Today’s Current Affairs: 27th March 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Earthquake struck off New Zealand’s South Island:
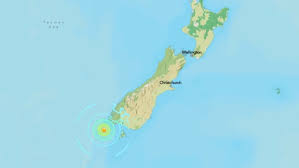
A strong 6.7 magnitude earthquake struck off New Zealand’s South Island recently.
- South Island is the larger and southernmost of the two principal islands of New Zealand, in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
- It is separated from North Island to the north by Cook Strait and from Stewart Island to the south by Foveaux Strait.
- Mountainous terrain occupies almost three-quarters of South Island, with a central mountain chain, the Southern Alps, trending southwest to northeast and culminating at Mount Cook (3,754 metres).
- The Southern Alps separate the narrow coastal strip of the Westland Plain (west) from the broad Canterbury Plains (east).
- Fiordland National Park in the southwest is a distinctive area with its numerous coastal fjords (inlets) and high lakes.
- The park is part of the Te Wāhipounamu (South West New Zealand) area of protected wilderness along the west side of the island that was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1990.
- Lakes: Includes Lake Tekapo, Lake Wakatipu, and Lake Pukaki.
Euclid Space Telescope : Released Data

The European Space Agency’s Euclid mission released its first batch of survey data, including a preview of its deep fields.
- Euclid Space Telescope named After: Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician known for his contributions to geometry.
- Part of ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme, which aims to explore the origin, components, and fundamental laws governing the universe.
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- Operational Lifespan: Minimum 6 years.
- Orbit: 5 million km above Earth, at the Lagrange Point 2 (L2), a stable gravitational point in space.
- Size: 7 meters tall and 3.7 meters in diameter.
- Image Quality: Four times sharper than ground-based telescopes.
- Objectives is to Investigate why the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate (a phenomenon attributed to dark energy), Study the distribution of dark matter by observing how galaxies and cosmic structures have evolved over billions of years,Map the large-scale structure of the universe in 3D to understand the effects of gravity and cosmic expansion.
Boilers Bill, 2024:

The Lok Sabha passed the Boilers Bill, 2024, replacing the century-old Boilers Act of 1923. The bill, which aims to decriminalise seven offences and promote ease of doing business.
- The Boilers Act of 1923 was enacted to regulate the manufacturing, installation, operation, alteration, and repair of steam boilers to ensure safety.
- The Act was last amended in 2007 to allow independent third-party inspections, but further reforms were needed.
- The Boilers Bill, 2024, aligns with the Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023, which focuses on decriminalization and ease of doing business (EoDB).
- The Bill is redrafted with modern drafting practices to improve clarity and efficiency.
- A boiler is a vessel where steam is generated under pressure. As of 2024, India has around 40 lakh steam boilers used in industries like power, manufacturing, and chemicals.
Key Features of the Boilers Bill, 2024:
- Replacement of Boilers Act, 1923: The new Bill repeals the century-old Boilers Act, 1923, aligning regulations with modern safety standards.
- Ease of Doing Business (EoDB): The Bill enhances business operations by decriminalizing 3 out of 7 offences, reducing legal hurdles.
- Categorisation of Offences: 4 major offences (risking life and property): Criminal penalties retained.
Other offences: These are converted into fiscal penalties, handled by an executive mechanism instead of courts. - Modern drafting practices: The Bill is simplified and structured into six chapters, consolidating similar provisions for clarity and accessibility.
- Enhanced safety measures: Ensure worker safety inside boilers. Mandates boiler repairs by qualified and competent persons.
- Redundant provisions: Outdated sections from pre-constitutional times omitted. New definitions and amendments were added for better clarity.
- Jan Vishwas Act, 2023 alignment: Follows the decriminalisation reforms under the Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023.
- Central & State Government roles: Clearly define powers and functions of the Central Government, State Governments, and Central Boilers Board to avoid confusion.
Parker Solar Probe:

On March 22, 2025 the Parker Solar probe made another attempt to get within 6 million km of the sun, considered a very small distance to be from the star
- On March 22, 2025, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe approached the Sun more closely, reaching 6 million km from its surface.
- The probe, launched in 2018, has set the record for being the closest spacecraft to the Sun and will continue making 24 close approaches to study solar activity.
- Parker Solar Probe launched by NASA on August 12, 2018, from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
- Designed to study the Sun’s corona, solar wind, and magnetic field to understand space weather and its effects on Earth.
- Moves in a highly elliptical orbit, using Venus’ gravity assist to spiral gradually closer to the Sun.
- The fastest human-made object, reaching 692,000 km/hr.
- It will come as close as 83 million miles (6.16 million km) from the Sun’s surface, about 7 times closer than any previous spacecraft.
Discovery:
-
- Discovery of “Magnetic Switchbacks”: The probe found sudden reversals in the solar wind’s magnetic field, which might help explain how the solar wind accelerates. Detection of Dust-Free Zones: Contrary to earlier beliefs, the probe found dust-free pockets near the Sun, altering our understanding of solar system dust distribution. First ‘Touch’ of the Sun (2021): In April 2021, the probe entered the Sun’s corona, crossing the Alfvén surface—a boundary beyond which solar wind escapes into space.
Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024 : Passed

The Parliament has passed the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, aiming to strengthen disaster response mechanisms.
Amendments:
- Disaster management plans: NDMA and SDMA will now prepare plans, replacing previous delegation to executive committees.
- Expanded functions of NDMA and SDMA:
- Periodic disaster risk assessments, including climate-related risks.
- Providing technical guidance and minimum relief standards.
- Preparing national and state-level disaster databases.
- Conducting post-disaster audits and assessing state preparedness.
- Urban Disaster Management Authorities:
- To be set up in state capitals and cities with municipal corporations.
- Headed by the Municipal Commissioner with District Collector as Vice-Chairperson.
- State Disaster Response Force (SDRF):
- Empowering states to form SDRFs with defined roles and service conditions.
- Statutory status:
- Given to the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) and the High-Level Committee (HLC) for disaster financial oversight.
- NDMA appointments:
- NDMA can now specify staffing needs and appoint experts with Centre’s approval.
Gold Monetisation Scheme: In News

The Government of India has discontinued Medium-Term and Long-Term Government Deposits (MLTGD) under the Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS) from March 26, 2025.
- November 2015, as an improved version of the existing Gold Deposit Scheme (GDS) and Gold Metal Loan (GML) Scheme.
- Allows individuals, institutions, and even government entities to deposit idle gold in banks and earn interest instead of storing it in lockers.
- Depositors can redeem the gold deposit in cash, gold bars, or coins upon maturity, but not in the same form (jewellery, bars, or coins).
- Objective is To mobilize idle gold held by households and institutions, To bring gold into the formal economy and reduce gold imports, thereby helping reduce the Current Account Deficit (CAD).
National e-Vidhan Application : Delhi Became 28th legislature
Delhi recently became the 28th legislature to join the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA).
- National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) is an online platform designed to digitize the legislative processes of all state and union territory assemblies.
- It is a device-neutral and member-centric application created to equip them to handle diverse House Business smartly by putting entire information regarding member contact details, rules of procedure, list of business, notices, bulletins, bills, starred/unstarred questions and answers, papers laid, committee reports, etc.
- The app allows all parliamentary members to access all house business information on their phones and tablets, enabling better handling of legislative tasks.
- The app allows Ministers and Members to manage all the parliamentary work, like access to house proceedings, replies to questions, etc, through the App.
- NeVA helps the government departments to manage operations by creating an inclusive digital department.
- Additionally, NeVA assists the Chair of the House in conducting proceedings smoothly while enabling members to fulfill their responsibilities efficiently.
- It is being hosted by Meghraj National Cloud, ensuring a secure, disaster-proof, reliable functioning for all legislatures
Global Energy Review 2024:

The International Energy Agency (IEA) released the Global Energy Review (GRE) 2024, analyzing trends in energy demand, supply, technology, and CO₂ emissions.
Key Highlights of GRE 2024:
- Global Energy Demand Growth: Increased by 2.2%, with emerging economies contributing 80% of the rise.
- Rise of Renewables & Natural Gas: Renewables accounted for 38% of growth, adding a record 700 GW. China (340 GW solar, 80 GW wind) and India (30 GW solar) were key contributors.
- Natural gas demand rose 2.7%, led by China’s LNG adoption.
- Coal Demand Trends: Globally rose 1%, with China (60% electricity from coal) and India (75%) as top consumers.
- Coal’s global electricity share fell to 35%, the lowest since 1974.
- Crude Oil Demand Slows: Growth was 0.8%, primarily due to the petrochemical sector, while EVs, LNG trucks, and high-speed rail reduced transport-related oil consumption.
Lyme Disease : New Study

Scientists have discovered that the enzyme BbLDH is crucial for the survival and infectivity of the Lyme disease bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
- Lyme Disease is caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi.
- The infection can lead to problems with the skin, heart, brain, and joints.
- It’s transmitted (spread) to humans through a tick bite.
- Not all tick bites cause Lyme disease. Only deer ticks (also called black-legged ticks) can spread the bacteria that cause Lyme disease.
- It cannot spread between humans, from pets to humans, through air, food, water, or lice, mosquitoes, fleas, and flies also do not transmit it.
- It is prevalent in wooded and grassy areas worldwide, particularly during warmer months. It is most commonly reported in North America, Europe, and some parts of Asia.
- Typical symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash called erythema migrans.
- If left untreated, infection can spread to joints, the heart, and the nervous system.
- Treatment with antibiotics usually cures Lyme disease, especially when started early.
Samarth Incubation Program:

The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT) has launched the ‘Samarth’ Incubation Program to foster innovation in Telecom and IT sectors by startup collaboration and attracting investments.
- It aims to support DPIIT- recognized startups developing next-generation technologies in Telecom Software, Cyber Security, 5G/6G, AI, IoT, and Quantum Technologies.
- It will provide sustainable and scalable business models, cutting-edge resources, and facilitate startup growth from ideation to commercialization.
- Implemented in partnership with Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) under MeitY.
- Programme supports 36 startups in 2 six-month cohorts, offering hybrid learning, mentorship, infrastructure, and investor access to foster innovation in telecom and IT.
- Startups are offered Rs 5 lakh grants, 6-month C-DOT’s office space & lab facilities and mentorship.
- Successful startups may gain future collaboration opportunities under the C-DOT Collaborative Research Program.
- The C-DoT is an autonomous R&D center under DoT, established in 1984, focusing on indigenous telecom innovations like 5G, IoT, AI etc to support Atma Nirbhar Bharat.
Third Report on the State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture:

The FAO released the Third Report on the State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture on March 24, 2025.
- The report highlighted alarming dependency on nine crops and threats to global plant genetic diversity. State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (SoW-PGRFA) is a comprehensive assessment of the conservation, use, and status of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA) at global, regional, and national levels.
- Report released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
- Aim is to evaluate trends, gaps, and priorities in in situ and ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources and To guide global action plans for safeguarding plant biodiversity and food security.
Third Report (2025):
- Crop concentration: 60% of global food comes from just nine crops (sugarcane, maize, rice, wheat, potatoes, soybeans, oil palm, sugar beet, cassava).
- Threatened diversity: Globally, 6% of farmers’ varieties (FV/LR) are threatened; in nine sub-regions, this exceeds 18%.
- Highest risk regions: Southern Africa, Caribbean, and Western Asia face the highest loss of genetic diversity.
- India’s scenario: Over 50% of documented FV/LRs across five agroecological zones are under threat.
- Ex situ collections: Over 5.9 million accessions conserved globally, with 41% safety-duplicated, many in the Svalbard Global Seed Vault.
- On-farm efforts: Around 35 million hectares in 51 countries cultivated with FV/LR to conserve genetic diversity.
- Climate threat: Frequent disasters impact crop diversity, with poor germplasm adaptation to local conditions post-disasters.
Baalpan ki Kavita initiative:
The Ministry of Education has launched the “Baalpan ki Kavita initiative” to restore and promote Indian rhymes and poems for young children. It is a national initiative to compile nursery rhymes and poems in all Bhartiya Bhasha and English focusing on culturally relevant themes for young children.Launched by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L) under the Ministry of Education. Aim is to create a joyful and relatable learning environment for children by making them familiar with their cultural roots through poetry in their mother tongue.
India’s First Indigenously Developed MRI Scanner:
AIIMS New Delhi is set to install India’s first indigenously developed MRI scanner for clinical evaluation.The initiative aims to reduce dependency on imported medical devices and promote ‘Make in India’ innovation.The first fully indigenously developed 1.5 Tesla MRI scanner designed for advanced medical imaging and clinical trials. Developed by SAMEER (Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research), an autonomous R&D body under Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY). Planned installation at AIIMS New Delhi by October 2025 for clinical evaluation and feedback.Developed under the national mission SCAN-ERA (Swadeshi Chumbakiya Anu-naad Chitran – Ek Rashtriya Abhiyaan), started in December 2014.
Dare2eraD TB Initiative:
The Department of Biotechnology has completed sequencing 10,000 TB genome samples under the Dare2eraD TB initiative.Data-Driven Research to Eradicate TB (Dare2eraD TB) is a flagship program using genome sequencing to tackle drug-resistant tuberculosis in India launched on World TB Day, March 24, 2022. Led by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under Ministry of Science & Technology, in collaboration with ICMR and CSIR, along with the Indian Tuberculosis Genomic Surveillance Consortium (InTGS).
24% hike in the salaries and pensions of Members of Parliament (MPs):
The Central government has notified a 24% hike in the salaries and pensions of Members of Parliament (MPs) with retrospective effect from 1st April 2023. However, the India Employment Report (IER) 2024 reveals stagnation and decline in real wages for India’s working population, highlighting the growing economic divide.Since 2018, salaries and pensions of MPs are revised every five years based on the Cost Inflation Index (CII) instead of requiring a separate parliamentary approval.
India’s first zoo to preserve DNA samples:
Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park in Darjeeling has become India’s first zoo to preserve DNA samples of Himalayan wildlife.Situated in Darjeeling, West Bengal, at an altitude of 2,150 metres (7,050 feet). Founded on 14th August 1958, as a joint venture of the Government of India and the Government of West Bengal.The initiative aims to create a genetic bank or “frozen zoo” to aid future conservation efforts.
Rushikonda Beach regained Blue Flag certification:
Rushikonda Beach in Visakhapatnam has regained its prestigious Blue Flag certification after temporary withdrawal due to compliance issues. The Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), Denmark, administers and monitors the Blue Flag certification globally. In each country, a National Operator designated by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) is responsible for conducting scheduled and surprise control visits to Blue Flag beaches. In India, Blue Flag India under the Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM) acts as the National Operator.




