub-Saharan Africa to northern coastal states and on to Europe.
Assets Under Management:

The Asset Under Management (AUM) of India’s Mutual Fund (MF) industry was estimated at ₹74.40 lakh crore, marking a more than sevenfold growth in 10 years, according to a recent report.
- AUM is a crucial metric in the financial industry, particularly in mutual funds.
- AUM refers to the total market value of the assets that a financial institution or investment company manages on behalf of its clients.
- These assets can include stocks, bonds, and other financial investments.
- AUM is affected by:
- Market fluctuations
- Net investor inflows (new investments)
- Redemptions or withdrawals
- Dividend reinvestments
- AUM is an essential measure of the size and success of a mutual fund, as it provides investors with insight into the fund’s popularity and credibility.
- It also indicates the financial institution’s expertise and ability to attract and retain clients.
- Additionally, investors often use AUM to assess the fund’s liquidity and stability.
- The larger the AUM, the more resources and diversification potential the fund may have, which can attract investors seeking long-term growth and stability.
- A mutual fund’s AUM can have a large impact on the fees that an investor usually pays to invest in the mutual fund. For example, some larger funds might have a very high minimum investment.
Mahabodhi Temple : In News

The Supreme Court recently agreed to review a petition seeking the repeal of the Bodh Gaya Temple Act of 1949, advocating for its replacement with a central law to better manage the Mahabodhi Temple in Bihar.
- Mahabodhi Temple is one of the four most sacred sites of Buddhism, marking the location where Buddha attained Enlightenment (Bodhi), along with:
- Lumbini (Buddha’s birthplace)
- Sarnath (Buddha’s first sermon)
- Kushinagar (Buddha’s parinirvana)
- Location: Bodh Gaya, Bihar, on the banks of the Niranjana River.
- The first temple at the site was constructed by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC.
- The present temple was built in the 5th–6th century AD, in the Gupta period.
- It is one of the earliest Buddhist temples built entirely in brick, still standing in India, from the late Gupta period.
- The temple was heavily restored in the 19th century, by Myanmar (Burmese) Buddhists and then by the British archaeologist Sir Alexander Cunningham.
- It was declared a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 2002.
- The temple structure is 180 feet (55 meters) in height.
- It is dominated by a pyramid-shaped central tower, called a shikhara.
- This tower comprises several layers of niches, arch motifs, and fine engravings.
- Four additional towers, each identical to the main tower but smaller in size, adorn the corners of the two-story structure.
- A shrine inside the temple holds a yellow sandstone statue of the Buddha encased in glass.
- Sacred Bodhi Tree: Believed to be a direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained Enlightenment.
- Vajrasana (Diamond Throne): A stone slab marking the exact spot where Buddha meditated and attained enlightenment.
- Stone railings surround the temple as well as the Bo tree.
- One of the most famous of Ashoka’s many pillars (on which he had engraved his proclamations and his understanding of religious doctrine) stands at the southeast corner of the temple.
- The 4.8-hectare complex includes ancient shrines and modern Buddhist structures built by devotees.
UN World Food Programme : In News

India launched a new collaborative initiative with the support of the UN World Food Programme to strengthen Rice Fortification and Supply Chain Management in Nepal.
- Report released by the WFP is the Global Report on Food Crisis which describes the scale of acute hunger in the world.
Headquarters: Rome, Italy. - It is a branch of the United Nations that deals with hunger eradication and promotes food security in the world.
- It is the world’s largest humanitarian agency and was established in 1961.
- The organization’s work is guided by Sustainable Development Goal 2, which aims to end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture by 2030.
- It operates in more than 120 countries, provides food assistance during emergencies and works with communities to enhance nutrition and generate resilience.
- Funding: WFP is funded by voluntary donations from governments, corporates and private donors.
- It is a member of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- India is a member of this organization and WEF has been functioning in India since 1963.
- WEF was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2020.
Ayurveda Aahara:

The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), in consultation with the Ministry of Ayush, has released a definitive list of Ayurvedic food preparations under the category of “Ayurveda Aahara”.
- Ayurveda Aahara refers to food products developed in line with the holistic dietary principles of Ayurveda, one of the world’s oldest systems of health and wellness.
- These preparations emphasise balance, seasonal suitability, and using natural ingredients and herbs known for their therapeutic benefits.
- This significant step brings India’s time-honoured food wisdom into the mainstream, following the introduction of the Food Safety and Standards (Ayurveda Aahara) Regulations in 2022.
- These regulations recognise foods based on recipes, ingredients, and processes from authoritative
- Ayurvedic texts, and the new list brings unprecedented clarity and confidence to consumers and businesses alike.
- The list, issued under Note (1) of Schedule B of the regulations, draws directly from classical Ayurvedic texts listed in Schedule A, ensuring the authenticity and traditional basis of these food formulations.
- This initiative aims to assist Food Business Operators (FBOs) by providing a clear and credible reference for the manufacture of Ayurveda Aahara products.
- This initiative marks a pivotal moment in enhancing regulatory clarity for industry stakeholders while promoting the widespread adoption of Ayurveda-based nutrition for better public health outcomes.
Asian Giant Tortoise:

The Asian giant tortoise, the largest tortoise in mainland Asia, has been reintroduced into the Zeliang Community Reserve in Nagaland’s Peren district.
- The Asian Giant Tortoise (Manouria emys phayrei) is the largest tortoise in Asia.
- It is considered to be one of the oldest tortoise lineages in the world. And these ancient tortoises share an interesting behavior with many crocodilians—to protect their eggs and maintain appropriate temperatures for incubation.
- As hatchlings, these tortoises appear a grayish brown, and become more charcoal colored as they mature into adulthood.
- The Asian Giant Tortoise can be found in the tropical and subtropical hill forests.
- They are found in Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, and Malaysia and other places.
- Diet: Bamboo shoots, tubers and other juicy vegetation and some invertebrates and frogs.
- Threats: Hunting for consumption, habitat loss, anthropogenic activities like construction and slash and burn.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II.
Seabuckthorn:

Seeds of seabuckthorn and buckwheat grown in the cold desert of Ladakh are part of the experiments on board the International Space Station flown by NASA’s Crew-11 mission.
- It is popularly known as the ‘Wonder Plant’, ‘Ladakh Gold’, ‘Golden Bush’, or ‘Gold Mine’ of cold deserts.
- Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) is a plant found throughout Europe and Asia.
- In India, it is found above the tree line in the Himalayan region, generally in dry areas such as the cold deserts of Ladakh and Spiti.
- It produces small orange or yellow-coloured berries that are sour in taste but rich in vitamins, especially vitamin C.
- The shrub can withstand extreme temperatures ranging from minus 43 degrees Celsius to 40 degrees Celsius and is considered drought-resistant.
- These two characteristics make the shrub an ideal plant species to establish in cold deserts.
- Sea Buckthorn berries have a unique characteristic of remaining intact on the shrub throughout the winter months despite the subzero temperature.
- It has been used traditionally for a variety of purposes.
- Every part of the plant–fruit, leaf, twig, root, and thorns has been traditionally used as medicine, nutritional supplement, fuel, and fence.
- Many bird species feed on the berries when other sources of food are limited in the region.
- The leaves serve as protein-rich fodder for cold desert animals like sheep, goats, donkeys, cattle, and double-humped camels.
India Electric Mobility Index:

NITI Aayog launched the India Electric Mobility Index
- It is a first-of-its-kind tool developed to comprehensively track and benchmark the progress of States and Union Territories (UTs) in achieving their Electric Mobility goals.
- The India Electric Mobility Index (IEMI) tracks, evaluates and scores all Indian States and UTs out of 100 across 16 indicators under three-core themes:
- Transport Electrification Progress to capture demand-side adoption,
- Charging Infrastructure Readiness to track allied charging infrastructure development and
- EV Research and Innovation Status: Covers supply-side ecosystem R&D efforts.
- It enables evaluation across States and Union Territories, identifying key drivers of success as well as areas requiring targeted interventions.
- The Index aims to inform decision-making, foster healthy competition among states, and promote sharing of best practices.
- The Index underscores the importance of state-level coordination, integrated planning, and cross-sectoral collaboration in achieving India’s electric mobility vision.
- By identifying strengths and gaps, the Index aims to support states in aligning with national goals while addressing local needs.
- It provides a transparent, comparative framework to assess progress across key themes such as electrification, infrastructure, and innovation.
- It enables states to benchmark their efforts, identify gaps, and learn from each other’s successes.
Enhancing Northeast Connectivity for Act East Policy:
India’s Act East Policy aims to transform the North-East into a gateway to Southeast Asia. The commissioning of the 51.38-km Bairabi–Sairang rail line in Mizoram is a key step toward this.
- The region has seen remarkable development in roads, railways, airports, and digital networks under initiatives like the Act East Policy and the North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS).
- Historic advances have been made in Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram, including Mizoram receiving its first passenger train in independent India’s history. Railway connectivity has also been extended to Manipur and Nagaland.
- The Bairabi–Sairang Rail Project in Mizoram is a key strategic initiative under India’s Act East Policy, aimed at boosting connectivity in the Northeast.
- Originally, Mizoram had only a 1.5 km metre-gauge line linking Bairabi (Kolasib district) to Silchar (Assam).
- Despite challenges like difficult terrain and manpower shortages, the project includes 48 tunnels (totaling 12.85 km) and 142 bridges, and received safety clearance in June 2025.
- Ro-Ro ferry services have been revived on the Brahmaputra, offering cost-effective cargo transport and boosting economic activity.
- Digital infrastructure has expanded with programs like BharatNet and 4G saturation, connecting remote villages and bridging the digital divide.
- The Government of India sanctioned 90 projects, under NESIDS to upgrade healthcare, education, drinking water, and public infrastructure, with 30 projects already completed.
- This infrastructure revolution has improved the quality of life, attracted private investment, and fostered regional development, positioning Northeast India as an important gateway for national and regional integration.
IEA’s Electricity Mid-Year Update 2025:

The International Energy Agency’s Electricity Mid‑Year Update 2025 highlights rising power demand fueled by heatwaves, air conditioners, data centres, and electric vehicles, while solar, wind, and nuclear energy rapidly reshape the global electricity mix.
Key Highlights:
- Global electricity demand is projected to grow by 3.3% in 2025 and 3.7% in 2026, well above the 2015–2023 average of 2.6%.
- India and China will together contribute 60% of global demand growth through 2026, with India growing at 4% in 2025 and 6.6% in 2026.
- Solar and wind are set to surpass coal generation by 2025 or 2026, with their share growing from 15% in 2024 to 20% by 2026. Solar and wind will account for over 90% of the increase in electricity demand in 2025.
- As a result, coal’s share in total generation is set to drop below 33% for the first time in the last 100 years.
- Global nuclear power generation is set to reach a record high in 2025, rising by 2% over 2025-26, driven by new reactor installations (in China, India, South Korea) and plant restarts (in Japan).
- Blackouts in Chile and Spain/Portugal emphasize the need for robust grid infrastructure, secure supply chains, and flexibility resources to ensure electricity security.
- Global emissions rose by only 1.2% in 2024, despite extreme weather.
- Low-emission sources (renewables + nuclear) are offsetting fossil fuel use, though unpredictable weather still affects year-to-year trends.
AI-designed Proteins:

Harvard scientists have used AI-designed proteins to generate large numbers of immune cells, boosting immunity against diseases like cancer and viral infections.
- They engineered a synthetic activator for the Notch signalling pathway, which is crucial for transforming immune progenitors into T cells.
- Notch signalling helps maintain tissue balance and stability in the body.
- Progenitor cells are intermediate cells between stem cells and mature cells that divide and differentiate into specific cell types, essential for tissue development and regeneration.
- Using AI-based protein design techniques, researchers engineered synthetic protein activators that are safe and effective for use within the human body.
- David Baker was awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his groundbreaking work in computational protein design, leveraging AI-based techniques.
- Impact & Applications:
- Enabled large-scale T cell production in lab bioreactors, aiding CAR-T therapies.
- In animal trials, these proteins enhanced T cell response and promoted long-lasting Memory T cells, boosting vaccine efficacy.
- Potential for future therapies, targeted protein designs could connect T cells to cancer cells, enhance anti-tumor immunity, and counter tumor-induced immune suppression.
- T cells are a type of white blood cell (WBC) essential to the immune system, responsible for identifying and responding to pathogens.
Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) City Index 2025:

Bengaluru has secured the 26th rank in the Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) City Index 2025, emerging as India’s top AI R&D and data centre hub.
Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) City Index 2025:
- A global benchmarking report that evaluates cities on their capacity, investment, and innovation in artificial intelligence.
- Published by Market research firm Counterpoint Research.
- Objective is to identify and rank leading global urban centres driving AI development across R&D, infrastructure, governance, and real-world AI use
- India’s Performance in AI City Index 2025:
- Bengaluru ranked 26th globally; India’s top AI city with a vibrant startup and data ecosystem.
- Mumbai and Delhi leverage AI in traffic and public security, with growth potential.
- Other Indian cities in top national ranks include Chennai and Kolkata.
- Report flags need for stronger AI roadmap and regulatory frameworks in India.
- Top Global Rankings Global AI City Index:
- Singapore
- Seoul
- Beijing
- Dubai
- San Francisco
1st-ever BIMSTEC Traditional Music Festival:

The first-ever BIMSTEC Traditional Music Festival is being held in New Delhi at Bharat Mandapam, showcasing the rich musical heritage of all seven BIMSTEC countries.
- A regional cultural event featuring traditional music performances by artists from Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand under the BIMSTEC framework.
- Hosted in: New Delhi, at Bharat Mandapam, symbolizing India’s role as a cultural anchor in the region.
- Theme: “SaptaSur: Seven Nations, One Melody” — celebrating unity in diversity through musical traditions.
- Organised by Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) under the Ministry of External Affairs.
- Aim is to promote regional integration, foster cultural dialogue, and deepen people-to-people ties among BIMSTEC member countries.
- Artists from all seven BIMSTEC nations present their indigenous music, building regional camaraderie.
- The festival is free and open to all, encouraging inclusive public participation and awareness.
- Reinforces India’s use of cultural diplomacy to lead BIMSTEC’s cultural cooperation track.
- Follow-up to BIMSTEC Summit Commitment: Implements Prime Minister of India announcement at the April 2025 BIMSTEC Summit in Thailand.
- Symbol of BIMSTEC Cultural Integration marks a shift from economic focus to a holistic regional identity, integrating art, music, and heritage.
Tata Motors’ PB Balaji Appointed as New CEO of Jaguar Land Rover:
Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), the luxury automotive arm of Tata Motors, has named PB Balaji as its new Chief Executive Officer (CEO). He will succeed Adrian Mardell, who is set to retire after an illustrious 35-year career at JLR. The leadership change will take effect on 17 November 2025, marking a new era for the iconic British automaker.Adrian Mardell, who joined JLR over three decades ago, has been instrumental in guiding the company through its most transformative years. As CEO since 2022, he spearheaded JLR’s ‘Reimagine’ strategy, leading the automaker into a new phase of electrification and sustainability. He will officially retire on 31 December 2025.
LTIMindtree Bags ₹811.5 Crore PAN 2.0 Project from Income Tax Department:
The Income Tax Department has selected LTIMindtree Ltd, a Larsen & Toubro subsidiary, to execute the PAN 2.0 project. Cleared by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs in November 2024, the project—worth ₹811.5 crore aims to modernize and streamline PAN and TAN services and is expected to go live within 18 months.The PAN 2.0 project is a technology-driven upgrade to India’s current Permanent Account Number (PAN) infrastructure.
Hiroshima Day 2025:
Every year on August 6, the world observes Hiroshima Day to remember the catastrophic moment in World War II when the United States dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima in 1945. The event left deep scars on humanity, with thousands killed instantly and survivors suffering from long-term radiation effects. As we observe Hiroshima Day 2025, it serves as a reminder not only of the immense loss but also of the urgent need for global peace, nuclear disarmament, and a world free of the fear of atomic destruction.Hiroshima witnessed unprecedented devastation when the atomic bomb was dropped, followed by another attack on Nagasaki three days later. The immediate blast wiped out a significant portion of the population, and survivors known as Hibakusha suffered radiation illnesses, trauma, and lifelong health complications. This moment did not just mark the end of the Second World War but also ushered in the nuclear age, altering world politics and security forever.




