Today’s Current Affairs: 26th November 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
CBSE Merit Scholarship Scheme for Single Girl Child:

The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has invited online applications for the single girl child merit scholarship scheme.
- CBSE Merit Scholarship Scheme for Single Girl Child aims to provide scholarships to meritorious female students who are the only children of their parents and have passed the CBSE Class X examination with 60% or more marks and are continuing their further school education in Class XI and Class XII.
- The scheme is aimed at recognizing the efforts of parents in promoting education among girls and to providing encouragement to meritorious students.
- It provides financial aid every month to the selected students, so they can continue their higher education.
- The applicant should be the single girl child of her parents and be an Indian national.
- To be eligible for the scholarship scheme, all single girl students must have 60 percent or more marks in the CBSE Class 10 Examination.
- They should be studying Class 11 and 12 in CBSE-affiliated schools with tuition fees not exceeding Rs 1,500 per month.
- NRI applicants of the Board are also eligible for the award. The tuition fee for the NRIs should be a maximum of Rs. 6,000/- per month.
- Students with gross parental/family income up to Rs. 8 lakh per annum are eligible for scholarships under the scheme.
- Students who are selected for the scholarship will receive an amount of ₹500/- per month.
- The amount is payable for a maximum period of two years. Payment will be made through ECS/NEFT.
- Existing scholarship holders can renew their scholarship for Class XII if they secured 50% or more marks in their Class XI exams.
Dongfeng-100:

China increased the range of its supersonic cruise missile DF-100, i.e., Dongfeng-100.
- Dongfeng-100, also known as Changjian-100 (CJ-100), is a Chinese supersonic cruise missile.
- It was publicly introduced during China’s 70th National Day parade on October 1, 2019.
- It is designed for precision strikes and features capabilities aimed at engaging a wide variety of targets, including land-based infrastructure, reinforced installations, underground bunkers, and large warships.
- The missile is a land-based system with a range reportedly between 3,000 and 4,000 kilometers.
- 10×10 transporter erector launchers are used to launch it. But it can also be launched from a bomber.
- It has a length exceeding 9 meters, a projectile diameter ranging between 0.7 and 1 meter, and a payload capacity of over 500 kilograms.
- The missile is powered by a ramjet engine and achieves speeds of Mach 5 during its terminal phase.
- It boasts supersonic speeds throughout nearly all phases of its flight, enhancing the missile’s survivability and ability to penetrate air defenses.
- This missile goes up to a height of 30 kilometers after launch, after which it turns towards the target.
- Its guidance system includes inertial navigation, terrain matching, scene matching and satellite positioning, providing high accuracy.
Antlions:

Researchers recently spotted a large-sized adult antlion, Palpares contrarius, that resembles a dragonfly for the first time in Tamil Nadu on the Madras Christian College (MCC) campus.
- Antlions are insects belonging to the order Neuroptera. They are classified in the family Myrmeliontidae.
- They are named for the predatory nature of the larvae, which commonly trap ants and other small insects in pits dug into the ground.
- Antlions are found throughout the world, primarily in dry, sandy regions.
- It is very difficult to spot them during the day and can be spotted at night near illuminated spots.
- Adult antlions resemble damselflies, but they have softer bodies, a lacy wing pattern, and long clubbed antennae.
- The bodies of antlions are long and slender and grayish in color.
- The wings are generally clear, but some species have spots on their wings.
- Antlions are weak fliers and can be found at night near lights.
- They come in various shapes and sizes, with larvae typically measuring from a few millimeters to several centimeters, depending on the species.
- Antlion larvae have rounded bodies with long sickle-shaped jaws. The larvae are found at the base of cone-shaped pits in sandy areas.
- They usually remain in the larval stage for one to two years, depending on the species.
- Once they pupate, they require up to one month to complete their development. Adult antlions survive for one to two months.
- Antlions are harmless and cause no damage to flowers, people, or structures.
- They are highly beneficial and feed on ants and other insects that fall into their traps.
Kyasanur Forest Disease : High Alert

The Chikkamagaluru District health officials are on high alert to prevent Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), also known as monkey fever, in the district.
- KFD, also referred to as Monkey Fever, is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic disease mostly found in southern India.
- The disease was first reported from the Kyasanur Forest of Karnataka in India in 1957; hence, it is known as Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD).
- The causal agent, Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus (family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus), is a member of the tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) complex.
- It is transmitted by a range of tick species, with Haemophysalis spinigera being considered the principal vector.
- A wide range of small rodents, monkeys and birds are thought to play a role in KFD virus transmission.
- Transmission to humans may occur after a tick bite or contact with an infected animal, most importantly a sick or recently dead monkey.
- No person-to-person transmission has been established yet.
- The epidemic period usually begins in October or November and peaks from January to April, then declines by May and June.
- Symptoms: Sudden onset of high-grade fever, prostration, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and occasionally neurological and haemorrhagic manifestations.
- Between 5 and 10% of people who are known to be affected by KFD die.
- There is no cure for KFD.
- Supportive care is crucial, including fluid balance, providing oxygen, managing blood pressure, and treating additional infections.
- Vaccine: A vaccine for KFD is available and recommended in the parts of India where KFD is found.
Narsapur lace Craft : GI Tag

The famous Narasapuram lace craft has bagged the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
- Narsapur is situated on the bank of Godavari River in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is believed that the women of the farming community of this region started creating highly attractive artefacts from colourful lace, about 150 years ago.
- The craft has survived the Indian famine (1899) and the Great Depression (1929). By the early 1900s, above 2,000 women were involved in the craft in the Godavari region.
- The lace work is done using thin threads and these are again woven with thin crochet needles of varying sizes.
- Narsapur’s famed hand-made crochet industry produces doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bed spreads, table-runners and tablecloths etc.
- Many of these products are exported to markets in the USA, UK and France.
Methanol Poisoning : Six Tourists Lost Their Lives
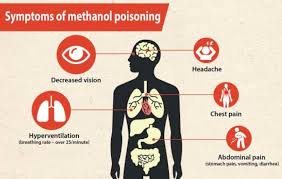
Six tourists tragically lost their lives in Laos due to suspected methanol poisoning which has raised global alarm.
- Methanol Poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when methanol, a type of alcohol widely used in industrial applications, is ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin.
- Methanol’s toxic effects emerge after the body metabolises it into harmful compounds like formaldehyde and formic acid.
- These byproducts can wreak havoc on the nervous system, optic nerves and other vital organs.
- It typically occurs when counterfeit or illicit alcohol, often containing methanol, is consumed instead of ethanol, the type of alcohol found in beverages.
- In the body, methanol is metabolised by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase into formaldehyde and then into formic acid, both of which are toxic.
- Methanol poisoning can indeed be fatal if left untreated. The toxic byproducts lead to complications.
- Metabolic Acidosis: A dangerous drop in blood pH levels.
- Optic Nerve Damage: Potentially resulting in partial or complete blindness.
- Central Nervous System Depression: Causing confusion, coma or death.
Guru Tegh Bahadur : Martyrdom Day

Guru Tegh Bahadur Martyrdom Day is observed every year on 24 November to honour the sacrifice of the ninth Sikh Guru.
- Guru Teg Bahadur’s name earlier was Teyag Mal and he was the ninth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion.
- His father and the sixth Guru of Sikhs, Guru Hargobind Sahib (1595-1644) changed the name to Teg Bahadur.
- He got his name from his fighting and sword skills on the battlefield.
- He was known as Hind ki Chadar, or the ‘Shield of India.
- He built the city of Anandpur Sahib (in Rupnagar/Ropar district, on the edge of Shivalik Hills, near the Sutlej River, in Punjab).
- Here the last two Sikh Gurus lived and where Guru Gobind Singh founded the Khalsa Panth in 1699.
- He contributed more than 100 poetic hymns to Granth Sahib which cover various topics, such as the nature of God, human attachments, body, mind, dignity, service etc.
- He was instrumental in the conciliation between Raja Bishan Singh and Raja Paranpal, thus avoiding a war.
Martyrdom: - He was first arrested by the Mughals on the orders of Aurangzeb in 1665.
- He was publicly beheaded in 1675 on the orders of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in Delhi.
- His martyrdom is remembered as the Shaheedi Divas every year on 24 November, according to the Nanakshahi calendar released by the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee in 2003.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) forum:

India’s Defence Minister addressed the 11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) forum held in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
- He emphasised the role of Buddhist principles in resolving conflicts and celebrated a decade of India’s Act East policy (AEP).
Key Highlights of the 11th ADMM Meeting-Plus:
- India highlighted the need for adherence to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), 1982 for freedom of navigation and overflight in the Indo-Pacific region.
- India advocated for a Code of Conduct that protects the rights and interests of nations that remain consistent with international law.
- India called for greater adoption of Buddhist principles of peaceful coexistence in a world that is increasingly polarised into blocks and camps.
- India’s approach to border disputes, trade agreements, and other challenges demonstrates its belief in open communication to foster trust, understanding, and cooperation.
- India described the 21st century as the “Asian Century,” emphasising ASEAN’s economic dynamism and its vibrant trade, commerce, and cultural exchanges.
- India Highlighted the success of India’s Act East Policy, which has strengthened ties with ASEAN and Indo-Pacific nations over the past decade.
- The Act East Policy was launched in November 2014 at the 12th ASEAN-India Summit 2014 held in Myanmar capital Naypyidaw.
- India proposed the development of an ADMM-Plus Defence Strategy on Climate Change to tackle interlinked security and environmental challenges.
- India underscored the importance of safeguarding Global Commons, which include shared natural resources beyond national boundaries.
- Global Commons include High Seas, Atmosphere, Antarctica and Outer Space.
Access To Medicine Foundation : 2024 Index Report

The Access to Medicine Foundation released its 2024 Index Report, evaluating pharmaceutical companies’ efforts to enhance medicine access in low and middle-income countries (LMICs) despite ongoing challenges.
Highlights of the Access to Medicine Index Report 2024:
- LMICs, despite being home to 80% of the global population, account for only 43% of all clinical trials conducted worldwide.
- This limits the participation of LMIC populations in the development of new medicines and delays their access to innovative treatments.
- Voluntary licensing and technology transfers are concentrated in countries like Brazil, China, and India, leaving much of sub-Saharan Africa excluded, which limits the availability of medicines in many low-income regions.
- While some companies are adopting inclusive business models, over 61% of products assessed lack specific strategies for low-income countries.
- This underscores persistent inequities, as access efforts remain concentrated in upper-middle-income regions.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly moving away from R&D for priority diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which disproportionately affect LMICs.
- The report highlighted the urgent need for pharmaceutical companies to enhance efforts and create transparent strategies for equitable access to medicines.
6th AITIGA Joint Committee Meetings:

The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings were held in New Delhi.
- It marked a crucial phase in reviewing the AITIGA to enhance trade relations between India and ASEAN nations
- India had sought a review of the AITIGA, originally implemented in 2010, citing disproportionate trade benefits for ASEAN countries.
- While India’s exports to ASEAN increased from USD 25.62 billion (FY 2010-11) to USD 41.2 billion (FY 2023-24), imports surged from USD 30.6 billion to USD 79.66 billion in the same period.
- India wants ASEAN countries, particularly Vietnam, to make greater market-opening commitments for Indian goods.
- India seeks more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from being routed through ASEAN nations at preferential rates.
- India and ASEAN made initial progress towards initiating tariff negotiations, a crucial step in the review process.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue:

The Prime Minister of India announced the ‘Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue’ (VBYLD) to be held in January in Delhi, coinciding with Swami Vivekananda’s 162nd birth anniversary, and highlighted the National Cadet Corps (NCC) role in youth development.
- VBYLD aims to engage young minds from across India with no political background in politics, marking a significant initiative for youth empowerment.
- The event will host 2,000 selected youth, with the PM engaging them alongside national and international experts to present innovative ideas for the nation’s progress, helping to create a roadmap for India’s future.
- The NCC was established in 1948 (on the recommendation of H. N. Kunzru Committee-1946), under the NCC Act of 1948, with the aim to develop character, comradeship, leadership, and service ideals in the youth.
- It also seeks to stimulate interest in national defence and build a reserve for the Armed Forces in emergencies.
- The NCC was preceded by the University Corps (1917), later evolving into the University Training Corps (UTC) in 1920, and the University Officers Training Corps (UOTC) in 1942.
- NCC is headed by a Director General, an Army Officer of the rank of Lieutenant General, who oversees its operations from the NCC Headquarters in Delhi.
Urban Civic Bodies:
A recent RBI report highlights challenges in municipal corporations’ revenue generation, heavy dependence on government transfers, and insufficient capacity to meet urban development demands.
Nayi Chetna 3.0 – Pahal Badlaav Ki:
Union Ministers will launch Nayi Chetna 3.0 – Pahal Badlaav Ki, a month-long campaign against gender-based violence, under DAY-NRLM to promote awareness and grassroots action.Nayi Chetna – Pahal Badlaav Ki launched By: Ministry of Rural Development under DAY-NRLM. Campaign Duration: 25th November to 23rd December 2024. Slogan: “Ek Saath, Ek Awaaz, Hinsa Ke Khilaaf.”
Constitution Museum:
India’s first Constitution Museum was inaugurated at OP Jindal Global University in Sonipat, Haryana, to commemorate and celebrate the drafting, principles, and evolution of the Indian Constitution.
ICA Global Cooperative Conference 2024:
Prime Minister will inaugurate ICA Global Cooperative Conference 2024 and launch the UN International Year of Cooperatives 2025 on 25th November at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.International Cooperative Alliance established in 1895 during the 1st Cooperative Congress in London, England.One of the oldest NGOs, representing over 1 billion cooperative members globally across 105 countries.
National Gopal Ratna Awards, 2024:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA) this is one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024. National Gopal Ratna Award 2024 presented by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD), Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying. Initiated to promote and recognize excellence in the livestock and dairy sector.Aim to encourage farmers, technicians, and cooperatives working in dairy and indigenous cattle rearing to achieve excellence and boost development in the sector.




