Today’s Current Affairs: 4th April 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Sagaing Fault:
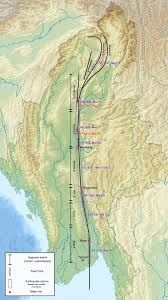
The recent Myanmar earthquake occurred due to strike-slip faulting along the Sagaing Fault, which separates the Indian Plate from the Eurasian Plate.
- The Sagaing Fault is a major active tectonic boundary running north to south through Myanmar, separating the Indian and Eurasian Plates.
- It is one of the longest and most active strike-slip faults globally, extending 1,500 km from the Andaman Sea in the south to the Eastern Himalayas in the north.
- The Indian Plate is moving northward, causing stress buildup along the fault, leading to large earthquakes over time.
Kannadippaya:

Kannadippaya, a traditional tribal handicraft from Kerala, has been awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
- “Kannadippaya” (meaning ‘mirror mat’) originates from its distinct reflective design.
- It is woven using reed bamboo’s soft inner layers, which give it remarkable thermal properties—it provides warmth in winter and a cooling effect in summer.
- It is primarily crafted by tribal communities such as the Oorali, Mannan, Muthuva, Malayan, and Kadar tribes, along with Ulladan, Malayarayan, and Hill Pulaya artisans in the Idukki, Thrissur, Ernakulam, and Palakkad
- The finest Kannadippaya is made from Teinostachyum wightii, locally known by various names such as Njoonjileetta, Njoojoora, Ponneetta, Meieeta, and Neytheetta.
- Other bamboo species, like Ochlandra sp. (locally called Kareetta, Pereetta, Velleeta, Chitoora, and Kanjoora), are also used.
- Kannadippaya is the first tribal handicraft from Kerala to receive a GI tag.
Heard & Mcdonald Islands:

The US President imposed a 10% tariff on imports from the Heard and McDonald Islands, despite the islands having no known exports to the US.
- The Heard and McDonald Islands are a remote sub-Antarctic volcanic island group, located in the southern Indian Ocean, about 4,100 km southwest of Perth (Australia) and 1,600 km north of Antarctica.
- They are one of Australia’s seven external territories and are governed directly by the Australian government.
- The islands are volcanic in origin, with Big Ben volcano on Heard Island reaching 2,745 meters (Mawson Peak), making it Australia’s highest mountain outside mainland and Tasmania.
- McDonald Island is much smaller but has shown recent volcanic activity, with eruptions in the late 1990s and 2000s doubling its size.
- They are the only volcanically active sub-Antarctic islands, making them a natural laboratory for studying earth’s crustal processes, oceanic and atmospheric warming, and glacial dynamics.
- The islands are part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site (since 1997) due to their pristine sub-Antarctic ecosystem, managed as a strict nature reserve (IUCN Category Ia).
- They support large populations of marine birds and mammals, including penguins, elephant seals, and seabirds.
- Importantly, the islands are free of invasive species, making them ideal for biodiversity and evolutionary studies.
Seaweed:

Seaweed farming is gaining global recognition as a sustainable and profitable industry.
- The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) aims to boost India’s seaweed production to 1.12 million tonnes over five years.
- The $5.6 billion global seaweed industry is expanding rapidly, with India’s contribution increasing steadily.
- Seaweed is a marine plant that grows in oceans and seas.
- It is nutrient-dense, containing 54 trace elements, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
- It helps combat cancer, diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, and high blood pressure while also boosting immunity.
- Unlike traditional crops, seaweed does not require land, freshwater, fertilizers, or pesticides, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable agricultural resource.
- Microscopic seaweeds, such as phytoplankton, form the foundation of marine food chains and play a key role in oceanic primary productivity.
- Large seaweeds, like giant kelp, create dense underwater forests that serve as biodiversity hotspots, offering shelter and food to a variety of species.
- Seaweeds contribute to oxygen generation and carbon sequestration, playing a significant role in climate regulation.
Artificial Rains:

Delhi’s Environment Minister recently chaired a meeting with key government agencies to explore the feasibility of artificial rain through cloud seeding.
- Artificial rain refers to the process of inducing precipitation through cloud seeding, a weather modification technique.
- It is primarily used to enhance rainfall, combat drought conditions, and reduce air pollution.
- The method involves dispersing chemicals like silver iodide, potassium iodide, and dry ice into clouds to encourage the formation of raindrops using aircraft or helicopters.
- These chemicals act as nuclei around which water vapour condenses to form larger droplets, eventually leading to rainfall.
- The success of cloud seeding depends on the presence of sufficient moisture and appropriate atmospheric conditions.
- Types of Cloud Seeding
- Hygroscopic Cloud Seeding: Accelerates the merging of droplets in liquid clouds, making them large enough to fall as rain.
- Glaciogenic Cloud Seeding: Introduces ice-forming agents into supercooled clouds, converting water vapour into ice crystals, which then melt into rain.
Dhansiri River:

Environmentalists recently raised concerns with the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) over alleged hazardous effluent discharge from Numaligarh Refinery Limited (NRL) into the Dhansiri River, warning of severe ecological damage.
- Dhansiri is the main river of Golaghat District of Assam and the Dimapur District of Nagaland.
- It forms an important tributary to the Brahmaputra
- It originates from Laisang Peak of Nagaland.
- For the first 40 km from its source, the river flows in a northwesterly direction, and thereafter it flows northeast for about 76 km up to Dimapur.
- Beyond Dimapur, the direction of flow is generally northerly up to Golaghat, where the river takes an abrupt turn towards the northwest and ultimately joins the Brahmaputra at Dhansirimukh, Assam.
- The total length of the river from its source to outfall is approximately 352 km.
- Its total catchment area is 1,220 sq.km.
- It flows through the Nagaland -Assam border harbouring rich flora and fauna. On one side is the Dhansiri Reserved Forest, and on the other is Intanki National Park.
Mount Marapi:

Indonesia’s Mount Marapi erupted recently, sending a column of ash 1.5km (4,900ft) above its peak.
- Mount Marapi is an active volcano located in the Padang Highlands of western Sumatra, Indonesia.
- It is a stratovolcano composed of layers of hardened lava, ash, and rocks from previous eruptions.
- It is part of the Ring of Fire—a long, horseshoe-shaped, seismically active belt that rings the Pacific Ocean.
- The highest peak among several volcanoes in the highlands, Mount Marapi rises to 9,485 feet (2,891 meters) above sea level.
- Its summit contains the Bancah caldera—which has a diameter of 0.9 mile (1.4 km)—and is characterized by a series of overlapping craters.
- The volcano’s deadliest single event, which resulted in the deaths of 60 people, came in 1979 after heavy rains saturated a region of loose ash (called a lahar) on the slopes that was left over from an earlier eruption.
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:

Delhi’s forest and wildlife department is set to install 45 motion-based camera traps across the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary in the coming weeks, in order to collect data on wildlife.
- Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the South Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range on the Delhi-Haryana border, located in southern Delhi.
- The sanctuary is part of the Southern Ridge and has biodiversity significance as it merges with the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- It is an important part of the North Aravalli Leopard Wildlife Corridor, which starts from Sariska National Park in Rajasthan, passes through various districts of Haryana, and finally meets the Delhi Ridge.
- As per Champion & Seth (1968), the vegetation falls under the Northern Tropical Thorn Forests
- The native plants exhibit xerophytic adaptations such as thorny appendages, wax-coated, succulent, and tomentose leaves.
- The sanctuary’s flora includes trees like the Neem, Peepal, and Jamun.
- The sanctuary is also home to mammals like the Nilgai, Indian Porcupine, Indian Hare, and Indian Grey Mongoose.
- The sanctuary has over 200 species of birds, including the Indian Peafowl, Red Junglefowl, and the Indian Grey Hornbill.
Sohini Rajola Appointmented as Executive Director at NPCI:
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has appointed Sohini Rajola as its Executive Director. This decision is part of NPCI’s leadership enhancement strategy to drive the adoption of its payment solutions. Rajola’s vast experience in the payments and digital banking sectors will play a key role in the further development and adoption of NPCI’s solutions. The appointment comes at a time when UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is achieving record growth in both value and volume.
Veteran Actor Ravikumar Passes Away at 71:
Veteran actor Ravikumar, widely known for his romantic roles in Malayalam and Tamil films during the 1970s and 1980s, passed away on April 4, 2025, at a private hospital in Chennai. He was 71 years old. Ravikumar’s contribution to South Indian cinema, especially through his collaboration with iconic directors and melodious musical numbers, left an indelible mark in the film industry.
RBI’s Transition of Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs) to the PCA Framework:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will transition approximately 500 financially weak Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs) from the Supervisory Action Framework (SAF) to the Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) framework starting April 1, 2025. This move aims to strengthen regulatory oversight and ensure timely remedial action to restore the financial health of these institutions. The PCA framework provides early supervisory intervention while maintaining financial stability.
RBI Revises Norms on Government-Guaranteed Security Receipts:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced new guidelines for Government of India-guaranteed Security Receipts (SRs) issued by Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs). These regulations aim to differentiate sovereign-backed SRs from ordinary SRs, providing banks with greater flexibility in provisioning while ensuring stricter capital discipline. The move is expected to streamline bad loan resolutions, enhance investor confidence, and strengthen financial stability.
Warangal Chapata Chilli Receives GI Tag:
Development for farmers in Telangana, the Chapata Chilli, also known as Tomato Chilli, has received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag. This milestone is expected to benefit around 20,000 farmers in the Warangal region by increasing their income and boosting market demand for this unique chilli variety.The Warangal Chapata Chilli has been granted a GI tag, officially recognizing its uniqueness and regional significance. This recognition will not only protect the farmers’ rights but also open up new opportunities in export and processing industries.
RBI Conference on Strengthening Large NBFCs Held in Chennai:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) hosted a conference for large-sized Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) on March 28, 2025, in Chennai. The event was attended by Chairpersons of the Audit Committee of the Board (ACB), MD & CEOs, and Statutory Auditors of various NBFCs. Under the theme “Shared Vision, Shared Responsibility: Strengthening the NBFCs,” the conference aimed to reinforce regulatory supervision and address key industry concerns.
Revision in ATM withdrawal charges:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a revision in ATM withdrawal charges, which will come into effect from May 1, 2025. As per the new rule, banks can now charge customers up to Rs 23 per transaction for withdrawals exceeding the monthly free limit. This is an increase from the previous fee of Rs 21 per transaction.




