Today’s Current Affairs: 10th August 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
MEA and NSIL Sign MoU for Launch of Nepalese Munal Satellite:
The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), the commercial arm of ISRO, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to facilitate the launch of Nepal’s Munal satellite
- The MoU was formalized on Saturday, with Anurag Srivastava, Joint Secretary (North) from MEA, and Arunachalam A, Director from NSIL, representing their respective organizations
“King Khan” Receives Lifetime Award At Locarno Film Festival:
- Bollywood’s charismatic ‘King Khan’, graced the 77th Locarno Film Festival with his presence on August 10, receiving a career achievement award that further gilds his storied career.
- Shah Rukh delivered his acceptance speech to a rapt audience of 8,000 at Locarno’s famed Piazza Grande.
Government Restores Diamond Imprest Licence for Gems and Jewellery Sector:
Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal has announced the restoration of the Diamond Imprest Licence, a move aimed at revitalizing India’s gems and jewellery sector.
- The decision was made during the India International Jewellery Show (IIJS) 2024, organized by the Gem and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC).
Continuous Clearing Of Cheques:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced the implementation of Continuous Clearing of Cheques under the Cheque Truncation System (CTS), aimed at speeding up the cheque clearing process.
- Currently, CTS takes up to two working days to clear cheques.
- With the new system, cheques will be scanned, presented, and cleared within hours on a continuous basis during business hours, significantly reducing the clearing time.
- This change is intended to improve efficiency, reduce settlement risk, and enhance customer experience.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) 2.0 : Approved
The Union Cabinet has approved the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) 2.0, which aims to provide financial assistance to help one crore urban poor and middle-class families build, purchase, or rent affordable housing over five years.
- The scheme, targets families with no permanent house and offers subsidies on home loans for economically weaker sections (EWS), low-income groups (LIG), and middle-income groups (MIG).
- The program also includes support for rental housing and innovative construction technologies to ensure better living conditions in urban areas.
Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024:
A bill proposing changes to banking laws, including allowing up to four nominees for a bank account, was introduced in the Lok Sabha recently.
- The Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024, aims to strengthen banking governance, enhance reporting consistency to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and improve protection for depositors and investors.
- The Bill seeks to elevate audit quality in Public Sector Banks and extend the tenure of directors in cooperative banks, excluding the chairperson and whole-time director.
- These changes are designed to ensure better oversight and accountability within the banking sector.
Clean Plant Programme:

The Union Cabinet has approved the Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aimed at revolutionizing India’s horticulture sector.
- The CPP, part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture, will enhance the quality and productivity of fruit crops by providing virus-free, high-quality planting material.
- The program includes the establishment of nine state-of-the-art Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) across India, which will produce and maintain clean planting materials.
- It also introduces a robust certification and legal framework to ensure accountability and traceability in planting material production.
- The CPP aims to boost farmers’ incomes, improve consumer produce, increase India’s fruit exports, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
- The program will engage women farmers and address diverse agro-climatic conditions, with implementation overseen by the National Horticulture Board and ICAR.
UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission : In News

Three underwater geographical structures located in the Indian Ocean for which the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) have awarded names originally proposed by India.
- UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission promotes international cooperation in marine sciences to improve management of the ocean, coasts and marine resources.
- The IOC enables its 150 Member States, and India has been a member of this commission since 1946.
- It works together by coordinating programmes in capacity development, ocean observations and services, ocean science, tsunami warning and ocean literacy.
- The IOC is in charge of coordinating the United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development 2021-2030, the “Ocean Decade”.
- There are now seven structures in the Indian Ocean named mainly after Indian scientists or bear names proposed by India in this region of the Indian Ocean.
- All three recently named structures were discovered by oceanographers from the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa.
- These are located along the Southwest Indian Ridge area of the Indian Ocean and were discovered during an international survey exploration programme.
- Since 2004, India has been undertaking the Indian Southern Ocean Research Programme with NCPOR being the nodal agency.
Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds:

Studies have shown that with temperatures soaring across the world, wildfires are becoming more common and intense, which could be spiking the occurrence of pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
- Cumulonimbus Cloud (Cb) is a heavy and dense cloudof considerable vertical extent in the form of a mountain or huge tower, often associated with heavy precipitation, lightning, and thunder.
- More commonly known as thunderclouds, cumulonimbus is the only cloud type that can produce hail, thunder and lightning.
- The base of the cloud is often flat, with a very dark wall-like feature hanging underneath, and may only lie a few hundred feet above the Earth’s surface.
- The vertical extent of Cumulonimbus ranges from 3 km to rarely more than 15 km (10 000 – 50 000 ft).
Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds:
- They are thunderclouds created by intense heat from the Earth’s surface.
- They are formed similarly to cumulonimbus clouds, but the intense heat that results in the vigorous updraft comes from fire, either large wildfires or volcanic eruptions.
Grain ATM:

India’s first round-the-clock grain ATM was opened at Mancheswar in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
- Grain ATM is known as Annapurti Grain ATM which was designed and developed by the World Food Programme India.
- The Annapurti provides universal access: anyone with a Public Distribution System ration card valid in India, regardless of the State and Union Territory, can access their entitlement.
- It can dispense grain up to 50 kilograms in five minutes 24 hours a day, reducing waiting time by 70 percent.
- It is an automated multi-commodity dispensing solution that provides fast, clean and precise access to commodities (rice, wheat, grains) to beneficiaries, post biometric authentication.
- Once biometric authentication is completed, it provides consistent access to the full food ration.
- The modular design allows easy assembly based on available space.
- Annapurti is energy efficient and can be connected to solar panels for automatic refilling.
Silicosis:
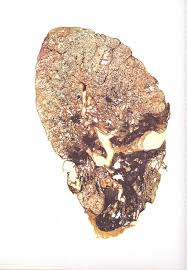
Researchers warned that silicosis could become as big a health problem as exposure to asbestos.
- Silicosis is a respiratory disease which causes a hardening of the lungs.
- It is caused by silica dust or silica crystals, which are found in soil, sand, concrete, mortar, granite and artificial stone.
- It is common in construction, mining, oil and gas extraction, kitchen engineering, dentistry, pottery and sculpting.
- People working in these industries are often exposed to silica every day and are at higher risk of developing silicosis as a result.
- It can take a long time for silicosis to develop — typically 10 to 20 years of occupational exposure to silica dust.
- The main symptoms of silicosis are: a persistent cough, persistent shortness of breath weakness and tiredness etc.
- Silicosis is a progressive disease and has no cure.
Investor Education And Protection Fund:

Union Finance Minister introduced the Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024 which proposes to enable the transfer of unclaimed dividends, shares and interest or redemption of bonds to the Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF).
- Investor Education and Protection Fund has been established under Section 205C of the Companies Act, 1956 by way of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 1999.
- The following amounts that remained unpaid and unclaimed for a period of seven years from the date they became due for payment are credited to the Fund:
- Amounts in the unpaid dividend accounts of the companies
- The application money received by companies for allotment of any securities and due for refund
- Matured deposits with companies
- Matured debentures with companies
- Grants and donations are given to the fund by the Central Government, State Governments, companies or any other institutions for the purposes of the Fund
- The interest or other income received out of the investments made from the fund
- This fund is managed by the Investor Education Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- IEPFA was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, of 2013.
- Nodal Ministry:Ministry of Corporate Affairs
NEOWISE Telescope:

Nasa’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) has concluded its mission, marking the end of a journey spanning over a decade.
- NEOWISE Telescope was launched in 2009 by NASA as the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE.
- The space telescope was originally designed to survey the sky in infrared, detecting asteroids, stars and some of the faintest galaxies in space.
- It had completed its primary mission in February 2011.
- Observations resumed in December 2013, when the telescope was taken out of hibernation and re-purposed for the NEOWISE project as an instrument to study near-Earth objects, or NEOs, as well as more distant asteroids and comets.
- It was formerly orbited at an altitude of 310 miles, NEOWISE now sits just 217 miles above Earth’s surface, its descent spurred by increasing solar activity.
- During its primary mission, NEOWISE detected more than 158,000 minor planets, 34,000 of which had never been discovered previously.
- NEOWISE data have been used to set limits on the numbers, orbits, sizes and probable compositions of asteroids throughout our solar system and enabled the discovery of the first known Earth Trojan asteroid.




