Today’s Current Affairs: 6th August 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Thadou People:

A section of the Thadou tribes represented by the Manipur-based Thadou Students’ Association (TSA) has formed a global platform to look into critical issues facing the community, particularly in Manipur.
- Thadou people are an indigenous people who live in the hill country adjacent to the Imphal Valley in the northeastern Indian state of Manipur.
- They are the second largest in terms of population in Manipur, next to Meitei,according to the Manipur Census 2011.
- They are also found in Assam, Nagaland, and Mizoram in India, and in Chin State and Sagaing Division in Burma/Myanmar.
- The Thadou language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
- Thadou subsistence activities include animal, cultivation, hunting and fishing. Jhum (slash-and-burn) agriculture is predominant.
- Thadou settlements are located in forests. Sites on the tops of ridges or just below ridges are preferred.
- Villages are not arranged according to an established urban plan, and there is no marking of the perimeter of a village.\
- Almost all Thadou claim to be followers of Christianity.
Astra Missile : Recent Update

The Indian Air Force (IAF) has given clearance to the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) to produce 200 Astra air-to-air missiles for its Su-3O and LCA Tejas fighter aircraft.
- Astra Missile is a Beyond-Visual-Range (BVR) air-to-air missile designed to be mounted on fighter aircraft.
- It is indigenously developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The missile was built to engage and destroy aerial targets, which have high maneuverability and supersonic speed.
- The missile is capable of advanced air combat, which allows it to engage in multiple high-performance targets.
- It is the best in its class of weapon systems in the world in the category of air-to-air missiles.
- The missile is being developed in multiple variants to meet specific requirements.
- Astra is 3.6 m long and with a diameter of 178 mm, weighing 154 kg.
- It has a range of 80 to 110 km in a head-on chase and can travel at 5 Mach speed (almost hypersonic).
- The missile uses an inertial guidance system driven by a fibre optic gyroscope with terminal guidance through active radar homing.
- It offers the pilot the option to choose between “Lock on Before Launch – LOBL” and “Lock on After Launch – LOAL” and later allows the aircraft to shoot and scoot to safety after firing the missile in the direction of the target.
- It is based on an advanced solid-fuel ducted ramjet (SFDR) engine technology.
- It is capable of operating under all weather conditions, both day and night and offers high overall reliability and a very high ”Single Shot Kill Probability – SSKP”.
Glioblastoma:
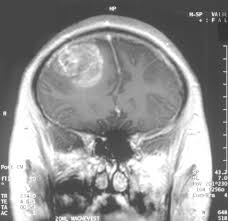
Glioblastoma is a type of cancer that starts as a growth of cells in the brain or spinal cord.
- Like all cancers, glioblastoma is caused by DNA mutations that result in uncontrolled cell growth. The underlying causes for these genetic cell mutations are largely unknown.
- Glioblastoma forms from cells called astrocytes that support nerve cells.
- Astrocytes help give your brain the nutrients it needs.
- Glioblastoma tumors make their own blood supply, which helps them grow. It’s easy for them to invade normal brain tissue.
- It grows quickly and can invade and destroy healthy tissue.
- It can happen at any age. However, it tends to happen more often in older adults.
- It accounts for almost half of all cancerous brain tumors in adults.
- Glioblastoma symptoms may include headaches that keep getting worse, nausea and vomiting, blurred or double vision, trouble speaking, altered sense of touch, and seizures.
- There also may be trouble with balance, coordination, and moving parts of the face or body.
- There’s no cure for glioblastoma. Treatments might slow cancer growth and reduce symptoms.
- The main treatments for glioblastomas are surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Lyme Disease:
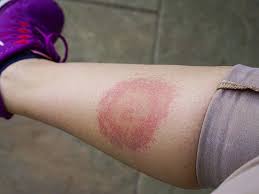
Lyme disease is a significant public health concern, affecting approximately 476,000 individuals in the US each year.
- Lyme disease is a vector-borne infectious disease caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
- It is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, often referred to as deer ticks.
- It cannot spread between humans, from pets to humans, through air, food, or water or lice, mosquitoes, fleas, and flies also do not transmit it.
- It is prevalent in wooded and grassy areas worldwide, particularly during warmer months. It is most commonly reported in North America, Europe and some parts of Asia.
- It starts between 3 to 30 days after an infected tick bites you.
- It commonly manifests with symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic “bull’s-eye” red rash called erythema migrans (EM).
- Erythema migrans serve as a hallmark sign, aiding in the early diagnosis and management of this tick-borne illness.
- If it is left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications affecting the joints, heart and nervous system.
- The standard treatment for Lyme disease is antibiotics, such as doxycycline or amoxicillin, especially in the early stages.
Bailey Bridge:

The Indian Army’s Madras Engineer Group or Madras Sappers built a “Bailey bridge”, which was assembled at Chooralmala, to reach Mundakkai village — one of the sites worst hit by the landslides.
- It is a type of modular bridge, one whose parts are pre-built so that they need minimal construction work and can be assembled quickly when needed.
- A US Army Engineer School manual notes that the Bailey bridge originated during wartime. Donald Coleman Bailey, an English civil engineer, invented it during World War 2 (1939-45).
- The pre-fabricated parts in a Bailey bridge include light steel panels linked through pins, which are big, screw-like objects.
- These help establish the guardrails of the bridge. Through the guardrails on either side, workers place beams to form the deck or path of the bridge.
- All beams were constructed such that they would lock in on the guardrails to ensure stability.
- After that, the bridge can be extended, and the lightness of the parts allows it to be mobile.
- No heavy installation equipment is needed. In disaster relief situations, this is ideal because parts can be transported in small trucks — something also of use during wartime.
Bent-Toed Geckos:

Scientists from India and the United Kingdom have described six new species of bent-toed geckos from Northeast India.
- Bent-Toed Geckos of the genus Cyrtodactylus are diverse.
- They are commonly known as bow-fingered geckos and forest geckos.
- Geckos are ectothermic, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature.
- Reproduction in this gecko species typically occurs during the warm and wet seasons.
- Bent-toed geckos have about 346 species distributed across multiple biogeographic zones in Peninsular India, Sri Lanka, the Himalayan foothills, Northeast India, Southeast Asia and the Solomon Islands.
- Namdapha bent-toed gecko: It was documented from the Namdapha Tiger Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh and is widespread within lowland evergreen forests of the Namdapha and Kamlang Tiger Reserves.
- Siang Valley Bent-Toed Gecko (Arunachal Pradesh): It was discovered in the Siang River valley, renowned for its unique biodiversity.
- Ngengpui bent-toed gecko (Mizoram): It was discovered in the Ngengpui Wildlife Sanctuary of Lawngtlai district. The site is located in one of the easternmost protected areas of the country.
- Manipur bent-toed gecko: It was discovered near the Lamdan Kabui village of Manipur.
- Kiphire bent-toed gecko and Barail Hill bent-toed gecko(Nagaland): These two were discovered in Nagaland.
Ol Doinyo Lengai Volcano:

According to a new study, the Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano which is filled with magma has been erupting beyond the ground hose and at the same time sinking for the past 10 years.
- Ol Doinyo Lengai Volcano is located in northern Tanzania, at the southern end of Lake Natron.
- It is known to the local Maasai people as the “Mountain of God.
- It is an active stratovolcano with unique geological characteristics.
- It rises to an elevation of 9,442 feet (2,878 metres) and is one of the many volcanoes situated along the East African Rift System.
- It contains basalts rich in sodium and potassium and is so alkaline that its lavas resemble washing soda.
- The volcano has more than one active centre and most of the recent eruptions were from its northern crater.
- This volcano is the only one existing on Earth which has an actively eruptingand extremely runny carbonatite magma.
- The magma is saturated with alkali elements, like calcium and sodium and is poor in silica.
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) Scheme:

The Centre is unlikely to extend the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate scheme that was made available for two years beyond its March 2025 deadline, according to official sources.
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) Scheme is a one-time scheme announced in Budget 2023 and will remain available for a two-year period, i.e., up to March 2025.
- It is a risk-free scheme dedicated towards women and girls of all age groups.
- The scheme offers a maximum deposit facility of up to Rs 2 lakh in the name of women or girls for a tenure of 2 years.
- It will encourage more women to adopt formal financial saving instruments.
- Eligibility: Any individual women .
- The minor account can also be opened by the guardian.
- The deposit amount under this scheme is limited.
- A minimum of Rs. 1000 and any sum in multiples of one hundred rupees may be deposited in an account subject to a maximum of Rs. 2 lakhs.
- It offers a fixed interest rate of 7.5 percent. Interest shall be compounded every quarter and credited to the account.
- The Maturity period/Lock-in period of the scheme is 2 years from the date of opening of the account.
- However, the account holder can withdraw up to 40% of the account balance after one year from the account opening date as a partial withdrawal.
- There is a provision for multiple account opening under this scheme with a condition that a woman can open a second MSSC account after a minimum gap of three months from the opening of the existing account.
- However, the total deposit, including all the accounts, should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- There are no tax benefits.




