Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease : Spreading Rapidly
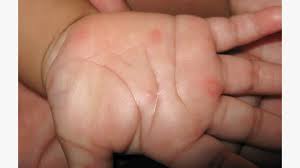
A viral infection known as Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is spreading rapidly among children across Delhi and neighbouring Haryana, prompting health experts and schools to issue advisories.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a very contagious illness caused by a virus.
- The disease gets its name from the blister-like rash that forms on your child’s hands and feet and painful sores that develop in their mouth.
- The rash can actually appear anywhere on their body, including their chest, back, arms, legs, genitals, and buttocks.
- Infants and children younger than 5 are most likely to get HFMD. It is extremely uncommon in adults; however, it is still a possibility.
- It tends to spread quickly among children in daycare and school
- Because several viruses can cause the disease, it’s possible to get HFMD multiple times.
- It is often confused with foot-and-mouth (also called hoof-and-mouth) disease, a disease of cattle, sheep, and swine; however, the two diseases are not related—they are caused by different viruses.
- Humans do not get the animal disease, and animals do not get the human disease.
- It easily spreads through contact with unwashed hands, feces, saliva , mucus from the nose, or fluid from the blisters.
- Symptoms: Fever, Sore throat, Painful mouth sores that blister, Rash commonly found on the hands and feet,Complications from HFMD are rare.
- There’s no cure for HFM and no vaccine to prevent it.
- Most people get better on their own in 7 to 10 days with minimal or no medical treatment.
- However, it can take children younger than 2 years old a little longer for their bodies to clear the virus.




