Foot-And-Mouth Disease : Study
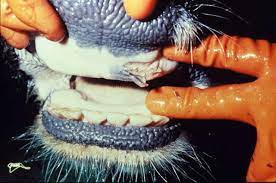
The Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) has affected around 60% of milch cattle in Pilibhit district, Uttar Pradesh.
- Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease of livestock that has a significant economic impact.
- The disease affects cattle, swine, sheep, goats and other cloven-hoofed ruminants.
- Intensively reared animals are more susceptible to the disease than traditional breeds.
- It does not affect horses, dogs, or cats.
- It is a Transboundary Animal Disease (TAD) that deeply affects the production of livestock and disrupts regional and international trade in animals and animal products.
- It is also not related to hand, foot and mouth disease, which is a common childhood illness caused by a different virus.
- The organism which causes FMD is an aphthovirus of the family Picornaviridae.
- There are seven strains (A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, and Asia1) which are endemic in different countries worldwide.
- Immunity to one type does not protect an animal against other types or subtypes.
- FMD is characterised by fever and blister-like sores on the tongue and lips, in the mouth, on the teats and between the hooves.
- The disease is rarely fatal in adult animals, but there is often high mortality in young animals.
- The disease causes severe production losses, and while the majority of affected animals recover, the disease often leaves them weakened and debilitated.
- It was the first disease for which the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE) established official status recognition.




