Today’s Current Affairs: 17th February 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Chincha Kingdom:

New archaeological evidence reveals that seabird guano – nutrient-rich bird droppings – may have been a major factor in the rise of Peru’s precolonial Chincha Kingdom.
- The ‘Chincha Kingdom,’ which was established in the coastal region of modern-day Peru, was a powerful ancient state that flourished before the rise of the Inca Empire.
- It ruled the Chincha Valley.
- The Chincha Kingdom and its culture were very strong between 900 CE and 1450 CE. This time is known as the Late Intermediate Period in pre-Columbian Peru.
- It was organised into specialist communities such as fisherfolk, farmers, and merchants.
- The Chinchas did not build enormous cities but left important marks in their religious and administrative constructions.
- Their temples, palaces, and fortresses were built mainly with adobe, a technique they mastered skillfully.
- They applied stucco to decorate walls, shaping figures of fish heads, gannets, and seabirds.
- The dwellings of most of their inhabitants were built around these enclosures, made with mats and reeds.
- An important old ruin linked to the Chincha is La Centinela, found near the city of Chincha Alta.
- Decline:
- Conquered by the Inca Empire around 1476 CE.
- Later affected by Spanish conquest in the 16th century.
- The population drastically declined due to diseases and colonization.
- A new analysis suggests that the secret to the Chincha Kingdom’s prosperity was seabird droppings (guano).
- The analysis indicates that the nutrient-rich droppings, high in nitrogen, acted as a fertilizer, increasing corn yields and significantly contributing to the economic development of the time.
White-Rumped Vulture:

Forest officials recently rescued a critically endangered White-rumped vulture found weak and grounded at Mampad near Nilambur, Kerala.
- It is a small Old World vulture native to South and Southeast Asia.
- Scientific name: Gyps bengalensis
- It is also known as Indian White-backed Vulture or Oriental White-backed Vulture.
- Like other vultures, it feeds mostly on carcasses, which it finds by soaring high in thermals and spotting other scavengers.
- Distribution: Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam.
- Found mostly in plains.
- The main reason for the big decline in its population is a medicine called diclofenac.
- This medicine, used for farm animals, poisons the vultures when they eat dead animals.
- It causes their kidneys to fail.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered.
Army Ant Species:

Researchers from Karnataka and Odisha have discovered two new species of army ants namely Aenictus chittoorensis and Aenictus lankamallensis in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh.
- Army ants are defined as a nomadic species of ants that lack a permanent nest.
- They belong to one of the subfamilies of ants called the Dorylinae.
- Army ants are highly aggressive predators found mainly in tropical ecosystems.
- Characteristics of Army Ant Species:
- They do not build permanent nests.
- They form temporary living structures known as ‘bivouacs’, made entirely from the bodies of worker ants
- They are social insects, form massive colonies that conduct coordinated raids, consuming insects and small animals in their path.
- They are distinguished by their large, sharp mandibles, stinging ability and heavy reliance on chemical pheromones to navigate and communicate.
- These ants are practically blind and rely on a pheromonal system with which they mark their paths and by which they follow paths taken by others.
- They have a single queen ant who lays all the eggs and female workers that tend the young and collect food for the colony.
- As keystone predators they play a critical role in regulating arthropod populations and shaping forest biodiversity by consuming large quantities of invertebrates on a daily basis.
PM-DAKSH scheme:

Data released in the Lok Sabha revealed that Less than half of the students trained under the PM-DAKSH scheme between 2021 and 2024 were placed.
- The Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana, is a Central Sector Scheme.
- Aim is to provide skills through good quality institutions so that candidates from its target group can find employment.
- There are four types of skill development training programmes under this namely, Up-skilling/Re-skilling, Short Term Training Programmes, Long Term Training Programmes, and Entrepreneurship Development Programme.
- Target Group: Scheduled Castes, Other Backward Castes, Economically Weaker Sections, and the De-notified Tribes in India (DNTs), ‘Safai Karamcharis’ or waste pickers.
- Eligibility
- Age: 18-45 years
- OBC and EWS candidates must have a family income below Rs. 3 lakh, while there is no income limit for SC, DNT, or Safai Mitras/Waste Pickers.
- It has been merged with the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana of Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
Cheer Pheasant:

It is observed that hunting and habitat degradation remain the biggest threats of ground-dwelling Cheer Pheasant.
- It is also known as Wallich’s pheasant or chir pheasant and belongs to the pheasant family, Phasianidae.
- It is found in steep, rocky hillsides studded with scrub, stunted trees and grassy slopes.
- Distribution: Western Himalayas from northern Pakistan through Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, to central Nepal.
- The cheer pheasant’s nest is a simple ground scrape, tucked beneath undergrowth or sheltered by rocks.
- It exhibits high natal philopatry—individuals often return to, or remain near, the area where they were born to breed.
- It depends on early successional grasslands created by traditional grass cutting and burning practice
- It depends on items such as roots, tubers, bulbs, buried seeds and possibly insect larvae and earthworms.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
PM RAHAT Scheme:

Government of India launched the PM RAHAT (Road Accident Victim Hospitalization and Assured Treatment) Scheme.
- It has prioritized life-saving intervention, financial certainty for hospitals, and a structured emergency response system for accident victims.
- It will be integrated with the Emergency Response Support System (ERSS) enabling victims, Good Samaritans to locate the nearest designated hospital and request ambulance assistance.
- Under the Scheme, every eligible road accident victim on any category of road will be entitled to cashless treatment up to ₹1.5 lakh per victim.
- It is implemented through amalgamating the Electronic Detailed Accident Report (eDAR) platform of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways with the Transaction Management System (TMS 2.0) of the National Health Authority.
- Reimbursement: To hospitals will be made through the Motor Vehicle Accident Fund (MVAF).
- In cases where the offending vehicle is insured, payment will be drawn from contributions made by General Insurance Companies.
- In uninsured and Hit & Run cases, payment will be made through budgetary allocation by Government of India.
- Grievances will be addressed by a Grievance Redressal Officer nominated by the District Road Safety Committee chaired by the District Collector / District Magistrate.
Startup India Fund of Funds 2.0:

The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister of India approved the establishment of the Startup India Fund of Funds 2.0 (Startup India FoF 2.0).
- It is launched under the Startup India initiative.
- It is designed to accelerate the next phase of India’s startup journey by mobilising long-term domestic capital, strengthening the venture capital ecosystem, and supporting innovation-led entrepreneurship across the country.
- It will have a targeted, segmented funding approach to support:
- Deep tech and tech-driven innovative manufacturing: Prioritizing breakthroughs in high-tech areas that require patient, long-term capital.
- Empowering early-growth stage founders: Providing a safety net for new and innovative ideas, reducing early-stage failures caused by lack of funding.
- National reach: Encouraging investment beyond major metros so that, the innovation thrives in every corner of the country.
- Designed to address high‑risk capital gaps: Directing greater capital to priority areas which are important for self-reliance and boosting economic growth.
- Strengthen India’s domestic venture capital base, particularly smaller funds to further boost the domestic investment landscape.
Urban Challenge Fund:

The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister of India approved the launch of the Urban Challenge Fund (UCF).
- It is a new centrally sponsored scheme of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The Fund aims to build resilient, productive, inclusive and climate-responsive cities, positioning those as key driver of the country’s next phase of economic growth.
- Features of the Urban Challenge Fund:
- A minimum of 50 per cent of project financing have to be mobilised from market sources, including municipal bonds, bank loans and Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs). The remaining share may be contributed by States, Union Territories (UTs), Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) or other sources.
- Projects will be selected through a transparent and competitive challenge mode, ensuring support to high-impact and reform-oriented proposals.
- A strong thrust on reforms across Urban Governance, Market & Financial systems, Operational efficiency, and Urban Planning
- The Fund will cover:
- All cities with a population of 10 lakh or more (2025 estimates);
- All State and Union Territory capitals not covered above; and
- Major industrial cities with a population of 1 lakh or more
- Additionally, all ULBs in hilly States, North-Eastern States, and smaller ULBs with population below 1 lakh will be eligible for support under the Credit Repayment Guarantee Scheme.
Phoenicia:
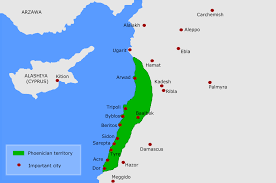
Archaeologists excavating near ruins on the island of Sardinia discovered an Iron Age scarab amulet that originated from ancient Phoenicia.
- Phoenicia was an ancient region at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea.
- It covered the land where the present day Lebanon is located.
- The Phoenicians lived on the seacoast and were skilled shipbuilders and navigators.
- Their trade routes reached as far as Spain and the British Isles.
- The Phoenicians traded wood, linen, dyes, and wine.
- They also carved wood and ivory and worked with metals and glass.
- The art of glassblowing was probably invented in Phoenicia.
- The Phoenician alphabet was the source of the Greek alphabet and of the Latin alphabet, which most people use today.
- They built the cities of Sidon, Tyre, and Berot (modern Beirut).
- The Phoenicians set up colonies all around the Mediterranean. Carthage, in North Africa, was a very successful colony.
- Decline:
- Over the centuries a number of foreign powers controlled all or parts of Phoenicia. They included Egypt, Assyria, Babylonia, and Persia.
- The Macedonians, led by Alexander the Great, conquered Phoenicia in 332 BCE.
- In 64 BCE Phoenicia became a part of the Roman Empire.
Lead Bank Scheme:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently issued the draft circular on the revised guidelines for the Lead Bank Scheme (LBS) for public comments.
- On the recommendations of the Nariman committee, the LBS was introduced by the Reserve Bank of India in 1969.
- Aim is Coordinating the activities of banks and other developmental agencies in order to achieve the objective of enhancing the flow of bank finance to the priority sector and other sectors and to promote banks’ role in the overall development of the rural sector
- For coordinating the activities in the district, a particular bank is assigned ‘Lead Bank’ responsibility of the district.
- The Lead Bank is expected to assume a leadership role for coordinating the efforts of the credit institutions and the Government.
- For the preparation of District Credit Plans and monitoring their implementation, a Lead bank Officer (LBO), now designated as Lead District Manager was appointed in 1979.
Chennakeshava Temple:

The Prime Minister’s new office complex, Seva Teerth has been built in the Indian architectural tradition inspired by the features of the 12th-century Chennakeshava Temple.
- The Chennakeshava Temple, also referred to as the Keshava, or Vijayanarayana Temple of Belur, is a 12th-century temple in Karnataka.
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- It was commissioned by King Vishnuvardhana in 1117 CE (after a major military victory in 1116 CE over the Cholas in the great battle of Talakkad), on the banks of the Yagachi River in Belur, also known as Velapura.
- The temple is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- It is a example of Hoysala architecture.
- The Hoysalas used soft soapstone for their structures, as they were found suitable for intricate carvings.
- Enclosed by a Prakara with a Gopura built in the Vijayanagar style, the temple stands on a platform, or Jagati, and looks like a huge casket.
- The outer walls of the temple are adorned with intricate carvings, which depict various gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures.
- There are Madanika sculptures in the temple, dancing, hunting, standing under canopies of trees.
- One of the unique features of the Chennakeshava Temple is the stepped well, which is located in the temple complex.
Combined Maritime Forces:

The Indian Navy has assumed command of Combined Task Force (CTF) 154, a key multinational training task force under the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF).
- It is a multinational maritime partnership that upholds the International Rules Based Order (IRBO) by countering illicit non-state actors on the high seas.
- It promotes security, stability and prosperity across international waters, which encompass some of the world’s most important shipping lanes
- Its main focus areas are counter-narcotics, counter-smuggling, suppressing piracy, encouraging regional cooperation, and engaging with regional and other partners to strengthen relevant capabilities and promote a safe maritime environment free from illicit non-state actors.
- CMF has five Combined Task Forces:
- CTF 150(Maritime Security Operations outside the Arabian Gulf)
- CTF 151(Counter-Piracy)
- CTF 152(Maritime Security Operations inside the Arabian Gulf)
- CTF 153(Red Sea Maritime Security)
- CTF 154(Maritime Security Training)
- Member Countries: It comprises 47 nations including India.
- The member countries are not bound by either a fixed political or military mandate.
Corruption Perception Index 2025:

The Transparency International released the Corruption Perception Index (CPI) 2025 that evaluated 182 countries based on perceived public sector corruption, using a scale from zero (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The report provides a comprehensive assessment of global corruption trends, their underlying drivers, societal impacts, and actionable recommendations.
- The global CPI average has dropped to just 42 out of 100. The vast majority of countries (122 out of 182) score below 50, indicating serious corruption problems worldwide.
- The number of countries scoring above 80 has shrunk from 12 a decade ago to just 5 this year (Denmark, Finland, Singapore, New Zealand, Norway).
- Top and Bottom Performers: Denmark (Score – 89) ranks highest for the 8th consecutive time, while Somalia and South Sudan (9) are at the bottom. Venezuela (10) and other conflict-affected or repressive regimes populate the lowest tiers.
- In 2025, India ranked 91st on the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) with a score of 39/100, improving slightly from its 96th rank in 2024.
- India (score 39, rank 91) outperforms most South Asian neighbors but lags behind Bhutan (71, 18), and China (43, 76).
- Maldives (39, 91),Others rank lower: Sri Lanka (35, 107), Nepal (34, 109), Pakistan (28, 136), Bangladesh (24, 150), with Afghanistan and Myanmar (16, 169).
Substantive Motion in Lok Sabha:

A Member of Parliament (MP) has invoked a Substantive Motion in the Lok Sabha against the Leader of the Opposition (LoP), seeking disqualification from Parliament and a lifetime ban from contesting elections over alleged conduct against national interest.
- In parliamentary proceedings, a ‘motion’ is a formal proposal made by a member to elicit a decision from the House.
- Every question decided by the House must be proposed as a motion, which is then resolved in either the affirmative or the negative.
- Motions are the fundamental basis for all discussions and decisions in Parliament.
- The Speaker decides the admissibility of a motion. Under Rule 186 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, a motion must satisfy specific criteria to be admitted, including:
- It must raise one definite issue.
- It must not contain arguments, ironical expressions, or defamatory statements.
- It must be restricted to a matter of recent occurrence.
- It must not relate to a matter currently under adjudication by a court (Sub-judice).
- It must be primarily the concern of the Government of India.
- Substantive Motions:A Substantive Motion is a self-contained proposal that stands on its own and is drafted to express a clear decision of the House without referring to any other motion.
- It is used for discussing the conduct of persons in high authority or for making major decisions.
- Example: All resolutions are substantive motions because they are complete in themselves and express the decision of the House.
- It is used for:
- Impeachment of the President.
- Removal of a Judge of the Supreme Court or High Court.
- Election of the Speaker or Deputy Speaker.
- Motion of Thanks on the President’s Address.
- Adjournment motion on a matter of public importance.
- Confidence or No-Confidence motion in the Council of Ministers.
- Resolution for removal of the Speaker or Deputy Speaker.
- Motion declaring a member’s seat vacant.
- Motions for discussion on matters of general public interest.
LHS 1903 System:

Astronomers utilizing the European Space Agency’s Cheops Space Telescope have discovered a unique four-planet system orbiting the red dwarf LHS 1903, featuring a planetary arrangement that challenges current planet formation theories.
- The system consists of four planets – two Super-Earths (rocky) and two mini-Neptunes (gaseous) orbiting a red dwarf star located 117 light-years from Earth.
- The Formation Paradox: Conventional models suggest rocky planets form near the star, while gas giants form farther away.
However, the outermost (fourth) planet of LHS 1903 is rocky, despite being positioned beyond its gaseous siblings. - Researchers suggest the planets formed one after another, depleting the available gas before the fourth planet formed, or that the fourth planet lost its atmosphere in a catastrophic event, leaving behind a rocky outer planet.
- The rocky planets are classified as Super-Earths, possessing a composition similar to Earth but with a mass two to ten times greater.
- Sub-Neptunian Neighbors: The two middle planets are mini-Neptunes, which are larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune, characterized by thick gaseous envelopes.
- Habitability Potential: The fourth planet is of particular scientific interest due to its estimated surface temperature of 60°C, placing it within a range that could potentially support habitability.
- Star Characteristics: The host star, LHS 1903, is a red dwarf with only 50% of the Sun’s mass and 5% of its luminosity, representing the most common type of star in the Milky Way
Nitric Oxide Against Drug-Resistant Pneumonia:
A study has shown that high-dose inhaled nitric oxide (300 ppm) significantly reduced drug-resistant pneumonia, offering a possible new strategy against antimicrobial resistance.Drug-resistant pneumonia, particularly caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is a serious complication in Intensive Care Units (ICUs), responsible for about one in five hospital pneumonias.It is an inflammatory condition of the lung alveoli caused by bacteria that exhibit resistance to one or more antibiotics typically used for treatment.Nitric oxide (NO) is a colorless gas, classified as an oxide of nitrogen. It is a stable free radical with an unpaired electron, making it highly reactive with a short half-life (seconds to minutes). It diffuses readily across cell membranes.In mammals, NO is synthesized from the amino acid L-arginine by a family of enzymes called nitric oxide synthases (NOS).
Chirality-Based Electronics:
A new study published in Nature has demonstrated a device that can separate electrons based on their chirality (handedness) without using powerful magnetic fields, marking progress towards low-power devices.Chirality in electrons: Similar to how the left and right hands are mirror images, electrons in topological semimetals possess left- or right-handed chirality.Chirality represents a specific quantum state of electrons moving inside a crystal lattice.Semimetals, or Metalloids, are brittle solids with a metallic appearance but nonmetal chemical properties. They are neither good electrical nor thermal conductors, yet they make excellent semiconductors and form amphoteric oxides.
UNEP FI Impact Centre:
UNEP Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) has launched the UNEP FI Impact Centre, consolidating its SDGs & Impact workstream into a dedicated centre of expertise.The UNEP FI Impact Centre is a specialised centre of expertise under the United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) focused on advancing impact management in financial institutions.It brings together UNEP FI’s work on aligning financial portfolios with internationally recognised environmental and social standards through a holistic impact methodology.It Provides a structured framework to align portfolios with global sustainability standards.It Covers impact methodology, interoperability, implementation support, advisory services, and consensus-building.




